Article contents
Invariant sets and nilpotency of endomorphisms of algebraic sofic shifts
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2024
Abstract
Let G be a group and let V be an algebraic variety over an algebraically closed field K. Let A denote the set of K-points of V. We introduce algebraic sofic subshifts 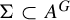 ${\Sigma \subset A^G}$ and study endomorphisms
${\Sigma \subset A^G}$ and study endomorphisms 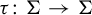 $\tau \colon \Sigma \to \Sigma $. We generalize several results for dynamical invariant sets and nilpotency of
$\tau \colon \Sigma \to \Sigma $. We generalize several results for dynamical invariant sets and nilpotency of 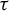 $\tau $ that are well known for finite alphabet cellular automata. Under mild assumptions, we prove that
$\tau $ that are well known for finite alphabet cellular automata. Under mild assumptions, we prove that 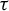 $\tau $ is nilpotent if and only if its limit set, that is, the intersection of the images of its iterates, is a singleton. If moreover G is infinite, finitely generated and
$\tau $ is nilpotent if and only if its limit set, that is, the intersection of the images of its iterates, is a singleton. If moreover G is infinite, finitely generated and 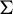 $\Sigma $ is topologically mixing, we show that
$\Sigma $ is topologically mixing, we show that 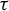 $\tau $ is nilpotent if and only if its limit set consists of periodic configurations and has a finite set of alphabet values.
$\tau $ is nilpotent if and only if its limit set consists of periodic configurations and has a finite set of alphabet values.
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 1
- Cited by



