Impact statement
Microplastics (MPs) are now widely documented in various environmental systems including water, air, soil, and biota. Examinations of their biological impacts and human health impacts are escalating. This review addresses a critical aspect of their biological impacts, namely the environmental toxicology of MPs in the marine environments. Despite the numerous studies conducted over the recent years, conclusions on the toxicological impacts are still elusive. There are significant needs to incorporate principles of toxicology (biochemistry and physiology) as well as ecology in studying the environmental toxicology of MPs in the marine systems.
Introduction
All plastics are polymers and cheap to produce and have been used in nearly all aspects of human life nowadays. The annual plastics production is expected to further double within the next decade. Life would be very different without these plastics. Eventually, all plastiware needs to be disposed of or recycled. Despite large campaigns by governments or public sectors, a significant proportion of these plastic wastes may still end up in the environment. There are various estimates (5–13-million tonnes) of plastic wastes entering aquatic environments annually (Rodrigues et al., Reference Rodrigues, Gonçalves, Gonçalves, Nogueira, Marques and Abrantes2018). Assuming an annual plastic production of 460-million metric tonnes worldwide in 2019, it is thus estimated that over 1%–3% of this plastiware may eventually enter the oceans on an annual basis. As a result, garbage patches consisting of small plastics are now documented from the water surface down to the seafloor, and news bulletins are often inundated with reports of plastic pollution in the ocean.
In the past, the majority of produced or manufactured plastics would end up in landfill, with only a small proportion of plastic products being recycled. Indiscriminate disposal and releases are accountable for plastic contamination. Once these plastics are in the real environment, various processes can degrade or transform them into smaller plastic objects. Physical processes include wind, wave action, and solar radiation, among others. Chemical reactions as well as microbial degradation or other biological transformation may decompose these plastics into small pieces (Yoshida et al., Reference Yoshida, Hiraga, Takehana, Taniguchi, Yamaji, Maeda, Toyohara, Miyamoto, Kimura and Oda2016). Marine debris is transported by water currents and becomes trapped in the ocean. Some of these municipal wastes are denser than seawater and would sink to the seafloor (Engler, Reference Engler2012), which may become a major sink of plastic wastes in the ocean.
Accumulation of large amounts of waste plastics in the environment may result in serious environmental problems. Thompson et al. (Reference Thompson, Moore, Andrady, Gregory, Takada and Weisberg2005) introduced the term ‘microplastics’ (MPs), which has since gradually raised substantial concerns on the parts of the public and academic communities, as well as environmental regulators. A search of literature using the keywords ‘marine’ and ‘MPs’ basically indicated an exponential increase in published papers over the period between 2006 and 2021 (Figure 1). MPs are mostly defined as small fragments of plastics within the size range of 1 μm to 5 mm, whereas plastics smaller than 1 μm are generally defined as nanoplastics (NPs). They can be classified by physical properties such as density, shape, color, surface polarity, and roughness, as well as by chemical properties. All these characteristics determine the transport or fate of MPs in the ocean due to hydrodynamics. However, these characteristics are dynamic when MPs are subjected to different environmental processes such as UV radiation, mechanical abrasion, or biofouling. There is a variety of different shapes of MPs such as fragments, fibers, beads, and pellets. Chemical composition is probably the most common means of classification of MPs, including polyvinyl chlorine (PVC), polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The majority of MP polymers found in the marine environment are PE, PP, PS, and PET (Lundebye et al., Reference Lundebye, Lusher and Bank2021). Due to their typically large surface area-to-volume ratios, they may adsorb other chemical pollutants, which raises another concern regarding the interactive effects of MPs and micropollutants in the environment.

Figure 1. Statistics of papers published on ‘microplastics’ and ‘marine’ since 2006 with citation numbers. Data mined from Web of Science on May 8, 2020.
MPs are also classified as primary MPs (initially small plastics from production or use) and secondary MPs (breakdown products of larger plastics). Primary MPs are generally designed for commercial uses such as microbeads in personal care products, whereas secondary MPs result from the fragmentation of large plastics after environmental weathering. Physical aging (collision and grinding process of MPs) as well as photo- and thermal oxidation result in changes in these secondary MPs. Temperature, humidity, salinity, and pH, and possibly the biological activity, can all affect the aging of MPs, which subsequently change the physical and chemical properties of MPs such as size, hardness, crystallinity, surface structure, and hydrophilicity. Other examples of secondary MPs include the nets used in fishing and PE mulching sheets used in agriculture, which can be easily fragmented into MPs (Huang et al., Reference Huang, Liu, Jia, Yan and Wang2020).
Despite the ubiquitous concerns for these MPs in the environment, many ecotoxicologists considered these pollutants as physical agents, and there are even schools of thought that these MPs are simply biologically inert (i.e., undigestible) to organisms. These views have indeed impeded significantly toxicological study until recently from the perspective of environmental chemistry and toxicology. In this review, I will focus on the two tenets of environmental toxicology of MPs in the aquatic environment: the bioaccumulation and toxicity of MPs (Figure 2). Following reviews of different studies on the bioaccumulation and toxicity of MPs, it is concluded that future studies should address the kinetics as well as the molecular mechanisms of MPs and be more environmentally relevant. Proper environmental risk assessments of MPs in the environment require toxicological studies to be environmentally relevant. I will finally highlight some critical issues to be addressed in future environmental toxicological studies of MPs in the marine environment.
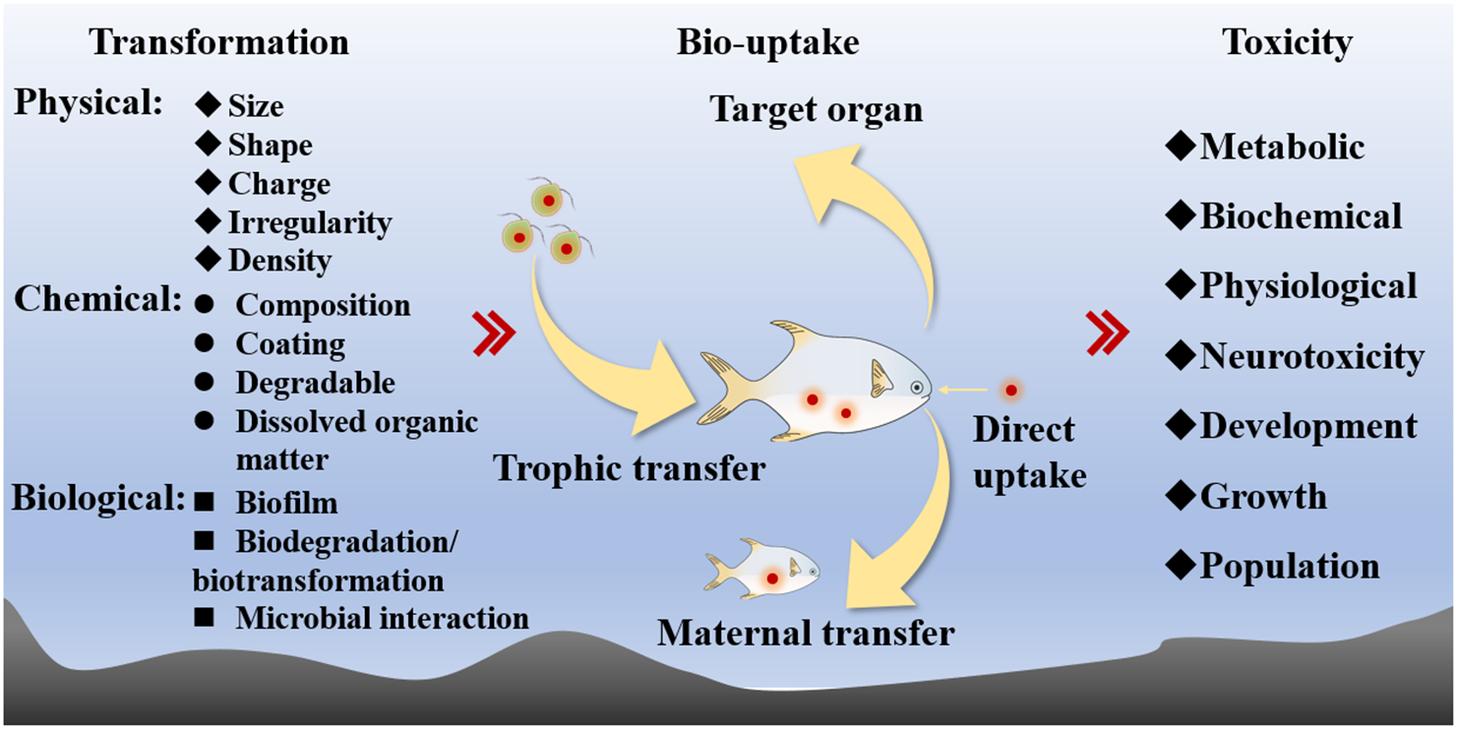
Figure 2. The basic scope of the environmental toxicology of microplastics.
Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer
Bioaccumulation is considered as the net uptake of MPs from the marine environment by all exposure routes (including ingestion, contact, and respiration) and sources (such as water, sediment, and prey). MPs are taken up by marine animals via various routes, including direct water uptake and ingestion (dietary exposure). In the former case, MPs may be accumulated by various pathways such as endocytosis/phagocytosis (Yan et al., Reference Yan, Tang and Wang2021), and the latter will be taken up by trophic transfer processes as well (e.g., from prey to predator). Given the small sizes of MPs, marine organisms can ingest them selectively or accidentally. A few reviews have addressed the ingestion of MPs by a variety of aquatic species such as fish, mammals, marine invertebrates, and seabirds (Andrady, Reference Andrady2011; da Costa et al., Reference da Costa, Santos, Duarte and Rocha-Santos2016; Ivleva et al., Reference Ivleva, Wiesheu and Niessner2017; Miller et al., Reference Miller, Hamann and Kroon2020; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Ge and Yu2020). The functional physiology of marine animals is critical in their interplay with MPs in the environment. Accumulation of MPs is dependent on whether MPs in the organism will gradually cross the intestinal barriers and be transported to other sites of the body after ingestion. The accumulated MPs in the digestive tract will be transported to the circulatory system, which is probably dependent on their particle structural composition and physicochemical properties of size, surface modification, and chemical composition. The smaller particles are probably more likely to enter and remain in the circulatory system, whereas larger-sized MPs stay in the intestinal tract to their large sizes (Shen et al., Reference Shen, Huang, Chen, Song, Zeng and Zhang2020). The possible transport of MPs along different food chains is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Transport of microplastics in different marine food chains with considerations of different properties of microplastics.
Zooplankton
MPs are ingested by a variety of zooplankton by filter feeding or by raptorial feeding (Cole et al., Reference Cole, Lindeque, Fileman, Halsband, Goodhead, Moger and Galloway2013, Reference Cole, Coppock, Lindeque, Altin, Teed, Pond, Sorensen, Galloway and Booth2019). Much research has focused on the ingestion of different types of MPs by different groups of copepods, with an aim to identify any selectivity of MPs ingested. Selection of MPs is highly dependent on both MPs type and the species of feeding animals. Functional ecology is of paramount importance in understanding the ingestion and accumulation of MPs by zooplankton in the real environment. Although some zooplankton may avoid the accidental consumption of MPs with specific chemoreception responses to algal cells or bacteria, MPs coated with biofilms might mislead them to ingest and accumulate marine MPs. Some zooplankton can distinguish their prey through surface characteristics or particle charges, while aged MPs may have modified the surface properties which may confuse the animals. Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Rodriguez-Torres, Rist, Nielsen, Hartman, Brun, Li and Almeda2022) showed that copepods were able to reject 80% of MPs with a strong taste behavioral response, which was independent of MPs type, shape, and presence of biofilms. Such a strong behavioral selection as well as the relatively low concentrations of MPs in the environments implied a low risk of MPs ingestion by copepods (Xu et al., Reference Xu, Fang, Wong and Cheung2022), although more subtle endpoints need to be further adopted and substantiated for such a conclusion. More recently, Rodriguez-Torres et al. (Reference Rodriguez-Torres, Almeda, Xu, Hartman, Rist, Brun and Nielsen2023) examined copepods with different foraging behaviors such as current-feeding, cruising, ambushing, and mixed feeding, and showed that the ingestion of MPs was about one order of magnitude lower than that of algae of similar sizes. Thus, the overall risk to marine copepods appeared to be low, including the limited trophic transfer of MPs from copepods to the next trophic level. However, the ingestion of MPs by copepods may be facilitated by a low concentration of phytoplankton, possibly due to the activation of chemosensory system (Cheng et al., Reference Cheng, Wang, Yi, Li, Liu and Ru2020).
Fibers and fragment shapes also showed different ingestion modes in zooplankton. Fibers may be preferentially ingested with a higher proportion (Taha et al., Reference Taha, Md Amin, Anuar, Nasser and Sohaimi2021; Zheng et al., Reference Zheng, Zhao, Liu, Liang, Zhu and Sun2021), which may be due to the relatively lower density of fibers making it possible for them to be suspended in the water column, and then increasing the possibility of their ingestion by zooplankton. In contrast, fragments rapidly sink in water and have a high possibility of being incorporated into sediments in estuaries (Taha et al., Reference Taha, Md Amin, Anuar, Nasser and Sohaimi2021). Aytan et al. (Reference Aytan, Esensoy and Senturk2022) collected samples of seawater from the Baltic Sea, in which MPs were mainly composed of fibers, followed by films and fragments. The MPs ingested by copepods were mainly fibers, indicating the possible selectivity of MPs ingestion by the copepods. In another study, Coppock et al. (Reference Coppock, Gallowway, Cole, Dileman, Queiros and Lindeque2019) also demonstrated that the selection of MPs by the copepod Calanus helgolandiscus was related to the size of MPs as well as the size of the phytoplanktonic algae present. Zheng et al. (Reference Zheng, Zhao, Liu, Liang, Zhu and Sun2021) examined the size, abundance, shape, and chemical composition of MPs ingested by copepods. Fiber MPs accounted for 92% of the total ingested MPs. For different chemical compositions of the MPs, 11 polymers were detected in copepods in Jiaozhou Bay, China during four seasons, with the main components being polyester and cellophane (41.9% and 25.7%, respectively). Sun et al. (Reference Sun, Liu, Zhu, Liang, Zhao and Zhang2018) analyzed the MPs in 10 groups of zooplankton from the East China Sea, and identified three MPS types including fibers, pellets, and fragments. The fibers (54.6%) were more common than the other two types, and polymerized oxidized organic material and polyester accounted for 35.9% and 25.6% of the polymers, respectively. Overall, the predominance of fibers in copepods may be due to their high environmental abundances as well as their low density.
Besides, MPs can adsorb info-chemicals such as dimethyl sulfide produced by phytoplankton and bacteria (Botterell et al., Reference Botterell, Beaumont, Dorrington, Steinke, Thompson and Lindeque2019), which may attract zooplankton by interfering with their chemosensory systems. Botterell et al. (Reference Botterell, Beaumont, Cole, Hopkins, Stenike, Thompson and Lindeque2020) studied the ingestion of MPs of different shapes and chemical coatings (dimethyl sulfide and dimethylsulfoniopropionate from algae) by copepods Calanus helgolandicus and Acartia tonsa and larvae of the European lobster Homarus gammarus. In this study, bioavailability to different species of zooplankton varied with different shapes as well as chemical coatings, again possibly due to the engagement of chemosensory systems to locate their prey.
Bivalves
Numerous works have been conducted on the feeding physiology of marine bivalves over the past 50 years, and MPs are only the newly added particle types to be considered in the countless literature published in this area (Ward et al., Reference Ward, Rosa and Shumway2019a). There have been numerous measurements of MPs in field-sampled bivalves (Bom and Sa, Reference Bom and Sa2021), but quantitative measurements of MPs uptake and depuration by bivalves are relatively few (Wang et al., Reference Wang, Hu, Zheng, Huang, Shang, Fang, Shi and Wang2021a). Such limitations are mostly due to the available methodology to actually track the movements of these MPs in bivalves. Many bivalves are filter feeders and ingest and retain MPs in their digestive tracts. Different properties of MPs such as size, type, coating, shape, and density greatly affected their distribution and depuration in bivalves (Sendra et al., Reference Sendra, Sparaventi and Figueras2021).
Browne et al. (Reference Browne, Dissanayake, Galloway, Lowe and Thompson2008) showed that PS MPs (3.0 or 9.6 μm) were transported from the mussel gut into its circulatory system, and persisted in the hemolymph for 48 days, which then elicited an immune response. When the mussels M. edulis were exposed to the free high-density PE MPs (0–80 μm), the MPs were first attached to the gills and then transported to the stomach (Von Moos et al., Reference Von Moos, Burkhardt-Holm and Köhler2012). After that, they were accumulated in the lysosomes causing a strong inflammatory response. The uptake efficiency and residence time were closely related to the particle size, concentration, and composition (Von Moos et al., Reference Von Moos, Burkhardt-Holm and Köhler2012; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Hu, Zheng, Huang, Shang, Fang, Shi and Wang2021a). MPs tended to unevenly distribute and clustered within endocytotic vacuoles. Setälä et al. (Reference Setälä, Norkko and Lehtiniemi2016) found that MPs accumulated in the blue mussel (Mytilus trossulus) gills after 24 h. MPs were also documented in the distinct parts of the digestive tract such as lumen, stomach, and digestive diverticula in mussels.
Woods et al. (Reference Woods, Stack, Fields, Shaw and Matrai2018) used flow cytometry to quantify the uptake and ingestion of MP-fibers by mussels (M. edulis). In this study, the filtration rate was reduced when the mussels fed on MP-fibers, with a 95% maximum ingestion rate of 5,227 MPF h−1 at a concentration of 13 MPF mL−1. Mussels displayed an obvious pre-ingestion selection of the fibers, with 71% of fibers being rejected as pseudofeces, and only 9% of fibers were ingested by the mussels. Fernandez and Albentosa (Reference Fernandez and Albentosa2019a) showed that smaller irregularly shaped high-density PE MPs (2–4 μm) were less efficiently ingested by the mussels than large MPs (>10 μm), which were, however, eliminated faster. Mussels accumulated MPs with increasing MPs concentration, and the clearance rate of these MPs, were comparable to microalgae of similar size. In a similar study, Fernandez and Albentosa (Reference Fernandez and Albentosa2019b) exposed the mussels to a single dose (3 mg L−1) of irregularly shaped high-density PE MPs (mainly ≤10 μm) and similarly demonstrated the ingestion of MPs into the digestive gland and gills, with faster processing and elimination for larger MPs. Small MPs were also transported from the digestive system to the gills. In a more recent biokinetic study, Heo et al. (Reference Heo, Cho, Maruthupandy, Kim and Park2022) examined two particle sizes (10 and 90 μm) of fluorophore-labeled PS-microbeads in Mytilus galloprovincialis. A size difference effect was only found in the gills, with the smaller-sized MPs being accumulated more than the larger-sized ones. Mussels required at least 7 days to depurate the ingested MPs.
A few studies have also investigated the kinetics of MPs in oysters. Oysters (Magallana gigas) were exposed to fluorescent PS MPs of different sizes (100, 250, and 500 μm), followed by depuration for 3 days (Graham et al., Reference Graham, Palazzo, de Lucia, Telfer, Baroli and Carboni2019). The majority of ingested MPs were eliminated (84.6%), and 15.4% were found inside the shell cavity, whereas no MPs were measured in the soft tissues of the oysters. Ward et al. (Reference Ward, Zhao, Holohan, Mladinich, Griffin, Wozniak and Shumway2019b) attempted to compare the selection of MPs of different sizes and properties (PS MPs, 19–1,000 μm; nylon fibers, lengths 75–1,075 × diameter 30 μm) in Eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica and blue mussels M. edulis. There was an obvious selective rejection of MPs by the two bivalves, with the majority of larger or longer MPs being rejected (98%). MPs were also differentially eliminated by the bivalves. Thus, the overall MPs ingested and remaining in the gut were highly related to the properties of the MPs. More recently, Weinstein et al. (Reference Weinstein, Ertel and Gray2022) characterized the rate constant of accumulation and depuration of MPs in Eastern oysters. The oysters were exposed to different types of MPs (PE fibers, nylon fragments, or crumb rubber) at five particles mL−1 for a period of 4 days and then depurated for 4 days, during which time the oysters were removed at different time intervals. Uptake rate constants (k u) were 0.0084, 0.0025, and 0.0077 mL g−1 h−1 for fibers, fragments, and crumb rubber, respectively. The ingestion of the MPs was bi-phasic, and the depuration rate constants (k d) for the second slow phase were 0.0084, 0.0205, and 0.0048 h−1 for fibers, fragments, and crumb rubber, respectively. The recommended depuration time of 44 h would reduce the MPs load by 56%–68%. This study provided one of the first sets of biokinetic data for MPs in bivalves.
Fish
Most uptake studies have been simply based on the measurements of MPs in the fish tissues, and have demonstrated that fish either intentionally or unintentionally ingest MPs (Roch et al., Reference Roch, Friedrich and Brinker2020; Müller, Reference Müller2021). For marine fish, there are several possible pathways for MPs to enter into the fish, including gill uptake, direction ingestion of MPs through feeding, or uptake into the gastro-intestine due to seawater drinking for osmoregulation purposes. Fish may be able to discern the MPs due to their different feeding behaviors. For example, visually foraging fish may feed more actively on MPs that are optically similar to their prey, and chemosensory foraging fish may be able to discern the food items (Roch et al., Reference Roch, Friedrich and Brinker2020). Ingestion of MPs was also dependent on the MPs concentration and size of fish, as well as on foraging behavior. Müller et al. (Reference Müller, Erzini, Teodósio, Pousão-Ferreira, Baptista and Ekau2020) compared the ingestion of MPs (pristine or biofilm-coated) as well as the physiological impacts on juvenile seabream Diplodus sargus at comparable concentrations to those in the field over 3.5 weeks of MPs exposure along with natural prey. Juveniles were able to differentiate between edible and nonedible foods, but had no preference for biofilm-coated versus pristine particles. At environmentally relevant concentrations, fish growth and condition were not affected by MPs exposure.
Earlier, Lu et al. (Reference Lu, Zhang, Deng, Jiang, Zhao, Geng, Ding and Ren2016) exposed zebrafish to PS MPs of two sizes (5 and 20 μm) for 7 days and showed the accumulation of 5 μm MPs in gills, liver, and gut, whereas 20 μm MPs were only accumulated in the gills and gut. These MPs induced inflammation and lipid accumulation in the liver as well as oxidative stress, with significant disturbance of lipid and energy metabolism. Ohkubo et al. (Reference Ohkubo, Ito, Hano, Kono and Mochida2020) quantified the uptake and retention of MPs by mummichogs (Fundulus heteroclitus) and red seabream (Pagrus major). Accumulation of MPs in the gastrointestinal tracts was related to MPs concentrations in water, and fish removed the majority of MPs (>95%) within 25 h. Elimination was not related to the MP size (which may be due to the mucus entanglement of MPs in the gut), but to the fish species and MPs shape. In another study, juvenile Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) were exposed to two sizes of PE MPs (20 and 200 μm) or PS MPs (2 and 20 μm) for 14 days (Liu et al., Reference Liu, Qiu, Xu, Takai, Ogawa, Shimasaki and Oshima2021). Again, different tissue distributions were found, with the gastrointestinal tract being the major accumulating organ, and some MPs were distributed into the gills and heads. Estimated bioconcentration factors (L kg−1) for MPs varied between the two types and sizes of MPs (e.g., 74.4 for 200 μm PE, 25.7 for 20 μm PE, 16.8 for 20 μm PS, and 139.9 for 2 μm PS, respectively). An exponential pattern of depuration was found within the first 5 days, and a small size (2 μm PS MPs) was still found in the gastrointestinal tract after 10 days of depuration. Uptake and depuration of MPs were also examined for Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) (Ohkubo et al., Reference Ohkubo, Yoneda, Ito, Hano and Kono2022). Size instead of color was important in the MPs uptake, and smaller-sized MPs were taken up more than the larger-sized MPs by the adult fish instead of juveniles. Over 90% of the MPs was removed within 20 h of ingestion, indicating that MPs were retained similarly to food processing. In another study, ingestion and retention of MPs (PP, longest length of 125–250 μm, and PET fibers with a length of 600–700 μm) by the damselfish Pomacentrus amboinensis were also examined at environmentally relevant concentrations (Santana et al., Reference Santana, Dawson, Motti, van Herwerden, Lefevre and Kroon2021). Fish showed a significant dependence on the types of MPs ingested. Accumulation of PET fiber was significantly greater, and depuration was significantly slower than for the PP particles.
Trophic transfer
An important question in ecotoxicology is whether these MPs, once ingested by the prey, are passed along food chains. Trophic transfer refers to the process when a predator consumes prey containing MPs, such that the predator indirectly intakes these particles. A few studies have examined the trophic transfer of MPs from prey to predator, and demonstrated the accumulation of these trophically available MPs in different tissues of the predators. In one study (Farrell and Nelson, Reference Farrell and Nelson2013), mussels were exposed to two sizes of fluorescent PS particles, followed by feeding their soft tissues to red female blue crabs (Carcinus maenas). MPs were transferred from the mussels and accumulated in the stomach, hepatopancreas, ovary, and gills of the crabs. MPs also appeared in the crabs’ hemolymph, reaching a maximum of 0.04% of the exposed MPs concentration at 24 h, but were almost completely removed by 21 days of depuration. Dominguez-Lopez et al. (Reference Dominguez-Lopez, Bellas, Sanchez-Ruiloba, Plana and Hernandez-Urcera2022) examined the transfer of MPs from copepods to the seahorse Hippocampus reidi juveniles by exposing the copepods to PE MPs (1–5 μm). Seahorses accumulated these MPs in their guts in proportion to their concentration in the copepods.
A few studies have also attempted to contrast the relative importance of direct MPs exposure versus trophic transfer in the predator. Xu et al. (Reference Xu, Rodriguez-Torres, Rist, Nielsen, Hartman, Brun, Li and Almeda2022) showed that dietary exposure of mussels Brachidontes variabilis was the dominant source of MPs accumulation by the predatory gastropod mollusk Reishia clavigera. Hasegawa and Nakaoka (Reference Hasegawa and Nakaoka2021) first exposed fluorescent PE beads (27–32 μm) at 200 and 2,000 μg L−1 to mysids (Neomysis spp.), and then fed the mysids to the benthic fish Myoxocephalus brandti. The difference in MPs accumulation in the fish was then compared with fish directly exposed to MPs in the water. Exposure to mysid diets resulted in 3–11 times more PE accumulation in the fish than that under direct water exposure, suggesting that trophic transfer is a dominant pathway for fish to accumulate MPs in their bodies. Furthermore, small particles may be translocated from the digestive system to other tissues. Costa et al. (2020) exposed the nauplii of the copepod Tigriopus fulvus to PE MPs (1–5 μm) and then fed them to the jellyfish Aurelia sp. Although trophic transfer of MPs occurred in this specific food chain, no obvious effects of MPs on the immobility and pulsation frequency of the jellyfish were documented. In a field study, Murray and Cowie (Reference Murray and Cowie2011) collected lobsters Homarus Gammarus from the Clyde Sea and found MPs in their digestive systems. They concluded that the animals may ingest the MPs either through passive ingestion of sediment or through trophic transfer. In the laboratory, fish pieces labeled with MPs were used as food. All fish-feeding lobsters also contained the MPs in their stomachs.
Biomagnification of MPs from a lower trophic level to a higher trophic level is still inconclusive with little evidence available. For example, there was limited transfer of MPs from the mussels to crabs (Farrell and Nelson, Reference Farrell and Nelson2013). Miller et al. (Reference Miller, Hamann and Kroon2020) conducted a review of published papers (field and laboratory studies) to identify whether MPs did bioaccumulate and biomagnify in marine food chains across five trophic levels. Such analysis led to the conclusion that there was no obvious evidence that MPs were biomagnified in situ.
Toxicity
One of the main tasks in environmental toxicology is to identify the environmental as well as biological factors modifying the toxicity of different pollutants, often with mechanistic explanations. Toxicity of MPs has been the subject of countless studies over the past few years using different levels of approaches, including molecular, metabolic, biochemical, and physiological approaches. Different types of MPs, different organisms employed, and different conditions used often led to contrasting conclusions on the toxicity of MPs. Thus, it is important to standardize the testing conditions or at least observe the following factors in designing a sound ecotoxicological study.
Property of MPs. This remains the most frequent parameter considered in numerous studies. Size, functional group, shape, polymer composition, charge, and color, among others, are the ones describing the properties of MPs, which will profoundly affect the accumulation and toxicity of MPs to marine organisms. Currently, the most studied properties are the size, type, or shape of MPs. For example, a pristine MPs may behave very differently from the aged or surface-coated MPs (or with the presence of biofilms). In fact, such differences in the properties of MPs may vastly explain the different observations in many previous studies with contrasting animal behavior to MPs. In addition, most MPs used were original particles used in industrial processes, with a lack of additives such as plasticisers. Results obtained from these pristine MPs may be profoundly different from those observed in actual environments where MPs have been degraded or transformed (Xiong et al., Reference Xiong, Zhang, Chen, Shi, Luo and Wu2018).
Concentration. In any ecotoxicological study, it is important to quantify the flux or dosage or exposure of pollutants to the tested organisms and determine whether such dosage is environmentally relevant. The dosage then determines the toxicity to the organisms. For MPs toxicological studies, these should also be first scrutinized. The abundance of MPs used in most toxicity studies on MPs exposure is usually based on the mass concentration such as mg L−1 or μg L−1. In contrast, there is no so-called method to actually determine the concentrations of MPs in real environmental samples, and most field surveys are based on concentrations as particles per volume (e.g., m3), which is difficult to be converted to mass concentration due to the different densities and shapes of plastic fragments or particles. It may be possible to make some rough conversions between the density and number of particles. For example, the densities of the common MP materials PVC, PS, and PE are 1.4, 1.05, and 0.915–0.97 g cm3, respectively, and the average density of the three is 1.13 g cm3. In addition, most experiments on MPs toxicity have used abundances of MPs that are much higher than those observed in natural seawater. The so-called ‘environmentally relevant concentration’ is now a major consideration in all toxicological studies of MPs in the environment.
Time of exposure. This remains another important consideration of toxicity experiments. In natural environmental conditions, the exposure of MPs to aquatic organisms is unlikely to be constant in nature, and pulse (e.g., intermittent) exposure should certainly be addressed since it may generate very contrasting responses of organisms to MPs as compared with constant exposure.
Pathways of exposure. The major MPs exposure pathways are ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact. Different routes of exposure may target very different organs. For example, water exposure may lead to the accumulation of these MPs in the gills of marine fish, whereas trophic transfer may predominantly result in the accumulation of MPs in their digestive systems. Furthermore, MPs may also be directly ingested into their digestive tracts, which is not considered as a process of trophic transfer. Such differences in exposure pathways should certainly be considered in designing environmentally relevant toxicological studies.
General mechanisms of MPs toxicity
Numerous mechanisms of the toxic effects of MPs have been explored, including oxidative stress, immune responses, dysregulation of genome expression, endocrine system disruption, neurotoxicity, reproductive abnormalities, embryotoxicity, and transgenerational toxicity in organisms (Kashiwada, Reference Kashiwada2006; Wan et al., Reference Wan, Wang, Zhou, Shen, Wang, Fu and Jin2019; Barboza et al., Reference Barboza, Lopes, Oliveira, Bessa, Otero, Henriques, Raimundo, Caetano, Vale and Guilhermino2020; Ding et al., Reference Ding, Huang, Liu, Zhang, Zou, Wang, Zhu and Geng2020).
Reduced mobility and food intake. Perhaps the most well-known manifestations of toxicity are behavioral responses. MPs limit the mobility of animals by aggregating on the swimming legs, appendages, antennae, and furca (Cole et al., Reference Cole, Lindeque, Fileman, Halsband, Goodhead, Moger and Galloway2013; Bhuyan, Reference Bhuyan2022). Persistent and nondegradable MPs might block the feeding appendages and the alimentary canal. A full blockage in the gut may limit the ingestion and digestion of animals. In many animals, the presence of MPs in the stomach causes mechanical damage to the digestive system (Cole et al., Reference Cole, Lindeque, Fileman, Halsband, Goodhead, Moger and Galloway2013) and triggers structural and functional changes in digestive systems (Bhuyan, Reference Bhuyan2022). In addition, different fish species diversify in their gastrointestinal structures, and some of these diverse structures (e.g., coiled intestines, complex stomachs, and narrow openings between the stomach and intestine) may cause a higher tendency to retain MPs (Jabeen et al., Reference Jabeen, Su, Li, Yang, Tong, Mu and Shi2017).
Oxidative stress. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generate oxidative stress and damage cells, and are the main source of MPs’ toxicity. Oxidative stress is a universal biomarker for contaminant exposure (Jeong et al., Reference Jeong, Won, Kang, Lee, Hwang, Hwang, Zhou, Souissi, S-J and Lee2016, Reference Jeong, Kang, Lee, Kim, Han, Hwang, Souissi, Lee, Shin, Park and Lee2017; Revel et al., Reference Revel, Lagarde, Perrein-Ettajani, Bruneau, Akcha, Sussarellu, Rouxel, Costil, Decottignies, Cognie, Châtel and Mouneyrac2019; Bhuyan, Reference Bhuyan2022). Numerous studies have demonstrated the production of ROS after MPs exposure in different organisms, with measurements of different antioxidant enzyme activities (Choi et al., Reference Choi, Jung, Hong, Hong and Park2018; Revel et al., Reference Revel, Lagarde, Perrein-Ettajani, Bruneau, Akcha, Sussarellu, Rouxel, Costil, Decottignies, Cognie, Châtel and Mouneyrac2019), for example, the oxidative stress defense enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) which catalyzes the transformation of the superoxide radical into less harmful hydrogen peroxide, and catalase (CAT) which removes hydrogen peroxide.
Immune system. MPs may damage the function of immune systems and inhibit immunity, and eventually damage tissues such as the liver (Rochman et al., Reference Rochman, Kurobe, Flores and Teh2014; Karami et al., Reference Karami, Romano, Galloway and Hamzah2016). Greven et al. (Reference Greven, Merk, Karagaz, Mohr, Klapper, Jovanovic and Palic2016) demonstrated that MPs triggered the degranulation of primary particles, stimulated the activity of oxidation bursts, and increased the release of neutrophils in the fish Pimephales promelas extracellular environments. The innate immunity was significantly inhibited, which may finally affect the fish’s resistance to disease. Liu et al. (Reference Liu, Liang, Zhou, Chang and Li2023) showed that MPs affected the activity and gene expression of immune system-related enzymes of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) larvae.
Endocrine disruption and neurotoxicity. Many compounds used in the manufacture of plastics are endocrine disruptors. The expression of fish endocrine marker genes was disrupted when they ingested MPs enriched with organic contaminants in seawater (Rochman et al., Reference Rochman, Kurobe, Flores and Teh2014). MPs may pass through the gastrointestinal barrier and enter the blood, and then may pass through the blood–brain barrier and cause neurotoxic effects (Ding et al., Reference Ding, Huang, Liu, Zhang, Zou, Wang, Zhu and Geng2020; Sökmen et al., Reference Sökmen, Sulukan, Türkoğlu, Baran, Özkaraca and Ceyhun2020; Guerrera et al., Reference Guerrera, Aragona, Porcino, Fazio, Laurà, Levanti, Montalbano, Germana, Abbate and Germanà2021).
Developmental toxicity. MPs may cause significant toxic effects on the embryonic and larval development of marine animals. Zebrafish embryos exposed to NPs accumulated NPs in the yolk sac, which were then transferred to the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, liver, pancreas, heart, and brain, causing a reduction in heart rate and larval swimming ability (Pitt et al., Reference Pitt, Trevisan, Massarsky, Kozal, Levin and Ti Giulio2018). Aminated NPs caused defects in the embryonic development of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus, but carboxylated NPs did not cause such effects (Frydkjær et al., Reference Frydkjær, Iversen and Roslev2017).
Reproduction and growth. MPs exposure may result in reduced reproductive efforts by animals. Sussarellu et al. (Reference Sussarellu, Suquet, Thomas, Lambert, Fabioux, Pernet, Le Goïc, Quillien, Mingant, Epelboin, Corporeau, Guyomarch, Robbens, Paul-Pont, Soudant and Huvet2016) demonstrated that Pacific oysters exposed to PS MPs (2 and 6 μm) for 8 weeks had reduced sperm viability, egg numbers, and size. Such effects were irrecoverable as the larvae continued to display reduced survival and growth. Lo and Chan (Reference Lo and Chan2018) fed 2 μm size MPs balls to the larvae of the gastropod mollusk Crepidula onyx and showed no negative effects on these larvae at 10 ng mL−1, while at higher abundances, the MP balls led to slow growth and premature settlement of the larvae.
Indirect toxic effects. In addition to the direct toxicity of MPs, their manufacturing process involves a large number of chemical additives, which may potentially cause toxicity. For example, polybrominated diphenyl ethers may be added to enhance the performance of polymers, and may be leached. Leaching of these chemicals may substantially confound the interpretation of toxicity results (Cai et al., Reference Cai, He, Liu, Li, Tang, Wang, Huang, Wei, Lin, Chen, Hu and Cen2018). Oliviero et al. (Reference Oliviero, Tato, Schiavo, Fernández, Manzo and Beiras2019) found that PS and high-density PE leachates had more toxic effects on common sea urchin (P. lividus) embryos than did virgin plastic pellets and aged plastic pellets. Moreover, the leachate of recycled plastics was lethally toxic to the larvae of barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite and significantly inhibited the ability of larvae to settle. There is a large body of works on the interactions between MPs and other environmental contaminants and will not be reviewed here.
Cellular mechanisms of MPs. MPs can interact both with macromolecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids and small molecules. In the external environments, proteins may potentially form corona-like aggregates and affect the endocytosis process. In embryonic zebrafish fibroblast cells ZF4, Yang and Wang (Reference Yang and Wang2022) showed the differential cytotoxicity of two different sizes of PS NPs (100 and 1,000 nm) as a result of different intracellular trafficking and impacts. Following cellular internalization, both NPs were transported to the lysosomes and either induced lysosomal acidification (for 1,000-nm size) or alkalization (for 100 nm) with resulting lysosome rupture. The 100 nm NPs subsequently caused a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and induced ROS production, which then stimulated caspases activation and irreversible cell death. Larger size (1,000 nm) NPs instead activated the autophagy and destroyed the integrity of cell membrane, while activated the caspases and triggered apoptosis of the cells. There was a clear interaction among different cellular processes (autophagy, apoptosis, lysosome damage, and mitochondria membrane), which explained the different cytotoxicity of NPs to the fish cells. In another study, Yang and Wang (Reference Yang and Wang2023) also showed that the uptake capacity of NPs was related to their functionality (e.g., pristine, -NH2, and -COOH), even though their uptake rates were similar. Exocytosis of these internalized NPs may be related to energy-dependent lysosomal process and the estimated half-lives of these internalized NPs were 10–15 h.
Toxicity to microalgae
Phytoplanktonic microalgae are ideal for toxicity assessment because of their sensitivity as well as laboratory convenience (Tato and Beiras, Reference Tato and Beiras2019). Any impact on microalgae may cause a cascading effect on a whole ecosystem. Various harmful effects of MPs on microalgae have been examined, especially on their shading effect, photosynthesis, and growth. MPs affected the photosynthesis, growth, gene expression, as well as colony size and morphology (Yokota et al., Reference Yokota, Waterfield, Hastings, Davidson, Kwietniewski and Wells2017). Nava and Leoni (Reference Nava and Leoni2021) suggested that more studies are required to reveal how the properties of MPs and environmental conditions affect microalgal growth. MPs may be physically toxic or interact with chemicals and then cause impacts on algal growth, photosynthetic activity, and morphology. In addition, MPs may reduce nutrient availability or even affect the higher trophic levels of organisms, indirectly affecting the population of phytoplankton (Prata et al., Reference Prata, da Costa, Lopes, Duarte and Rocha-Santos2019).
Mechanisms of toxicity of MPs on phytoplankton have mainly focused on adsorption, given the small size of MPs with a large specific surface area and adsorption capacity. In addition, leaching of chemical additives from MPs and their subsequent effects on microalgal physiology may also cause toxic effects on algae. Leaching of additives from MPs is dependent on the water chemistry and may pose ecological risks to algae (Luo et al., Reference Luo, Xiang, He, Li, Zhao, Wang and Pan2019). In Chlorella vulgaris, the maximum photochemical quantum efficiency of photosystem II decreased with leachate concentration (Luo et al., Reference Luo, Xiang, He, Li, Zhao, Wang and Pan2019).
MPs reduced chlorophyll content and photosynthetic efficiency, thus affecting the photosynthesis of algae. PP and PVC MPs at 5–500 mg L−1 reduced the chlorophyll levels of Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Microcystis hydrocystis, and Scenedesmus in freshwater (Barboza et al., Reference Barboza, Vieira, Branco, Figueiredo, Carvalhi, Carvalhi and Guihermino2018; Wu et al., Reference Wu, Guo, Zhang, Zhang, Xie and Deng2019). PVC is relatively more toxic than PP based on its inhibition values. PVC also significantly reduced the photosynthesis efficiency of microalgae (Bhattacharya et al., Reference Bhattacharya, Lin, Turner and Ke2010; Wu et al., Reference Wu, Guo, Zhang, Zhang, Xie and Deng2019) and inhibited the algal growth. In addition, MPs adsorption on microalgae reduced the exchanges of nutrients, gases, or metabolites (Prata et al., Reference Prata, da Costa, Lopes, Duarte and Rocha-Santos2019). Mao et al. (Reference Mao, Ai, Chen, Zhang, Zeng, Kang, Li, Gu, He and Li2018) showed that exposure of Chlorella to PS MPs caused distortion of thylakoids and damage of cell membranes. Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Chen, Wang and Tan2017) found that 1-μm PVC significantly inhibited the growth of the diatom Skeletonema costatum at 50 mg L−1, with a maximum growth inhibition of 39.7% after 4 days of exposure. MPs of 1-mm size did not cause any inhibition on growth. The inhibition of growth was not due to the shading effect, but was mainly due to the formation of heterodimers when MPs interacted with algal cells with the release of toxins (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Chen, Wang and Tan2017). Effects of MPs on phytoplankton photosynthesis became stronger with increasing MPs concentration, and varied among species and MPs size. PVC produced higher toxicity than PP MPs (Wu et al., Reference Wu, Guo, Zhang, Zhang, Xie and Deng2019). Smaller sizes of MPs inhibited algal growth and favored the formation of hetero-aggregates (Lagarde et al., Reference Lagarde, Olivier, Zanella, Daniel, Hiard and Caruso2016; Jin et al., Reference Jin, Li, Chen, Wang, Zhang, Yang, Wang, Fu, Yu, Cheng and Wu2022). The small size of MPs may act as a physical blockage on sunlight and oxygen, which also stimulate the formation of ROS. Seoane et al. (Reference Seoane, González-Fernández, Soudant, Huvet, Esperanza, Cid and Paul-Pont2019) examined the toxicity of 2.5-μg mL−1 amino-modified PS MPs of two sizes (0.5 and 2 μm) to the diatom Chaetoceros neogracile. MPs did not attach to the algal cell surfaces and did not affect the cell morphology, growth, photosynthesis, ROS, or membrane potential. However, neutral lipid content and cellular esterase activity were significantly reduced. Oil bodies are an energy source for maintaining a healthy cellular state, suggesting that microalgae exposed to MPs responded to adverse conditions by regulating the energy metabolism. A freshwater alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was exposed to different concentrations of MPs (5, 25, 50, and 100 mg L−1), with a maximum growth rate reduction by 46% (Li et al., Reference Li, Wang, Zhang, Zhou, Yin, Hu, Hu, Liu and Zhu2020a). The green alga C. pyrenoidosa was affected by PS and TPT particles, resulting in a breakdown of cell structure and inhibition of photosynthesis and growth (Yi et al., Reference Yi, Chi, Li, Wang, Yu, Wu and Zhou2019; Li et al., Reference Li, Yi, Zhou, Chi, Li and Yang2020b). Zhao et al. (Reference Zhao, Tan, Huang and Wang2019a) also demonstrated a decrease in Chl a content and photosynthesis of phytoplankton due to MPs exposure.
Chen et al. (Reference Chen, Ling, Li, Hu, Cao and He2020a) exposed different marine and freshwater phytoplankton species to PS MPs of different sizes (1–5 μm) at 10 mg L−1. Smaller-sized MPs were internalized by the phytoplankton cells, whereas larger-sized ones (3.0–5.0 μm) were not internalized. Smaller sizes (1.0–2.0 μm) of MPs then caused inhibition of algal growth and photosynthesis. In a similar study, Zhang et al. (Reference Zhang, Chen, Wang and Tan2017) examined the impact of MPs on the diatom S. costatum. MPs (1 μm) inhibited the algal growth, but larger-sized MPs (1 mm) did not affect the growth. Photosynthetic efficiency and Chl a content were reduced upon MPs exposure. One possible mechanism for such impact was the adsorption and aggregation of microalgae instead of the shading effect by MPs. Similar effects of MPs were also found for the green algae C. pyrenoidosa (Mao et al., Reference Mao, Ai, Chen, Zhang, Zeng, Kang, Li, Gu, He and Li2018) under PS exposure, which caused a dose-dependent effect on growth and photosynthetic activity of the algae. Interestingly, the algae were able to alleviate the impacts caused by MP by cell wall thickening and aggregation, which then increased photosynthesis and growth. More recently, Ye et al. (Reference Ye, Rao, Xiao, Zhou and Li2023) examined the toxicity of PS MPs of various sizes (0.2–5 μm) on 12 species of microalgae. Smaller sizes of MPs had the greatest impact on the microalgae growth, especially for those larger sizes of microalgae. Among the different species of phytoplankton, diatoms appeared to be especially susceptible to MPs. Both ROS and MDA increased under MPs exposure; thus, antioxidant systems were the main systems responding to MPs.
Toxicity to zooplankton
Botterell et al. (Reference Botterell, Beaumont, Dorrington, Steinke, Thompson and Lindeque2019) reviewed 22 studies on MPs and found that 39 species of zooplankton could ingest MP particles. Nearly half of these studies confirmed the negative effects of MPs on zooplankton feeding behavior, development, growth, reproduction, and life history, whereas there were other reports of no visible negative effects of MPs on zooplankton ingestion. For example, Beiras et al. (Reference Beiras, Bellas, Cachot, Cormier, Cousin, Engwall, Gambardella, Garaventa, Keither, Le Bihanic, Lopez-Ibanez, Piazza, Rial, Tato and Vidal-Linan2018) examined the toxicity of PE MPs on major groups of zooplankton including rotifers, copepods, and the larvae of bivalves, echinoderms, and fish. The results did not support environmental risks of MPs to marine zooplankton at typical concentrations likely to be encountered in the environment. Mechanisms of acute toxicity of MPs to zooplankton need to consider leachates of different materials and malnutrition due to gut blockage. Further, most environmental MPs are fibrous, and the releases of regular plastic fragments are relatively low.
Larvae of Amphibalanus amphitrite and Artemia franciscana accumulated 0.1-μm PS MP which produced sublethal effects such as oxidative stress and neurotoxicity (Gambardella et al., Reference Gambardella, Piazza, Albentosa, Bebianno, Cardoso, Faimali, Garaventa, Garrido, González, Pérez, Sendra and Beiras2019). PS MPs also affected the feeding, motility and molting processes of A. franciscana larvae. Rodriguez-Torres et al. (Reference Rodriguez-Torres, Almeda, Kristiansen, Rist, Windling and Nielsen2020) studied the ingestion of 20-μm PE MPs by three Arctic copepods (Calanus finmarchicus, C. glacialis, and C. hyperboreus). At the two exposed concentrations (200 and 20,000 MPs L−1) as well as different algal concentrations, egg production increased by eight times as compared to the controls, indicating a possible ‘hormesis’ type of copepod response to MPs.
PE-fibers and PE-microspheres showed a dose-dependent effect on the growth and reproduction of freshwater zooplankton Ceriodaphnia dubia (Rehse et al., Reference Rehse, Kloas and Zarfl2016). The toxicity of MPs on zooplankton was also size-dependent, for example, the 96-h EC50 for Daphnia magna was 57.4 mg L−1 for 1-μm PE MPs particles, but 100-μm PE MPs were not ingested and had no negative effect. Thirteen zooplankton species were shown to ingest small-size (1.7–30.6 μm) PS MPs, and exposure to small-size MPs (7.3 μm) inhibited the feeding of Centropages typicus. Thus, zooplankton may not be able to recognize MPs during feeding, and the prolonged presence of MPs in the gut affected the food intake. In addition to ingestion, MPs also affected egestion and food digestion, leading to the possibility of starvation (Kokalj et al., Reference Kokalj, Horvat, Kunej, Bele and Kržan2016; Pikuda et al., Reference Pikuda, Xu, Berk and Tufenkji2019).
Shore et al. (Reference Shore, deMayo and Pespeni2021) examined the effects of PS MPs (6.68 μm) on the growth, survival, fecundity, and egg quality, as well as fecal pellets produced by the copepod A. tonsa. Exposure to MPs reduced the body length, survival of nauplii, and size of eggs when copepods were exposed to MPs during oogenesis. Based on the life history impacts, it was estimated that population growth may decrease by 15%, eventually leading to a projected 30-fold decrease in abundance over 1 year or 20 generations under MP exposure. Choi et al. (Reference Choi, Hong and Park2020) exposed the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus to 50-nm and 10-μm PS microbeads. Both size and exposure time increased the ROS levels, and antioxidant-related gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activities were changed significantly. Koski et al. (Reference Koski, Sondergaard, Christensen and Nielsen2021) examined three different tire wear originated MPs (10–10,000 TWP L−1) on the feeding, reproduction as well as fecal pellet production of two coastal copepods at two food concentrations consisting of Rhodomonas sp. No effect of TWP on copepods at environmentally relevant concentrations of <10 TWP L−1 was observed. Copepod feeding and pellet production was affected at much higher TWP concentrations, but reproduction was unaffected.
Kim et al. (Reference Kim, Yoon, Choi, Jung and Park2022) examined the impacts of 30 days of chronic exposure to PS MPs of two sizes (50 nm and 2 μm) and at two concentrations (0.5 μg L−1 and 100 mg L−1) to the copepod T. japonicus. The LC50 of 50-nm and 2-μm PS MPs were 0.10 mg L−1 and 3.92 mg L−1, respectively. Smaller size of MPs also delayed development, whereas the larger size of MPs inhibited reproduction at low concentrations. ROS was produced after MPs exposure, whereas oxidative stress was not significantly affected by MPs at environmentally relevant concentrations.
Toxicity to bivalves
Bivalves have been the main group of organisms used in MPs toxicological studies, which considered different sizes, concentrations, pathways, and periods of MPs exposure. Baroja et al. (Reference Baroja, Christoforou, Lindstrom and Spatharis2021) reviewed the various studies on the effects of MPs on bivalves. Among the different bivalve species examined, mussels and oysters were most commonly examined. Most studies focused on the spherical types of MPs and used exposed concentrations that were a few orders of magnitude higher than those occurring in real field environments. More studies are needed for the other real MPs in the environment such as fibers involving lower exposure concentrations. Li et al. (Reference Li, Chang, Hu, Fang, Sokolova, Huang, Xu and Wang2022) conducted a bibliometrics analysis of MPs studies in marine bivalves. MPs produced oxidative stress by affecting antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and SOD within short periods of exposure. However, such effects became less obvious with longer periods of exposure or during depuration periods. Given the nonlinear response, these enzymes were not considered to be good biomarkers of MPs exposure. Instead, the levels of glutathione and CAT may be considered to be more suitable as oxidative stress biomarkers of sublethal MPs effects.
Wei et al. (Reference Wei, Hu, Zhang, Gu, Sun, Zhang, Shi, Chen and Wang2021) showed that PE and PS were accumulated in mussels (M. galloprovincialis), with the highest accumulation in the digestive gland and gill. Most of these ingested MPs were eliminated by the mussels within 6 days of depuration. SOD, CAT, and glutathione increased, indicating the oxidative stress caused by MPs. MPs also caused a perturbation of metabolism of mussels, especially in the case of the energy and lipid metabolism as well as TCA cytochrome and neurotoxicity. Opitz et al. (Reference Opitz, Benitez, Fernandez, Osores, Navarro, Rodriguez-Romero, Bohrmann and Lardies2021) exposed the mussel Choromytilus chorus to different concentrations (0, 100, and 1,000 particles L−1) for 40 days and demonstrated minimal effects of MPs on the physiology (scope for growth [SFG], size, and metabolism) of the mussels at all the studied concentrations. However, there was an obvious histopathological effect of MPs on the mussels. Abidli et al. (Reference Abidli, Pinheiro, Lahbib, Neuparth, Santos, Trigui and Menif2021) also evaluated the effects of PE MPs (40–48 μm) on the mussel M. galloprovincialis over a period of 14 days of exposure (1, 10, 100, and 1,000 μg L−1). The filtration rate of the mussels was reduced with increasing PE concentrations, and biochemical biomarkers (oxidative damage, CAT, and GST) were induced at the tested concentrations. Cole et al. (Reference Cole, Liddle, Consolandi, Drago, Hird, Lindeque and Galloway2020) exposed mussels (Mytilus spp.) at one concentration (500 ng mL−1) to 20-μm PS, 10 × 30-μm microfibers, or 50-nm PS NPs for 1 or 7 days, and then quantified the immune response, oxidative response, lysosomal stability, and genotoxic damage. NPs significantly affected the hyalinocyte–granulocyte ratios in the blood. SOD was induced after 1 day of exposure, but this effect disappeared after 7 days. In contrast, MPs did not cause lysosomal instability or genotoxic damage. Similarly, another mussel, Perna viridis, were exposed to PS (0.5, 5, and 50 μm) at 0.6 mg L−1 for 7 days followed by 7 days of depuration. Different biomarkers were then measured (Jong et al., Reference Jong, Li, Noor, He and Gin2022). NP exposure (0.5 μm) showed more obvious effects on lysosomal instability and antioxidant defenses, immunotoxicity, and genotoxicity than did MP exposure.
Digestive enzyme activities of M. galloprovincialis were measured following exposure to MPs of different types, sizes, and at different concentrations (Trestrail et al., Reference Trestrail, Walpitagama, Miranda, Nugegoda and Shimeta2021). PS MPs reduced the activities of the digestive enzymes’ amylase and xylanase, but increased the cellulase activity. MPs at a high concentration (5 × 104 MPs L−1) also caused an increase in total protease activity, whereas laminarinase, lipases, and lipolytic esterases were not affected by the type, size, and concentration of the MPs. Such changes may lead to changes in energy acquisition and reserves of the mussels. Huang et al. (Reference Huang, Wang, Chen, Xu, Luo, Zeng, Huan, Li and Wang2021) examined the toxicity of PS MS to mussels (Mytilus coruscus) by using a metabolomic approach. Exposure to MPs led to disruption of amino acid metabolism, oxidative stress, immunotoxicity, and neurotoxicity, and some of these influences were evidenced at environmentally relevant concentrations. Again, mussels showed a rapid recovery of their metabolic profiling following 7 days of depuration. Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Zhong, Li, Wang, Gu, Huang, Fang, Shi, Hu and Wang2021b) further showed that the presence of microalgae alleviated the impacts (energy budget, CAT, and MAD levels) caused by MPs exposure on the mussels M. coruscus, while MPs induced more effects than the NPs. In the case of oysters, Teng et al. (Reference Teng, Zhao, Zhu, Shan and Wang2021a) exposed Crassostrea gigas to irregular MPs of PE and PET at 10 and 1,000 μg L−1 for 21 days. These two types of MPs were ingested by the oysters, which then inhibited lipid metabolism and activated the enzymes involved in energy metabolism. Toxicity of MPs increased with increasing MPs concentration, and PET MPs were more toxic than the PE type. MPs did not have any obvious effect on physiological responses, but induced oxidative stress, and disturbed a few metabolic processes of the oysters. At the gene level, genes related to aerobic and lipid metabolism and apoptosis were affected. Bringer et al. (Reference Bringer, Cachot, Dubillot, Prunier, Huet, Clerandeau, Evin and Thomas2022) also exposed the oysters (C. gigas) to a cocktail of MPs for 2 months (mixture of PE, PP, and PVC polyvinyl chloride). MPs did not have any effect on the growth of oysters, but induced mortality at 0.1 and 10 mg L−1. Oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and environmental stress were also induced upon MPs exposure, with a significant increase of GST, MDA, and laccase, whereas SOD was not affected. MPs also had a negative impact on the swimming activity of larvae and development when the parent oysters were exposed.
Song et al. (Reference Song, Choi and Park2020) exposed the bay scallop Argopecten irradians to MPs (1 μm) at different concentrations (10–1,000 beads mL−1 for 7 days, and then measured the accumulation of MPs in digestive diverticula and defense responses at different periods. SOD, CAT, and H2O2 increased with increasing MPs concentration and duration of exposure. Jiang et al. (Reference Jiang, Fang, Du, Gao, Fang and Jiang2022) exposed the clam, Ruditapes philippinarum to MPs (5 and 10 μm), and measured subsequent physiological processes, growth, and reproduction. Accumulation of PS increased respiration and excretion but decreased feeding and absorption efficiency, eventually resulting in a reduced SFG and growth. Protein metabolism and insulin-related signaling pathways were also affected by PS exposure. Other studies examined the influences of MPs on the fertilization success of bivalves (Tegillarca granosa) (Shi et al., Reference Shi, Sun, Han, Tang, Zhou, Zhang, Du, Huang and Liu2022). MPs weakened sperm swimming by reducing ATP production and cell viability, as well as leading to gamete fusion failure by inducing oxidative stress.
Hemocytes are the main immune cells in bivalves to deal with foreign particles, and thus are recognized as the primary target of the immunotoxicity of MPs (Jovanović and Palić, Reference Jovanović and Palić2012). It is assumed that MPs are taken up by hemocytes through endocytosis and phagocytosis-dependent pathways, and then accumulated in lysosomes (Sendra et al., Reference Sendra, Carrasco-Braganza, Yeste, Vila and Blasco2020). Lysosomes represent the key sites for sequestration and detoxification of exogenous particles in hemocytes and are recognized as the main target organelles of MPs (Avio et al., Reference Avio, Gorbi, Milan, Benedetti, Fattorini, d’Errico, Pauletto, Bargelloni and Regoli2015; Pittura et al., Reference Pittura, Avio, Giuliani, d’Errico, Keiter, Cormier, Gorbi and Regoli2018; Capolupo et al., Reference Capolupo, Valbonesi and Fabbri2021; Ringwood, Reference Ringwood2021). Immunotoxicity is principally governed by lysosomal dysfunction and depressed phagocytosis, leading to a decreased ability for the bivalves to defend themselves against foreign substances (Jovanović and Palić, Reference Jovanović and Palić2012). Studies have indicated that amino-modified PS MPs (PS-NH2) cause the destabilization of the lysosomal membrane, ROS production, and decreased phagocytosis (Canesi et al., Reference Canesi, Ciacci, Bergami, Monopoli, Dawson, Papa, Canonico and Corsi2015, Reference Canesi, Ciacci, Fabbri, Balbi, Salis, Damonte, Cortese, Caratto, Marco, Monopoli, Dawson, Bergami and Corsi2016). Another study found that 1-μm PS MPs caused higher immune responses compared with 50 and 100 nm, which may be related to their higher stability in shape and size (Sendra et al., Reference Sendra, Carrasco-Braganza, Yeste, Vila and Blasco2020). This study showed the translocation of NPs into hemocytes, with subsequent immune effects. Currently, immune responses are widely employed to estimate the toxic effects of metallic nanoparticles on bivalves (Weng et al., Reference Weng, Meng, Huo, Wu and Wang2022).
Toxicity to fish
Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Ge and Yu2020) reviewed the bioavailability and toxicity of MPs to different fish species. Following exposure to MPs alone or in combination with other contaminants, fish can exhibit various health problems. Foley et al. (Reference Foley, Feiner, Malinich and Höök2018) conducted a meta-analysis of impacts of MPs exposure on the feeding, growth, reproduction, and survival of fish. Many of these responses were considered to be neutral, and such effects were highly variable across taxa. The most consistent effect was a reduction in consumption of natural prey when MPs were present due to the less attractive tastes. Toxicity of MPs to fish is highly dependent on the feeding and accumulation of MPs in the fish. Li et al. (Reference Li, Liang, Liu, Fu, Ma, Chen, Su, Craig and Shi2021) suggested that swallow-feeding fish ingested more MPs than the other feeding types of fish (e.g., filtering- and sucking-feeding). These fish sucked in microfibers rather passively, and showed rejection by coughing up microfibers mixed with mucus. Some of the microfibers ended up in the gastrointestinal tracts and gills of fish. Abarghouei et al. (Reference Abarghouei, Hedayati, Raeisi, Hadavand, Rezaei and Abed-Elmdoust2021) exposed the goldfish Carassius auratus to different sizes of PS MPs (0.25 and 8 μm) at different concentrations. Following 7 days of exposure to a high concentration (300 mg L−1), fish were subsequently exposed to low concentrations (0.05, 0.5, and 5 mg L−1) for 28 days. These MPs were accumulated in different tissues, and tissue lesions were documented in liver, gills, and intestine, with size- and dose-dependent relationships. Antioxidant SOD and CAT were induced with a significant expression of related genes such as CAT, SOD, and HSP70.
Many studies have used zebrafish or medaka as model fish species. PP and PVC caused morphological deformity of Danio rerio (Lu et al., Reference Lu, Zhang, Deng, Jiang, Zhao, Geng, Ding and Ren2016) and PS accumulation damaged the gills, liver, and gut tissues (Lu et al., Reference Lu, Zhang, Deng, Jiang, Zhao, Geng, Ding and Ren2016). PS also suppressed the locomotor activity (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Gundlach, Yang, Jiang, Velki, Yin and Hollert2017) and immune system (Veneman et al., Reference Veneman, Spaink, Brun, Bosker and Vijver2017) of D. rerio; thus, the fish were more suspectable to disease infection. PE disrupted the development of embryos and hepatic metabolism (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Bao, Wan, Fu and Jin2019b), as well as the nervous system such as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Gundlach, Yang, Jiang, Velki, Yin and Hollert2017). The predatory performance may be severely retarded with the potential neurotoxicity.
Capó et al. (Reference Capó, Company, Alomar, Compa, Sureda, Grau, Hansjosten, Lopez-Vazquez, Quintana, Rodil and Deudero2021) reported hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation in gilthead seabream following MP exposure. The seabream were fed a diet spiked with low-density PE MPs of 100–500-μm size for 3 months, followed by 1-month depuration. There was a progressive increase in CAT, SOD, GPx, and glutathione reductase in the fish livers. MDA in the liver (lipid oxidative damage) increased after exposure to MPs (Capó et al., Reference Capó, Company, Alomar, Compa, Sureda, Grau, Hansjosten, Lopez-Vazquez, Quintana, Rodil and Deudero2021). In addition to hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation, MPs inhibited the metabolic pathways of the liver (Ye et al., Reference Ye, Zhang, Liu, Liao, Zhang, Yan, Lin and Huang2021). Following MP exposure, most monosaccharides, organic acids, and amino acids in the medaka decreased significantly, whereas most fatty acids, fatty acid methyl esters, and ethyl esters increased significantly. Thus, PS MPs induced metabolic changes and the accumulation of various substances such as lipids in the liver. Nucleic acid metabolism and/or energy production in marine medaka were disrupted, and carbohydrate storage, transport, and assimilation were compromised as a result of MPs exposure. Although smaller-sized MPs were more likely to be retained in the tissues and potentially be more toxic (Rist et al., Reference Rist, Baun and Hartmann2017), larger-sized MPs caused faster stress responses and higher hepatic metabolic disturbances in livers compared to NPs (500 nm) (Yin et al., Reference Yin, Liu, Cui, Chen, Li and Wu2019).
MPs may clog the digestive tract, stomach, and intestinal lumen of animals. Lei et al. (Reference Lei, Wu, Lu, Liu, Song, Fu, Shi, Raley-Susman and He2018) found that MPs (70 μm) caused damage to the intestinal villi and lysis of intestinal cells in adult zebrafish. Spherical MPs may be defecated more readily than fragmented MPs (Mazurais et al., Reference Mazurais, Ernande, Quazuguel, Severe, Huelvan, Madec, Mouchel, Soudant, Robbens, Huvet and Zambonino-Infante2015). MPs fragments may increase the possibility of intestinal damage and retention of MPs in the gastrointestinal wall and gills (Karami et al., Reference Karami, Romano, Galloway and Hamzah2016). At the microbiota level, exposure of zebrafish to PS MPs (0.5 and 50 μm, 1 mg L−1) for 14 days resulted in significant changes in the intestinal microflora and caused certain degrees of inflammatory response (Jin et al., Reference Jin, Xia, Pan, Yang, Wang and Fu2018), which then resulted in dysfunction and pathogenesis (Lu et al., Reference Lu, Luo, Zhao, Cai, Fu and Jin2019). MPs can contribute to intestinal inflammation and metabolic disorders in adult zebrafish by altering the microbiota composition in their gut (Jin et al., Reference Jin, Xia, Pan, Yang, Wang and Fu2018; Wan et al., Reference Wan, Wang, Zhou, Shen, Wang, Fu and Jin2019). In addition, MPs entering the fish gut had a negative impact on their intestinal cells. In seabass, MPs caused deterioration in the structure and function of intestines. During the initial period of exposure, the intestine secreted mucus and there was an increase in the number of small intestinal cells. Subsequently, vacuolization of enterocytes and coalescence of villi occurred. Deterioration in inflammation became more pronounced with increasing MPs exposure (Pedà et al., Reference Pedà, Caccamo, Fossi, Gai, Andaloro, Genovese, Perdichizzi, Romeo and Maricchiolo2016).
MPs are highly neurotoxic (Xiong et al., Reference Xiong, Liu, Xu, Huang, Wang, Li, Wang, Zhang, Pu and Sun2022). NPs are likely to cross the barrier and cause a high degree of neurotoxicity by increasing oxidative stress and inhibiting AChE activity as a key enzyme in neurotransmission. Inhibition of AChE resulted in excessive accumulation of acetylcholine, which overexcited nerves and led to disorders. Santos et al. (Reference Santos, Felix, Luzio, Parra, Cabecinha and Bellas2020) showed that MPs strongly inhibited AChE activity in the zebrafish brain, leading to lipid peroxidation and inhibition of related enzyme activities, thus causing neurotoxicity. Histological study of the brain revealed increased numbers of inflammatory cells, neuronal necrosis, and cytoplasmic vacuolization. At the behavioral level, fish displayed depression, low frequency of food intake, and reduced activity (Umamaheswari et al., Reference Umamaheswari, Priyadarshinee, Bhattacharjee, Kadirvelu and Ramesh2021).
However, significant increases in fish mortality, and growth and reproduction have also been documented in the literature (Cong et al., Reference Cong, Jin, Tian, Wang, Shi, Wang and Mu2019; Xia et al., Reference Xia, Sun, Zhou, Chang and Li2020). MPs may damage the internal tissues of fish, be translocated to different tissues, and affect their ability to swim (Yang et al., Reference Yang, Xiong, Mi, Xue, Wei and Zhang2020). There was also a reduction in the head/body ratio in terms of appearance (Pannetier et al., Reference Pannetier, Morin, Le Bihanic, Dubreil, Clérandeau, Chouvellon, Van Arkel, Danion and Cachot2020). Declines in overall marine fish populations can result from reduced hatchability and reduced responsiveness to olfactory threats (Lonnstedt and Eklov, Reference Lonnstedt and Eklov2016; Li et al., Reference Li, Wang, Yang, Lu, Zheng, Zhang, Zhang, Tian, Wang and Ru2019). Chen et al. (Reference Chen, Gundlach, Yang, Jiang, Velki, Yin and Hollert2017) demonstrated that zebrafish larvae became smaller under PS NPs exposure. PVC MPs exposure inhibited the growth of carp larvae, and the inhibition by MPs on marine medaka larvae was positively related to the exposure concentration. One possible explanation was the hyperactivity of the larvae which activated a pro-inflammatory immune response and resulted in an increased energy expenditure. Chen et al. (Reference Chen, Chen, Fang, Zheng, Jiang, Zhang, Wang, Bailey, Segner and Bo2020b) demonstrated that the exposure of vinyl chloride MPs caused significant changes in heart rate, hatching time, hatching rate, as well as the deformity rate and deformity type of marine medaka larvae. The presence of these MPs in the intestine led to reduced food intake and digestibility (Yin et al., Reference Yin, Liu, Cui, Chen, Li and Wu2019).
MP exposure may also significantly affect the reproductive performance of fish, including developmental abnormality in their offspring with transgenerational effect (Pitt et al., Reference Pitt, Trevisan, Massarsky, Kozal, Levin and Ti Giulio2018). MPs at 50 and 200 nm were found to penetrate the chorionic villus membrane and negatively affected the embryos (Pitt et al., Reference Pitt, Trevisan, Massarsky, Kozal, Levin and Ti Giulio2018). MPs may attach to the surface of chorion and inhibited oxygen uptake by the embryo (Van Pomeren et al., Reference Van Pomeren, Brun, Peijnenburg and Vijver2017). The production of oxidative stress may lead to impaired gamete binding and embryotoxicity. In addition, MPs had toxic effects on the next generation. MPs can reduce glutathione reductase activity and thiol levels by transferring to the yolk sac, gastrointestinal tract, liver, and pancreas of offspring, disrupting the antioxidant system of offspring and causing developmental disorders (Pitt et al., Reference Pitt, Trevisan, Massarsky, Kozal, Levin and Ti Giulio2018). Jin et al. (Reference Jin, Kurobe, Hammock, Lam, Swee and Teh2020) tested juveniles of Oryzias melastigma exposed for 50 days and studied the effects of PS exposure on the growth, reproduction, and embryonic development of offspring. The results showed that long-term exposure to PS had no significant effect on the growth and reproduction of the parents but had adverse effects on the embryonic development of the offspring.
Further research
This review summarizes the many recent works on the toxicological impacts of MPs in the marine environment. It is concluded that many studies are still at the ‘observational’ stage, simply exposing different animals to MPs under different conditions for a certain period of time, followed by measurements of the organism’s responses at different levels ranging from molecular to the organism. At the initial stage of environmental toxicology study, such approaches are certainly to be encouraged with an overall objective to identify the potential concerns and risks of MPs in the environment. Nevertheless, with increasing progression of MP toxicological research, it is highly desirable to place traditional ecotoxicology in a better context, by focusing on the most relevant questions in environmental toxicology. MPs have been traditionally envisioned as ‘physical agents’ and considered to be ‘inert’. Such perception should be fundamentally changed by treating MPs as physical, chemical, and biological entities. It is important to reveal the microenvironment of MPs and how such microenvironments interact with marine organisms, which then leads to their eventual toxicity. Specifically, there are a few major questions that remain to be addressed in future environmental toxicological studies of MPs.
Environmental relevancy. Toxicologists are interested in evidence of toxicity. Although the toxicity of MPs has been tested in many animal systems, one important question is their applicability to the real environment. MP concentrations in the ocean remain relatively low so that they seldom display acute toxicity. To make experiments more ecological relevant, exposure levels normally documented in the environment should be adopted. However, chronic effects of MP exposure could be far more difficult to observe. To understand the biochemical, physiological, and ecological effects of MPs, it is also often necessary to use concentrations that are well above the environmental ones. Furthermore, the often underestimation of the environmental impacts of MPs may have been due to the methods deployed, which were unable to detect MPs at low levels in the environments. A second relevant factor is the MPs type. Most toxicologists have used MPs that were manufactured under ideal conditions, often putting the feasibility of the MPs’ source as the top priority. Actual MPs in the environment (e.g., microfibers and irregular shape) will be in vast contrast from those employed in the laboratory. The presence of biofilms on the MPs’ surfaces will be very different from those pristine MPs used in the laboratory. The third relevant issue is the actual exposure scenario. As described earlier, there are many different exposure pathways for MPs to the animals. There are also very rare cases where these exposures can be constant. Spontaneous or intermittent exposure of MPs may be more common in the real environment. All these factors should be taken into consideration when designing a sound ecotoxicological study of MPs. Thus, there is a major need to standardize all testing conditions, without which more studies will be added to the literature, while making comparisons between studies difficult. Without solving these critical questions, it is still premature to make the conclusion that MPs present high risk or no risk to marine organisms.
Cause–effect relationship. A cause–effect relationship is the central tenet in environmental toxicology, and without exception, this remains to be established for MPs. Given the very diverse functional physiologies of marine organisms, establishing such relationship is a difficult task. One factor to be incorporated is the presence of different accumulation organs (site of action) for MPs in different organisms. Currently, there are very few reports of such relationships, including the dose–response relationship. Further addition in this area is the establishment of a database on MP toxicity (similar to many ecotox databases available, i.e., ECOTOX by U.S. EPA). These basic toxicological data can be gathered from the literature and may provide important information for the screening of environmental benchmark values for MPs. Future development of MPs standards in the environment may heavily depend on the availability of such a database.
Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics. There are very limited reports of the kinetics of MPs in marine organisms, without which toxicological study is considered as a black box experiment (Wang, Reference Wang, Ge and Yu2011). The lack of toxicokinetic data for MPs is primarily due to the limitations of available technology that can actually track and quantify the movement and transport of MPs. For traditional contaminants such as metals, gamma-emitting radiotracers are excellent tools to trace (noninvasively) metal behavior in organisms. Other techniques such as stable isotopes or betta isotopes are also available for the tracking of organic contaminants. In a few studies, fluorescent particles have been used to track MPs, but such fluorescent particles often suffer from the lack of photostability. It is thus difficult to track the movement of MPs over long-term periods (e.g., days or weeks). Developing reliable tracer technology will present a major breakthrough in monitoring and quantifying MPs in different biota (cells or tissues). With these available tracers, it will then be possible to develop models that can simulate and predict the bioaccumulation and transport of MPs in different trophic levels of animals (Wang and Tan, Reference Wang and Tan2019).
Modeling is an important tool in simulating the distribution and concentration of MPs in the ocean. Modeling the effects of MP exposure could be far more complicated given the many factors and processes interacting with each other in the environment. With the anticipation of more quantitative studies involving kinetics and toxicity, it is anticipated that modeling will be an important area in MPs research.
Biomarker screening. Among the numerous biomarkers that are quantified nowadays, there are very few considered to be specific to MPs exposure and toxicity. Identifying specific biomarkers (at different levels) to MPs exposure will be an important challenge to toxicologists. Recently, there have been identified some promising markers involving gut microbiota interactions. For example, Zheng and Wang (Reference Zheng and Wang2023) demonstrated that MPs profoundly affect the gut microbiota in medaka, which then caused changes in ion disturbances and physiological functions of the fish gills. Identification of some of these specific biomarkers may also include specific microbiota given the very unique gut behavior of MPs in the animals.
Studies on the environmental toxicology of marine MP pollution will continue to pile up, and it is important to put the organism physiology, biochemistry, and ecology in perspectives. It is also important to examine the various properties of MPs in the real environmental settings. Coupling the diversity of functional physiology of marine organisms and the MPs property provides numerous opportunities for environmental toxicologists in their research. Modeling the transport and toxicology of MPs in marine organisms may be the ultimate goal of these researches.
Open peer review
To view the open peer review materials for this article, please visit http://doi.org/10.1017/plc.2023.9.
Author contribution
W.-X.W. wrote the whole review paper.
Financial support
This study was funded by the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (CityU 11103022).
Competing interest
The author declares that he has no competing interest.







Comments
Dear Editor:
This is an invited review on the environmental toxicology of microplastics in the marine environment. Much appreciated for your invitation!