Article contents
Dimensions of random affine code tree fractals
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 January 2013
Abstract
We study the dimension of code tree fractals, a class of fractals generated by a set of iterated function systems. We first consider deterministic affine code tree fractals, extending to the code tree fractal setting the classical result of Falconer and Solomyak on the Hausdorff dimension of self-affine fractals generated by a single iterated function system. We then calculate the almost sure Hausdorff, packing and box counting dimensions of a general class of random affine planar code tree fractals. The set of probability measures describing the randomness includes natural measures in random 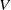 $V$-variable and homogeneous Markov constructions.
$V$-variable and homogeneous Markov constructions.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- ©2013 Cambridge University Press
References
- 7
- Cited by


