Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 March 2015
In [1], the authors consider a random walk (Zn,1, . . ., Zn,K+1) ∈ 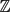 ${\mathbb{Z}}$K+1 with the constraint that each coordinate of the walk is at distance one from the following coordinate. A functional central limit theorem for the first coordinate is proved and the limit variance is explicited. In this paper, we study an extended version of this model by conditioning the extremal coordinates to be at some fixed distance at every time. We prove a functional central limit theorem for this random walk. Using combinatorial tools, we give a precise formula of the variance and compare it with that obtained in [1].
${\mathbb{Z}}$K+1 with the constraint that each coordinate of the walk is at distance one from the following coordinate. A functional central limit theorem for the first coordinate is proved and the limit variance is explicited. In this paper, we study an extended version of this model by conditioning the extremal coordinates to be at some fixed distance at every time. We prove a functional central limit theorem for this random walk. Using combinatorial tools, we give a precise formula of the variance and compare it with that obtained in [1].