Article contents
Directional Kronecker algebra for 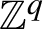 $\mathbb {Z}^q$-actions
$\mathbb {Z}^q$-actions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 January 2022
Abstract
In this paper, directional sequence entropy and directional Kronecker algebra for
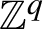 $\mathbb {Z}^q$
-systems are introduced. The relation between sequence entropy and directional sequence entropy are established. Meanwhile, directional discrete spectrum systems and directional null systems are defined. It is shown that a
$\mathbb {Z}^q$
-systems are introduced. The relation between sequence entropy and directional sequence entropy are established. Meanwhile, directional discrete spectrum systems and directional null systems are defined. It is shown that a
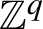 $\mathbb {Z}^q$
-system has directional discrete spectrum if and only if it is directional null. Moreover, it turns out that a
$\mathbb {Z}^q$
-system has directional discrete spectrum if and only if it is directional null. Moreover, it turns out that a
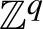 $\mathbb {Z}^q$
-system has directional discrete spectrum along q linearly independent directions if and only if it has discrete spectrum.
$\mathbb {Z}^q$
-system has directional discrete spectrum along q linearly independent directions if and only if it has discrete spectrum.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 2
- Cited by



