Article contents
Spectrality of a Class of Moran Measures
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 January 2020
Abstract
Let 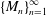 $\{M_{n}\}_{n=1}^{\infty }$ be a sequence of expanding matrices with
$\{M_{n}\}_{n=1}^{\infty }$ be a sequence of expanding matrices with 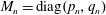 $M_{n}=\operatorname{diag}(p_{n},q_{n})$, and let
$M_{n}=\operatorname{diag}(p_{n},q_{n})$, and let 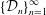 $\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}_{n=1}^{\infty }$ be a sequence of digit sets with
$\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}_{n=1}^{\infty }$ be a sequence of digit sets with 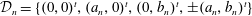 ${\mathcal{D}}_{n}=\{(0,0)^{t},(a_{n},0)^{t},(0,b_{n})^{t},\pm (a_{n},b_{n})^{t}\}$, where
${\mathcal{D}}_{n}=\{(0,0)^{t},(a_{n},0)^{t},(0,b_{n})^{t},\pm (a_{n},b_{n})^{t}\}$, where 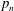 $p_{n}$,
$p_{n}$, 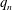 $q_{n}$,
$q_{n}$, 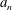 $a_{n}$ and
$a_{n}$ and 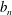 $b_{n}$ are positive integers for all
$b_{n}$ are positive integers for all 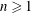 $n\geqslant 1$. If
$n\geqslant 1$. If 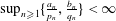 $\sup _{n\geqslant 1}\{\frac{a_{n}}{p_{n}},\frac{b_{n}}{q_{n}}\}<\infty$, then the infinite convolution
$\sup _{n\geqslant 1}\{\frac{a_{n}}{p_{n}},\frac{b_{n}}{q_{n}}\}<\infty$, then the infinite convolution 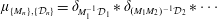 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{\{M_{n}\},\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{M_{1}^{-1}{\mathcal{D}}_{1}}\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{(M_{1}M_{2})^{-1}{\mathcal{D}}_{2}}\ast \cdots \,$ is a Borel probability measure (Cantor–Dust–Moran measure). In this paper, we investigate whenever there exists a discrete set
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{\{M_{n}\},\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{M_{1}^{-1}{\mathcal{D}}_{1}}\ast \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{(M_{1}M_{2})^{-1}{\mathcal{D}}_{2}}\ast \cdots \,$ is a Borel probability measure (Cantor–Dust–Moran measure). In this paper, we investigate whenever there exists a discrete set 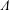 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$ such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$ such that 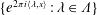 $\{e^{2\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}i\langle \unicode[STIX]{x1D706},x\rangle }:\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\}$ is an orthonormal basis for
$\{e^{2\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}i\langle \unicode[STIX]{x1D706},x\rangle }:\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\}$ is an orthonormal basis for 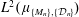 $L^{2}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{\{M_{n}\},\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}})$.
$L^{2}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}_{\{M_{n}\},\{{\mathcal{D}}_{n}\}})$.
MSC classification
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2019
Footnotes
This research is supported in part by the NNSF of China (Nos. 11401053, 11771457, 11571104 and 11971500) and the SRF of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Nos. 17B158 and 14C0046). Author X.-Y. W. is the corresponding author.
References
- 9
- Cited by


