Article contents
Note on Cubature Formulae and Designs Obtained from Group Orbits
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
In 1960, Sobolev proved that for a finite reflection group 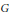 $G$, a
$G$, a 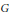 $G$-invariant cubature formula is of degree
$G$-invariant cubature formula is of degree 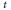 $t$ if and only if it is exact for all
$t$ if and only if it is exact for all 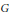 $G$-invariant polynomials of degree at most
$G$-invariant polynomials of degree at most 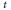 $t$. In this paper, we make some observations on invariant cubature formulas and Euclidean designs in connection with the Sobolev theorem. First, we give an alternative proof of theorems by Xu (1998) on necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of cubature formulas with some strong symmetry. The new proof is shorter and simpler compared to the original one by Xu, and, moreover, gives a general interpretation of the analytically-written conditions of Xu's theorems. Second, we extend a theorem by Neumaier and Seidel (1988) on Euclidean designs to invariant Euclidean designs, and thereby classify tight Euclidean designs obtained from unions of the orbits of the corner vectors. This result generalizes a theorem of Bajnok (2007), which classifies tight Euclidean designs invariant under the Weyl group of type
$t$. In this paper, we make some observations on invariant cubature formulas and Euclidean designs in connection with the Sobolev theorem. First, we give an alternative proof of theorems by Xu (1998) on necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of cubature formulas with some strong symmetry. The new proof is shorter and simpler compared to the original one by Xu, and, moreover, gives a general interpretation of the analytically-written conditions of Xu's theorems. Second, we extend a theorem by Neumaier and Seidel (1988) on Euclidean designs to invariant Euclidean designs, and thereby classify tight Euclidean designs obtained from unions of the orbits of the corner vectors. This result generalizes a theorem of Bajnok (2007), which classifies tight Euclidean designs invariant under the Weyl group of type 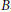 $B$, to other finite reflection groups.
$B$, to other finite reflection groups.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2012
References
- 6
- Cited by


