Article contents
On the Geometry of the Moduli Space of Real Binary Octics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
The moduli space of smooth real binary octics has five connected components. They parametrize the real binary octics whose defining equations have 0, … , 4 complex-conjugate pairs of roots respectively. We show that each of these five components has a real hyperbolic structure in the sense that each is isomorphic as a real-analytic manifold to the quotient of an open dense subset of 5-dimensional real hyperbolic space 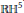 $\mathbb{R}{{\mathbb{H}}^{5}}$ by the action of an arithmetic subgroup of Isom
$\mathbb{R}{{\mathbb{H}}^{5}}$ by the action of an arithmetic subgroup of Isom $\left( \mathbb{R}{{\mathbb{H}}^{5}} \right)$. These subgroups are commensurable to discrete hyperbolic reflection groups, and the Vinberg diagrams of the latter are computed.
$\left( \mathbb{R}{{\mathbb{H}}^{5}} \right)$. These subgroups are commensurable to discrete hyperbolic reflection groups, and the Vinberg diagrams of the latter are computed.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2011
References
- 2
- Cited by


