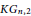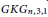Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Ganesamurthy, S.
and
Paulraja, P.
2018.
Existence of a P2k+1-decomposition in the Kneser graph KGt,2
.
Discrete Mathematics,
Vol. 341,
Issue. 7,
p.
2113.