Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Taylor, Walter
1981.
Laws obeyed by topological algebras— extending results of Hopf and Adams.
Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 1,
p.
75.
Bateson, Ann
1982.
Fundamental groups of topological 𝑅-modules.
Transactions of the American Mathematical Society,
Vol. 270,
Issue. 2,
p.
525.
Artamonov, V. A.
1991.
Universal algebras.
Journal of Soviet Mathematics,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 2,
p.
2959.
Coleman, J. P.
1996.
Separation in topological algebras.
Algebra Universalis,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 1,
p.
72.
Rowan, W. H.
1996.
Enveloping ringoids.
Algebra Universalis,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 2,
p.
202.
Kearnes, Keith A.
and
Szendrei, Ágnes
1998.
The Relationship Between Two Commutators.
International Journal of Algebra and Computation,
Vol. 08,
Issue. 04,
p.
497.
Salibra, A.
2001.
A continuum of theories of lambda calculus without semantics.
p.
334.
Salibra, Antonino
2001.
Towards Lambda Calculus Order-Incompleteness.
Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 2,
p.
145.
Larose, Benoit
and
Zádori, László
2003.
The Complexity of the Extendibility Problem for Finite Posets.
SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 1,
p.
114.
Larose, Benoit
and
Tardif, Claude
2004.
A discrete homotopy theory for binary reflexive structures.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 189,
Issue. 2,
p.
268.
Krokhin, Andrei
Bulatov, Andrei
and
Jeavons, Peter
2005.
Structural Theory of Automata, Semigroups, and Universal Algebra.
Vol. 207,
Issue. ,
p.
181.
LAROSE, BENOIT
and
ZÁDORI, LÁSZLÓ
2006.
TAYLOR TERMS, CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION AND THE COMPLEXITY OF POLYNOMIAL EQUATIONS OVER FINITE ALGEBRAS.
International Journal of Algebra and Computation,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 03,
p.
563.
ZÁDORI, LÁSZLÓ
2007.
SOLVABILITY OF SYSTEMS OF POLYNOMIAL EQUATIONS OVER FINITE ALGEBRAS.
International Journal of Algebra and Computation,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 04,
p.
821.
Barto, Libor
Kozik, Marcin
and
Niven, Todd
2008.
Graphs, polymorphisms and the complexity of homomorphism problems.
p.
789.
Barto, Libor
Kozik, Marcin
and
Niven, Todd
2009.
The CSP Dichotomy Holds for Digraphs with No Sources and No Sinks (A Positive Answer to a Conjecture of Bang-Jensen and Hell).
SIAM Journal on Computing,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 5,
p.
1782.
Taylor, Walter
2009.
Simple equations on real intervals.
Algebra universalis,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 2,
p.
213.
Barto, Libor
and
Kozik, Marcin
2010.
New Conditions for Taylor Varieties and CSP.
p.
100.
Siggers, Mark H.
2010.
A strong Mal’cev condition for locally finite varieties omitting the unary type.
Algebra universalis,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
15.
Zádori, László
2011.
On solvability of systems of polynomial equations.
Algebra universalis,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 3,
p.
277.
Barto, Libor
and
Kozik, Marcin
2012.
Absorbing Subalgebras, Cyclic Terms, and the Constraint Satisfaction Problem.
Logical Methods in Computer Science,
Vol. Volume 8, Issue 1,
Issue. ,


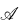 influences its topological structure in a way which is profound but not well understood. (See § 7 below for various examples.) Here we examine this influence rather generally, and give a fairly complete analysis of one of the many forms it can take, namely, the influence of the identities of
influences its topological structure in a way which is profound but not well understood. (See § 7 below for various examples.) Here we examine this influence rather generally, and give a fairly complete analysis of one of the many forms it can take, namely, the influence of the identities of 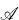 on the group identities obeyed by the homotopy group (or groups of the components) of
on the group identities obeyed by the homotopy group (or groups of the components) of 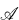 .
.