Article contents
Criteria for Groups with Representations of the Second Kind and for Simple Phase Groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Extract
In this paper we consider matrix representations of compact groups over the field of the complex numbers. We shall deal mainly with finite groups.
The Kronecker product of two irreducible representations σ1 and σ2 of a group 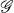 is in general a reducible representation of
is in general a reducible representation of 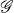 . The explicit reduction of such a product to irreducible representations σ3 can be performed by means of a unitary matrix, the elements of which are called Wigner coefficients or Clebsch-Gordan coefficients [1; 25; 27].
. The explicit reduction of such a product to irreducible representations σ3 can be performed by means of a unitary matrix, the elements of which are called Wigner coefficients or Clebsch-Gordan coefficients [1; 25; 27].
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 1975
References
- 5
- Cited by


