Article contents
Spherical subgroups in simple algebraic groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 February 2015
Abstract
Let 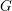 $G$ be a simple algebraic group. A closed subgroup
$G$ be a simple algebraic group. A closed subgroup 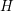 $H$ of
$H$ of 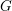 $G$ is said to be spherical if it has a dense orbit on the flag variety
$G$ is said to be spherical if it has a dense orbit on the flag variety 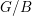 $G/B$ of
$G/B$ of 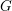 $G$. Reductive spherical subgroups of simple Lie groups were classified by Krämer in 1979. In 1997, Brundan showed that each example from Krämer’s list also gives rise to a spherical subgroup in the corresponding simple algebraic group in any positive characteristic. Nevertheless, up to now there has been no classification of all such instances in positive characteristic. The goal of this paper is to complete this classification. It turns out that there is only one additional instance (up to isogeny) in characteristic 2 which has no counterpart in Krämer’s classification. As one of our key tools, we prove a general deformation result for subgroup schemes that allows us to deduce the sphericality of subgroups in positive characteristic from the same property for subgroups in characteristic zero.
$G$. Reductive spherical subgroups of simple Lie groups were classified by Krämer in 1979. In 1997, Brundan showed that each example from Krämer’s list also gives rise to a spherical subgroup in the corresponding simple algebraic group in any positive characteristic. Nevertheless, up to now there has been no classification of all such instances in positive characteristic. The goal of this paper is to complete this classification. It turns out that there is only one additional instance (up to isogeny) in characteristic 2 which has no counterpart in Krämer’s classification. As one of our key tools, we prove a general deformation result for subgroup schemes that allows us to deduce the sphericality of subgroups in positive characteristic from the same property for subgroups in characteristic zero.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Authors 2015
References
- 3
- Cited by


