Article contents
Entropy ratio for infinite sequences with positive entropy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 August 2018
Abstract
The complexity function of an infinite word 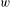 $w$ on a finite alphabet
$w$ on a finite alphabet  $A$ is the sequence counting, for each non-negative
$A$ is the sequence counting, for each non-negative  $n$, the number of words of length
$n$, the number of words of length  $n$ on the alphabet
$n$ on the alphabet  $A$ that are factors of the infinite word
$A$ that are factors of the infinite word 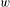 $w$. For any given function
$w$. For any given function 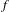 $f$ with exponential growth, we introduced in [Complexity and fractal dimensions for infinite sequences with positive entropy. Commun. Contemp. Math. to appear] the notion of word entropy
$f$ with exponential growth, we introduced in [Complexity and fractal dimensions for infinite sequences with positive entropy. Commun. Contemp. Math. to appear] the notion of word entropy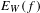 $E_{W}(f)$ associated to
$E_{W}(f)$ associated to 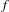 $f$ and we described the combinatorial structure of sets of infinite words with a complexity function bounded by
$f$ and we described the combinatorial structure of sets of infinite words with a complexity function bounded by 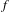 $f$. The goal of this work is to give estimates on the word entropy
$f$. The goal of this work is to give estimates on the word entropy 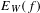 $E_{W}(f)$ in terms of the limiting lower exponential growth rate of
$E_{W}(f)$ in terms of the limiting lower exponential growth rate of  $f$.
$f$.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2018
References
- 1
- Cited by


