No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Continuous phase transitions on Galton–Watson trees
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 July 2021
Abstract
Distinguishing between continuous and first-order phase transitions is a major challenge in random discrete systems. We study the topic for events with recursive structure on Galton–Watson trees. For example, let 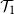 $\mathcal{T}_1$
be the event that a Galton–Watson tree is infinite and let
$\mathcal{T}_1$
be the event that a Galton–Watson tree is infinite and let 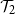 $\mathcal{T}_2$
be the event that it contains an infinite binary tree starting from its root. These events satisfy similar recursive properties:
$\mathcal{T}_2$
be the event that it contains an infinite binary tree starting from its root. These events satisfy similar recursive properties: 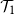 $\mathcal{T}_1$
holds if and only if
$\mathcal{T}_1$
holds if and only if 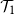 $\mathcal{T}_1$
holds for at least one of the trees initiated by children of the root, and
$\mathcal{T}_1$
holds for at least one of the trees initiated by children of the root, and 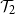 $\mathcal{T}_2$
holds if and only if
$\mathcal{T}_2$
holds if and only if 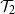 $\mathcal{T}_2$
holds for at least two of these trees. The probability of
$\mathcal{T}_2$
holds for at least two of these trees. The probability of 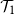 $\mathcal{T}_1$
has a continuous phase transition, increasing from 0 when the mean of the child distribution increases above 1. On the other hand, the probability of
$\mathcal{T}_1$
has a continuous phase transition, increasing from 0 when the mean of the child distribution increases above 1. On the other hand, the probability of 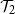 $\mathcal{T}_2$
has a first-order phase transition, jumping discontinuously to a non-zero value at criticality. Given the recursive property satisfied by the event, we describe the critical child distributions where a continuous phase transition takes place. In many cases, we also characterise the event undergoing the phase transition.
$\mathcal{T}_2$
has a first-order phase transition, jumping discontinuously to a non-zero value at criticality. Given the recursive property satisfied by the event, we describe the critical child distributions where a continuous phase transition takes place. In many cases, we also characterise the event undergoing the phase transition.
- Type
- Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
Footnotes
The author received support from NSF grant DMS-1811952 and PSC-CUNY Award #62628-00 50.



