An inverse association between alcohol consumption and risk of CHD in diverse populations has been reported in over forty prospective studies(Reference Rimm and Moats1). Numerous epidemiological studies have shown beneficial effects of both alcohol and n-3 fatty acid intakes on cardiovascular function (see Table 1) (Reference Harris, Miller, Tighe, Davidson and Schaefer2, Reference Rimm, Williams, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer3). It is known that HDL-cholesterol increases with alcohol intake, particularly the HDL2 and HDL3 components. Therefore, the well-documented relationship between moderate alcohol intake and lower risk of CHD may be partly explained by alcohol's relation to increased levels of HDL-cholesterol(Reference Rimm, Williams, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer3).
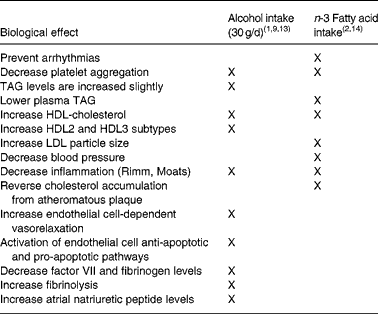
Table 1 Beneficial effects of alcohol and n-3 fatty acid intake on vascular and biochemical functions that may influence the risk of developing CHD
DeLorgeril et al. (Reference deLorgeril, Salen, Martin, Boucher and de Leiris4) recently reported higher plasma n-3 fatty acids in CHD patients who consumed a moderate amount of wine each day compared with those who abstained. Specifically, plasma n-3 fatty acids increased significantly by 50 % and 37 % in CHD patients, who consumed high or low amounts of α-linolenic acid each day, respectively, and who also drank wine. In a paper published in this issue of the BJN, Guiraud and colleagues demonstrated improved plasma, erythrocyte membrane and mitochondria phospholipid n-3 fatty acids with habitual alcohol consumption in a rat model(Reference Guiraud, de Lorgeril, Zeghichi, Laporte, Salen, Saks, Berraud, Boucher and de Leiris5). After 7 and 18 weeks of chronic alcohol consumption, n-3 fatty acids increased in rats fed 6 % or 12 % ethanol in their drinking water (along with their usual rat chow diet). Cardiac mitochondrial function and left ventricular function were not significantly different with 12 % ethanol consumption, but infarct size after 30 min was smaller in rats consuming 12 % ethanol over 18 weeks. We can conclude from this study that habitual alcohol consumption moderates fatty acid metabolism in rats. The effect of alcohol on plasma fatty acids in this study is similar to the rise of plasma fatty acids with fish consumption(Reference He, Song, Daviglus, Liu, Van Horn, Dyer and Greenland6).
Although benefits of alcohol consumption are seen with beer, spirits or wine(Reference Rimm and Moats1), red wine polyphenols are particularly beneficial in reducing the effect of oxidized fats in foods. In a randomized, crossover study in adults, red wine consumed during a meal including fatty foods reduced the production of malondialdehyde, a bi-product of fat digestion that is known to increase the risk of CVD(Reference Gorelik, Ligumski, Kohen and Kanner7). These study findings demonstrate that the composition of the dietary pattern is important to avoid the harmful effects of high-fat foods. The Mediterranean diet pattern, which is associated with a lower risk of chronic disease, is an excellent example of a diet pattern consisting of a variety of fruit, vegetables, grains, meat and fish, nuts, and alcohol(Reference de Lorgeril and Salen8).
The association of alcohol intake with CVD and stroke is U-shaped. Studies of alcohol and mortality show that up to 30 g of alcohol per day is associated with lowest risk compared with no alcohol or high alcohol intakes(Reference Rimm and Moats1). In a meta-analysis, Rimm et al. (Reference Rimm, Willaims, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer9) showed lower level of lipids and haemostatic factors with moderate consumption of any type of alcohol. What is a moderate amount of alcohol? Even though current policy guidelines in the USA and the UK do not recommend consumption of alcohol, the suggested amount related to cardiovascular health, according to the USA Dietary Guidelines for Americans(10), is 1–2 drinks/d for women and 2–3 drinks/d for men. Two drinks contain approximately 30 g of alcohol. In the UK, the guideline for men is no more than 3–4 units and for women no more than 2–3 units in a single session(11). The American Heart Association recommends consumption of fish at least once per week(Reference Lichtenstein, Appel, Brands, Howard, Karanja, Lefevre, Rudel and Sacks12); however, AHA does not recommend any dose of alcohol consumption, given there are no studies of its long-term effects.
The study by Giuraud et al. provides support for habitual alcohol consumption increasing plasma and cell membrane n-3 fatty acids, albeit in rats. Further research is warranted to identity the mechanism by which alcohol mediates n-3 fatty acid metabolism.



An inverse association between alcohol consumption and risk of CHD in diverse populations has been reported in over forty prospective studies(Reference Rimm and Moats1). Numerous epidemiological studies have shown beneficial effects of both alcohol and n-3 fatty acid intakes on cardiovascular function (see Table 1) (Reference Harris, Miller, Tighe, Davidson and Schaefer2, Reference Rimm, Williams, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer3). It is known that HDL-cholesterol increases with alcohol intake, particularly the HDL2 and HDL3 components. Therefore, the well-documented relationship between moderate alcohol intake and lower risk of CHD may be partly explained by alcohol's relation to increased levels of HDL-cholesterol(Reference Rimm, Williams, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer3).
Table 1 Beneficial effects of alcohol and n-3 fatty acid intake on vascular and biochemical functions that may influence the risk of developing CHD
DeLorgeril et al. (Reference deLorgeril, Salen, Martin, Boucher and de Leiris4) recently reported higher plasma n-3 fatty acids in CHD patients who consumed a moderate amount of wine each day compared with those who abstained. Specifically, plasma n-3 fatty acids increased significantly by 50 % and 37 % in CHD patients, who consumed high or low amounts of α-linolenic acid each day, respectively, and who also drank wine. In a paper published in this issue of the BJN, Guiraud and colleagues demonstrated improved plasma, erythrocyte membrane and mitochondria phospholipid n-3 fatty acids with habitual alcohol consumption in a rat model(Reference Guiraud, de Lorgeril, Zeghichi, Laporte, Salen, Saks, Berraud, Boucher and de Leiris5). After 7 and 18 weeks of chronic alcohol consumption, n-3 fatty acids increased in rats fed 6 % or 12 % ethanol in their drinking water (along with their usual rat chow diet). Cardiac mitochondrial function and left ventricular function were not significantly different with 12 % ethanol consumption, but infarct size after 30 min was smaller in rats consuming 12 % ethanol over 18 weeks. We can conclude from this study that habitual alcohol consumption moderates fatty acid metabolism in rats. The effect of alcohol on plasma fatty acids in this study is similar to the rise of plasma fatty acids with fish consumption(Reference He, Song, Daviglus, Liu, Van Horn, Dyer and Greenland6).
Although benefits of alcohol consumption are seen with beer, spirits or wine(Reference Rimm and Moats1), red wine polyphenols are particularly beneficial in reducing the effect of oxidized fats in foods. In a randomized, crossover study in adults, red wine consumed during a meal including fatty foods reduced the production of malondialdehyde, a bi-product of fat digestion that is known to increase the risk of CVD(Reference Gorelik, Ligumski, Kohen and Kanner7). These study findings demonstrate that the composition of the dietary pattern is important to avoid the harmful effects of high-fat foods. The Mediterranean diet pattern, which is associated with a lower risk of chronic disease, is an excellent example of a diet pattern consisting of a variety of fruit, vegetables, grains, meat and fish, nuts, and alcohol(Reference de Lorgeril and Salen8).
The association of alcohol intake with CVD and stroke is U-shaped. Studies of alcohol and mortality show that up to 30 g of alcohol per day is associated with lowest risk compared with no alcohol or high alcohol intakes(Reference Rimm and Moats1). In a meta-analysis, Rimm et al. (Reference Rimm, Willaims, Fosher, Criqui and Stampfer9) showed lower level of lipids and haemostatic factors with moderate consumption of any type of alcohol. What is a moderate amount of alcohol? Even though current policy guidelines in the USA and the UK do not recommend consumption of alcohol, the suggested amount related to cardiovascular health, according to the USA Dietary Guidelines for Americans(10), is 1–2 drinks/d for women and 2–3 drinks/d for men. Two drinks contain approximately 30 g of alcohol. In the UK, the guideline for men is no more than 3–4 units and for women no more than 2–3 units in a single session(11). The American Heart Association recommends consumption of fish at least once per week(Reference Lichtenstein, Appel, Brands, Howard, Karanja, Lefevre, Rudel and Sacks12); however, AHA does not recommend any dose of alcohol consumption, given there are no studies of its long-term effects.
The study by Giuraud et al. provides support for habitual alcohol consumption increasing plasma and cell membrane n-3 fatty acids, albeit in rats. Further research is warranted to identity the mechanism by which alcohol mediates n-3 fatty acid metabolism.