Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
In the study of algorithms for the iterative solution of an arbitrary analytic equation f(z) = 0, acceleration procedures are of importance in practice and of considerable interest in the theory of the subject. Let
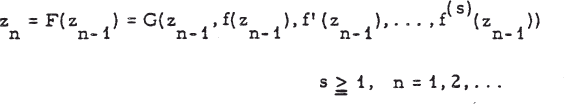 .
.
be an iteration formula which has a zero ξ of f(z) as attractive fixed point. An algorithm of this type is said to converge towards a root ξ of f(z) = 0 for all initial approximations z = z0 in a vicinity of ξ, of order k > 0, when
1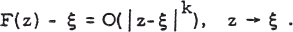 .
.