Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Kuang, Wenxing
Facey, Glenn A.
and
Detellier, Christian
2004.
Dehydration and rehydration of palygorskite and the influence of water on the nanopores.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 5,
p.
635.
Yalçin, Hüseyin
and
Bozkaya, Ömer
2004.
Ultramafic-Rock-Hosted Vein Sepiolite Occurrences in the Ankara Ophiolitic Mélange, Central Anatolia, Turkey.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 2,
p.
227.
Samson, Sherry D.
Nagy, Kathryn L.
and
Cotton, Worth B.
2005.
Transient and quasi-steady-state dissolution of biotite at 22–25°C in high pH, sodium, nitrate, and aluminate solutions.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,
Vol. 69,
Issue. 2,
p.
399.
Zaaboub, Noureddine
Abdeljaouad, Saadi
and
López-Galindo, Alberto
2005.
Origin of fibrous clays in Tunisian Paleogene continental deposits.
Journal of African Earth Sciences,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 5,
p.
491.
Yalçin, Hüseyin
and
Bozkaya, Ömer
2006.
Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Paleocene Ultramafic- and Sedimentary-Hosted Talc Deposits in the Southern Part of the Sivas Basin, Turkey.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 3,
p.
333.
Owliaie, H.R.
Abtahi, A.
and
Heck, R.J.
2006.
Pedogenesis and clay mineralogical investigation of soils formed on gypsiferous and calcareous materials, on a transect, southwestern Iran.
Geoderma,
Vol. 134,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
62.
Galán, E.
2006.
Handbook of Clay Science.
Vol. 1,
Issue. ,
p.
1129.
Carrado, K.A.
Decarreau, A.
Petit, S.
Bergaya, F.
and
Lagaly, G.
2006.
Handbook of Clay Science.
Vol. 1,
Issue. ,
p.
115.
Achyuthan, Hema
Kar, Amal
and
Eastoe, Chris
2007.
Late Quaternary-Holocene lake-level changes in the eastern margin of the Thar Desert, India.
Journal of Paleolimnology,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 4,
p.
493.
Yeniyol, M.
2007.
Characterization of a Mg-rich and low-charge saponite from the Neogene lacustrine basin of Eskisşehir, Turkey.
Clay Minerals,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
541.
García-Romero, E.
Suárez, M.
Santarén, J.
and
Alvarez, A.
2007.
Crystallochemical characterization of the palygorskite and sepiolite from the Allou Kagne deposit, Senegal.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 6,
p.
606.
Boschetti, Tiziano
and
Toscani, Lorenzo
2008.
Springs and streams of the Taro–Ceno Valleys (Northern Apennine, Italy): Reaction path modeling of waters interacting with serpentinized ultramafic rocks.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 257,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
76.
Arranz, Enrique
Lago, Marceliano
Bastida, Joaquín
Galé, Carlos
Soriano, Jesús
and
Ubide, Teresa
2008.
Hydrothermal macroscopic Fe-sepiolite from Oujda Mounts (Middle Atlas, Eastern Morocco).
Journal of African Earth Sciences,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 3,
p.
81.
Furquim, Sheila Aparecida Correia
Graham, Robert C.
Barbiero, Laurent
de Queiroz Neto, José Pereira
and
Vallès, Vincent
2008.
Mineralogy and Genesis of Smectites in an Alkaline-Saline Environment of Pantanal Wetland, Brazil.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 5,
p.
579.
Burzo, E.
2009.
Phyllosilicates.
Vol. 27I5b,
Issue. ,
p.
444.
Wang, Ming Kuang
Tseng, Pao Chung
Chang, Shyun Sheng
Ray, Dah Tong
Shau, Yen Hong
Shen, Yun Wei
Chen, Ruey Chyong
and
Chiang, Po Neng
2009.
Origin and Mineralogy of Sepiolite and Palygorskite From the Tuluanshan Formation, Eastern Taiwan.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 5,
p.
521.
Macpherson, G.L.
2009.
CO2 distribution in groundwater and the impact of groundwater extraction on the global C cycle.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 264,
Issue. 1-4,
p.
328.
Hojati, Saeid
Khademi, Hossein
and
Cano, Angel Faz
2010.
Palygorskite Formation Under the Influence of Saline and Alkaline Groundwater in Central Iranian Soils.
Soil Science,
Vol. 175,
Issue. 6,
p.
303.
Tlili, A.
Felhi, M.
and
Montacer, M.
2010.
Origin and Depositional Environment of Palygorskite and Sepiolite from the Ypresian Phosphatic Series, Southwestern Tunisia.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 4,
p.
573.
Galán, Emilio
and
Pozo, Manuel
2011.
Developments in Palygorskite-Sepiolite Research.
Vol. 3,
Issue. ,
p.
125.
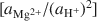 vs. log [aH4SiO4o]
vs. log [aH4SiO4o]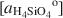 , using the activities for log [aAl3+/(aH+)3]
, using the activities for log [aAl3+/(aH+)3]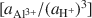 defined by an arbitrarily chosen value and the approximate saturation limits of pyrophyllite + amorphous silica, kaolinite + amorphous silica, kaolinite + pyrophyllite, pyrophyllite + quartz and gibbsite. The formation of sepiolite-palygorskite from solution is more favored in the presence of amorphous silica than quartz. Lower aqueous aluminum activities favor the non-aluminum phases sepiolite and kerolite relative to the aluminum-containing phases palygorskite and saponite. The stability ranges of worldwide associations of magnesite and dolomite with sepiolite and palygorskite are also illustrated as a function of aluminum activity.
defined by an arbitrarily chosen value and the approximate saturation limits of pyrophyllite + amorphous silica, kaolinite + amorphous silica, kaolinite + pyrophyllite, pyrophyllite + quartz and gibbsite. The formation of sepiolite-palygorskite from solution is more favored in the presence of amorphous silica than quartz. Lower aqueous aluminum activities favor the non-aluminum phases sepiolite and kerolite relative to the aluminum-containing phases palygorskite and saponite. The stability ranges of worldwide associations of magnesite and dolomite with sepiolite and palygorskite are also illustrated as a function of aluminum activity.

