No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
NEW SUPERCONGRUENCES INVOLVING PRODUCTS OF TWO BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 August 2019
Abstract
Let  $p>3$ be a prime and let
$p>3$ be a prime and let  $a$ be a rational
$a$ be a rational 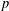 $p$-adic integer with
$p$-adic integer with 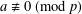 $a\not \equiv 0\;(\text{mod}\;p)$. We evaluate modulo
$a\not \equiv 0\;(\text{mod}\;p)$. We evaluate modulo 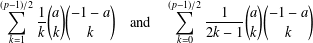 $$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{k=1}^{(p-1)/2}\frac{1}{k}\binom{a}{k}\binom{-1-a}{k}\quad \text{and}\quad \mathop{\sum }_{k=0}^{(p-1)/2}\frac{1}{2k-1}\binom{a}{k}\binom{-1-a}{k}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{k=1}^{(p-1)/2}\frac{1}{k}\binom{a}{k}\binom{-1-a}{k}\quad \text{and}\quad \mathop{\sum }_{k=0}^{(p-1)/2}\frac{1}{2k-1}\binom{a}{k}\binom{-1-a}{k}\end{eqnarray}$$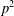 $p^{2}$ in terms of Bernoulli and Euler polynomials.
$p^{2}$ in terms of Bernoulli and Euler polynomials.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
Footnotes
The author is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 11771173).
References
Granville, A. and Sun, Z. W., ‘Values of Bernoulli polynomials’, Pacific J. Math. 172 (1996), 117–137.10.2140/pjm.1996.172.117Google Scholar
Ireland, K. and Rosen, M., A Classical Introduction to Modern Number Theory, 2nd edn (Springer, New York, 1990).10.1007/978-1-4757-2103-4Google Scholar
Lehmer, E., ‘On congruences involving Bernoulli numbers and the quotients of Fermat and Wilson’, Ann. of Math. (2) 39 (1938), 350–360.10.2307/1968791Google Scholar
Magnus, W., Oberhettinger, F. and Soni, R. P., Formulas and Theorems for the Special Functions of Mathematical Physics, 3rd edn (Springer, New York, 1966), 25–32.10.1007/978-3-662-11761-3Google Scholar
Mao, G. S. and Sun, Z. W., ‘New congruences involving products of two binomial coefficients’, Ramanujan J. 49 (2019), 237–256.10.1007/s11139-018-0089-5Google Scholar
Mortenson, E., ‘A supercongruence conjecture of Rodriguez–Villegas for a certain truncated hypergeometric function’, J. Number Theory 99 (2003), 139–147.10.1016/S0022-314X(02)00052-5Google Scholar
Mortenson, E., ‘Supercongruences between truncated 2F 1 hypergeometric functions and their Gaussian analogs’, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 355 (2003), 987–1007.10.1090/S0002-9947-02-03172-0Google Scholar
Rodriguez-Villegas, F., ‘Hypergeometric families of Calabi–Yau manifolds’, in: Calabi–Yau Varieties and Mirror Symmetry, (Toronto, ON, 2001), Fields Institute Communications, 38 (eds. Yui, N. and Lewis, J. D.) (American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 2003), 223–231.Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Congruences for Bernoulli numbers and Bernoulli polynomials’, Discrete Math. 163 (1997), 153–163.10.1016/S0012-365X(97)81050-3Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Congruences concerning Bernoulli numbers and Bernoulli polynomials’, Discrete Appl. Math. 105 (2000), 193–223.Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Congruences involving Bernoulli polynomials’, Discrete Math. 308 (2008), 71–112.10.1016/j.disc.2007.03.038Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Identities and congruences for a new sequence’, Int. J. Number Theory 8 (2012), 207–225.10.1142/S1793042112500121Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Generalized Legendre polynomials and related supercongruences’, J. Number Theory 143 (2014), 293–319.10.1016/j.jnt.2014.04.012Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Super congruences concerning Bernoulli polynomials’, Int. J. Number Theory 11 (2015), 2393–2404.10.1142/S1793042115501110Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Supercongruences involving Bernoulli polynomials’, Int. J. Number Theory 12 (2016), 1259–1271.10.1142/S1793042116500779Google Scholar
Sun, Z. H., ‘Supercongruences involving Euler polynomials’, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 144 (2016), 3295–3308.10.1090/proc/13005Google Scholar
Sun, Z. W., ‘p-adic congruences motivated by series’, J. Number Theory 134 (2014), 181–196.10.1016/j.jnt.2013.07.011Google Scholar


