Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 November 2022
Let 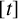 $[t]$ be the integral part of the real number t and let
$[t]$ be the integral part of the real number t and let 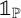 $\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}$ be the characteristic function of the primes. Denote by
$\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}$ be the characteristic function of the primes. Denote by 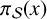 $\pi _{\mathcal {S}}(x)$ the number of primes in the floor function set
$\pi _{\mathcal {S}}(x)$ the number of primes in the floor function set 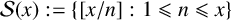 $\mathcal {S}(x) := \{[{x}/{n}] : 1\leqslant n\leqslant x\}$ and by
$\mathcal {S}(x) := \{[{x}/{n}] : 1\leqslant n\leqslant x\}$ and by 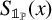 $S_{\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}}(x)$ the number of primes in the sequence
$S_{\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}}(x)$ the number of primes in the sequence 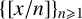 $\{[{x}/{n}]\}_{n\geqslant 1}$. Improving a result of Heyman [‘Primes in floor function sets’, Integers 22 (2022), Article no. A59], we show
$\{[{x}/{n}]\}_{n\geqslant 1}$. Improving a result of Heyman [‘Primes in floor function sets’, Integers 22 (2022), Article no. A59], we show 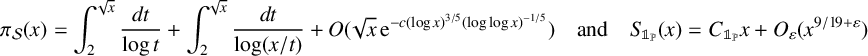 $$ \begin{align*} \pi_{\mathcal{S}}(x) = \int_2^{\sqrt{x}} \frac{d t}{\log t} + \int_2^{\sqrt{x}} \frac{d t}{\log(x/t)} + O(\sqrt{x}\,\mathrm{e}^{-c(\log x)^{3/5}(\log\log x)^{-1/5}}) \quad\mbox{and}\quad S_{\mathbb{1}_{{\mathbb P}}}(x) = C_{\mathbb{1}_{{\mathbb P}}} x + O_{\varepsilon}(x^{9/19+\varepsilon}) \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \pi_{\mathcal{S}}(x) = \int_2^{\sqrt{x}} \frac{d t}{\log t} + \int_2^{\sqrt{x}} \frac{d t}{\log(x/t)} + O(\sqrt{x}\,\mathrm{e}^{-c(\log x)^{3/5}(\log\log x)^{-1/5}}) \quad\mbox{and}\quad S_{\mathbb{1}_{{\mathbb P}}}(x) = C_{\mathbb{1}_{{\mathbb P}}} x + O_{\varepsilon}(x^{9/19+\varepsilon}) \end{align*} $$
for 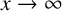 $x\to \infty $, where
$x\to \infty $, where 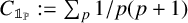 $C_{\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}} := \sum _{p} {1}/{p(p+1)}$,
$C_{\mathbb {1}_{{\mathbb P}}} := \sum _{p} {1}/{p(p+1)}$, 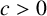 $c>0$ is a positive constant and
$c>0$ is a positive constant and 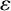 $\varepsilon $ is an arbitrarily small positive number.
$\varepsilon $ is an arbitrarily small positive number.
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11971370 and 12071375).