Article contents
ADDITIVE AND SUBTRACTIVE BASES OF  $\mathbb {Z}_m$ IN AVERAGE
$\mathbb {Z}_m$ IN AVERAGE
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 November 2024
Abstract
Given a positive integer m, let  $\mathbb {Z}_m$ be the set of residue classes mod m. For
$\mathbb {Z}_m$ be the set of residue classes mod m. For 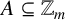 $A\subseteq \mathbb {Z}_m$ and
$A\subseteq \mathbb {Z}_m$ and 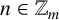 $n\in \mathbb {Z}_m$, let
$n\in \mathbb {Z}_m$, let 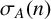 $\sigma _A(n)$ be the number of solutions to the equation
$\sigma _A(n)$ be the number of solutions to the equation 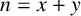 $n=x+y$ with
$n=x+y$ with 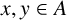 $x,y\in A$. Let
$x,y\in A$. Let 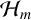 $\mathcal {H}_m$ be the set of subsets
$\mathcal {H}_m$ be the set of subsets 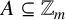 $A\subseteq \mathbb {Z}_m$ such that
$A\subseteq \mathbb {Z}_m$ such that 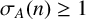 $\sigma _A(n)\geq 1$ for all
$\sigma _A(n)\geq 1$ for all 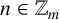 $n\in \mathbb {Z}_m$. Let
$n\in \mathbb {Z}_m$. Let 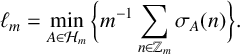 $$ \begin{align*} \ell_m=\min\limits_{A\in \mathcal{H}_m}\bigg\lbrace m^{-1}\sum_{n\in \mathbb{Z}_m}\sigma_A(n)\bigg\rbrace. \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \ell_m=\min\limits_{A\in \mathcal{H}_m}\bigg\lbrace m^{-1}\sum_{n\in \mathbb{Z}_m}\sigma_A(n)\bigg\rbrace. \end{align*} $$
Ding and Zhao [‘A new upper bound on Ruzsa’s numbers on the Erdős–Turán conjecture’, Int. J. Number Theory 20 (2024), 1515–1523] showed that 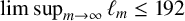 $\limsup _{m\rightarrow \infty }\ell _m\le 192$. We prove
$\limsup _{m\rightarrow \infty }\ell _m\le 192$. We prove 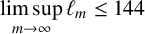 $$ \begin{align*} \limsup\limits_{m\rightarrow\infty}\ell_m\leq 144 \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \limsup\limits_{m\rightarrow\infty}\ell_m\leq 144 \end{align*} $$
and investigate parallel results on subtractive bases of  $ \mathbb {Z}_m$.
$ \mathbb {Z}_m$.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
References
A correction has been issued for this article:
- 1
- Cited by
Linked content
Please note a has been issued for this article.



