Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Gutiérrez, Susana
Rivas, Judith
and
Vega, Luis
2003.
Formation of Singularities and Self-Similar Vortex Motion Under the Localized Induction Approximation†.
Communications in Partial Differential Equations,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 5-6,
p.
927.
Lee, Ji-Eun
Suh, Young-Jin
and
Lee, Hyun-Jin
2012.
C-parallel Mean Curvature Vector Fields along Slant Curves in Sasakian 3-manifolds.
Kyungpook mathematical journal,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 1,
p.
49.
Inoguchi, Jun-ichi
and
Lee, Ji-Eun
2012.
Almost contact curves in normal almost contact 3-manifolds.
Journal of Geometry,
Vol. 103,
Issue. 3,
p.
457.
Zeki Okuyucu, O.
Gök, İ.
Yayli, Y.
and
Ekmekci, N.
2013.
Slant helices in three dimensional Lie groups.
Applied Mathematics and Computation,
Vol. 221,
Issue. ,
p.
672.
Uçum, Ali
Camci, Çetin
and
İlarslan, Kazım
2016.
General Helices with Timelike Slope Axis in Minkowski 3-Space.
Advances in Applied Clifford Algebras,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 2,
p.
793.
Acet, Bilal Eftal
2017.
Some characterizations for Legendre curves having proper mean curvature vector in Lorentz-Sasakian manifolds.
Vol. 1833,
Issue. ,
p.
020040.
İlarslan, Kazım
2018.
New results for general helix in Euclidean 3-space.
Vol. 1926,
Issue. ,
p.
020017.
Lee, Ji-Eun
2018.
Laplacians and Legendre Surfaces in Pseudo-Hermitian Geometry.
Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 4,
p.
899.
Uçum, Ali
Camci, Çetin
and
İlarslan, Kazım
2019.
General helices with spacelike slope axis in Minkowski 3-space.
Asian-European Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 05,
p.
1950076.


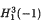 with proper mean curvature function.
with proper mean curvature function.