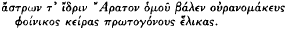Research Article
Robert Maxwell Ogilvie
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, p. 1
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Return of Odysseus: A Homeric Theoxeny1
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 2-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Argive Elders, The Discerning Shepherd and the Fawning Dog: Misleading Communication in the Agamemnon*
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 9-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
‘The Customary Meanings of Words were Changed’ – Or were they? A Note on Thucydides 3.82.4
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 18-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aristophanes and Kallistratos
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 21-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Parabasis in Aristophanes: Prolegomena, Acharnians
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 27-40
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Portrait of The Artist as a Young Woman*
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 41-55
-
- Article
- Export citation
Euripides, Helen 115–123
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 56-58
-
- Article
- Export citation
The ‘Choriambic Dimeter’ of Euripides
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 59-74
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Date of the Union of Corinth and Argos
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 75-83
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Pyrrhic Victory: Gorgias 474b-477a1
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 84-88
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aristotle on the Period (Rhet. 3. 9)
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 89-99
-
- Article
- Export citation
ΦAnta∑ia In Aristotle, De Anima 3. 3
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 100-113
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Theoretical Possibility of Extensive Infanticide in the Graeco-Roman World
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 114-116
-
- Article
- Export citation
Teuthis and Callimachus, Aetia Book 1
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 117-120
-
- Article
- Export citation
Some Watchers of the Skies
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 121-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
Light and Heavy Syllables as Dramatic Colouring in Plautus and Others
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 124-133
-
- Article
- Export citation
How Terence's Hecyra Failed
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 134-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Legal Issue In Cicero, Pro Balbo
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 136-147
-
- Article
- Export citation
Procne's Absence Again
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 148-151
-
- Article
- Export citation

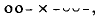 is favoured by Euripides. Aeschylus does not use this colon,
is favoured by Euripides. Aeschylus does not use this colon,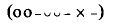 in all of his middle and later plays except Tro
in all of his middle and later plays except Tro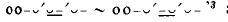 and indeed some scholars give the name ‘glyc’ to the colon.
and indeed some scholars give the name ‘glyc’ to the colon.