An elevated concentration of ammonia in the blood (hyperammonaemia, above 300 µmol/l) is toxic and has deleterious effects on the central nervous system, as observed in patients with hepatic disorders, mitochondrial dysfunction or oxidative stress in skeletal muscles( Reference Felipo and Butterworth 1 – Reference Davuluri, Allawy and Thapaliya 3 ). Hyperammonaemia can also occur during exercise via both amino acid and AMP deamination in an intensity- and duration-dependent manner; urate is the final metabolite of inosine monophosphate (IMP), which is generated by AMP deamination( Reference Wilkinson, Smeeton and Watt 4 ).
In addition, higher blood ammonia concentrations can result from a low-carbohydrate diet (termed a ‘ketogenic diet’), and ammonia concentrations can be increased by both branched-chain amino acids oxidation and purine nucleotide metabolism( Reference Wagenmakers, Beckers and Brouns 5 , Reference Langfort, Czarnowski and Zendzian-Piotrowska 6 ). It has been suggested that hyperammonaemia may have a significant impact during intense endurance exercise under different environmental conditions and that it could induce neurological disturbances similar to the symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy, thus impairing athletic performance( Reference Banister and Cameron 7 , Reference Nybo 8 ). Therefore, it is believed that controlling the increase in blood ammonia concentration can improve exercise performance( Reference Wilkinson, Smeeton and Watt 4 ).
Our group has been investigating ammonia metabolism in both humans and animals under exercise-induced stress in combination with different diets( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 – Reference Lima, Camerino and França 17 ). In these studies, animals can be preferentially selected and assessed as good models to study general principles, and the results can then be compared with those obtained from humans. Recently, we demonstrated that keto analogues and amino acids (KAAA) supplementation can reduce blood ammonia concentrations during moderate prolonged exercise in athletes fed a ketogenic diet under thermoneutral conditions( Reference Camerino, Lima and Franca 18 ) and in rats during resistance exercise( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ). In both cases, we postulate that KAAA supplementation increases glucose availability for exercise through gluconeogenesis. Diets are known to modify metabolic responses, especially during exercise( Reference Langfort, Czarnowski and Zendzian-Piotrowska 6 ), and here, we present new information on the metabolic differences associated with KAAA supplementation in association with two different diets.
To the best of our knowledge, information is not available on the effects of KAAA supplementation on ammonia metabolism after high-intensity exercise in rats fed a ketogenic diet. We hypothesised that KAAA supplementation reduces blood ammonia concentrations under these conditions. Therefore, in the present study, we evaluated the acute effects of KAAA supplementation on ammonia metabolism during extenuating endurance exercise in rats fed a ketogenic diet.
Methods
Animals
Male Fischer rats (90 d of age, with an initial and final body mass of 203·9 (se 0·9) and 382·5 (se 29·9) g, respectively) were randomly divided into eight groups of ten animals each as follows: untrained control diet (UC); untrained ketogenic diet (UK); untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA (UCKa); untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA (UKKa); trained control diet (TC); trained ketogenic diet (TK); trained control diet supplemented with KAAA (TCKa) and trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA (TKKa). The animals were kept in individual cages under controlled environmental conditions (23±1°C, 55±10) % relative humidity, 12 h dark–12 h light cycle). Rats showing abnormal behaviour or rapid weight loss were excluded. This study followed the animal care procedures regulated by the Brazilian College of Animal Experimentation, and the study protocol was submitted to and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Ouro Preto Federal University (036/2008).
Procedures
The groups supplemented with KAAA received 0·1 g Ketosteril® (Fresenius Kabi) in 2·0 ml of water (0·3 g/kg). The composition of the KAAA mixture per tablet was as follows: α-keto analogues of isoleucine (335 mg), leucine (505 mg), phenylalanine (430 mg) and valine (340 mg); an α-hydroxy analogue of methionine (295 mg); l-lysine acetate (75 mg); l-threonine (265 mg); l-tryptophan (115 mg); l-histidine (190 mg) and l-tyrosine (150 mg). All other groups received 2·0 ml of 0·9 % NaCl orally 1 h before exercise and served as control groups.
The trained groups received training that consisted of an adapted version of the swimming protocol used in an animal study conducted by Gobatto et al.( Reference Gobatto, de Mello and Sibuya 19 ). The animals were trained for 30 min 5 d a week over a 79-d period. Training began at the same time each day (08.30 hours), and the water temperature was maintained at 31±1°C. During the first 7 d, the animals were allowed to adapt to the training protocol by incrementally increasing the water level daily until they were no longer able to touch the bottom of the tank with their tail. On days 8 through 78, the load was incrementally increased by 1 % of the animal’s body mass by attaching a load to the animal’s back. Furthermore, on days 8 through 69 of training, all animals received a balanced rodent diet (Labina®; Purina). The groups were then randomly divided. On days 70 through 79, the animals received either the ketogenic( Reference Bough, Valiyil and Han 20 ) or control( Reference Reeves, Nielsen and Fahey 21 ) diet ad libitum during the course of the protocol (Table 1). On the 80th day, the training protocol was administered to promote extenuating endurance exercise according to previously described methods( Reference Contarteze, Manchado Fde and Gobatto 22 ). The exhaustion test (termed ‘extenuating exercise’) was conducted using a load equal to 15 % of the animal’s body mass. In addition, on the 80th day, blood, hepatic and muscle glycogen concentrations were determined (Fig. 1(a)).
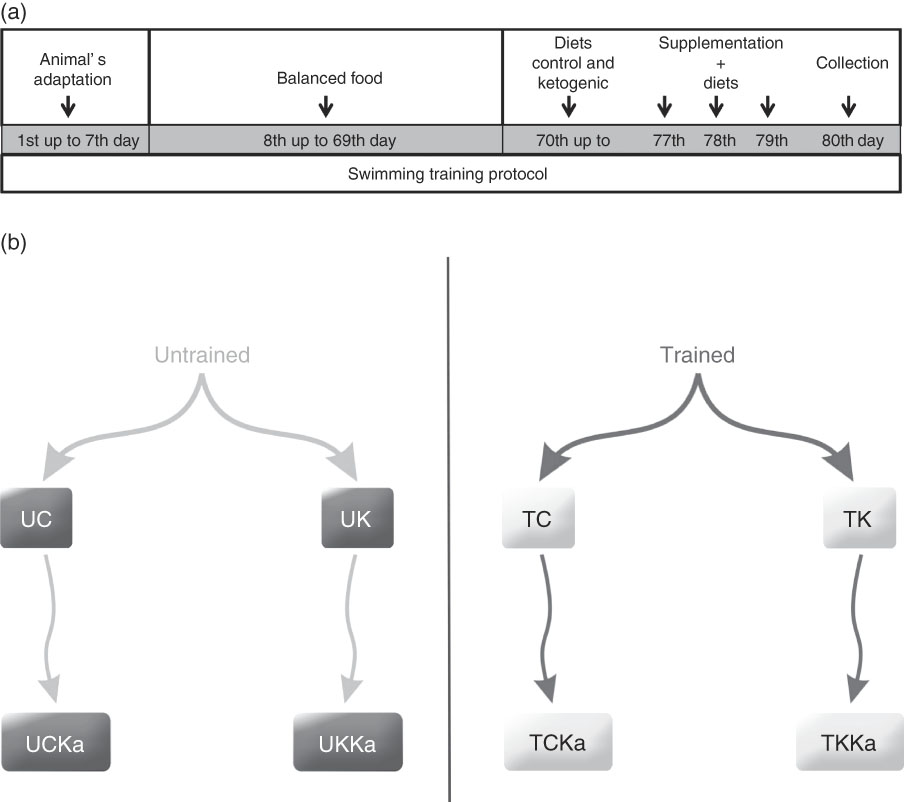
Fig. 1 Experimental design and timeline. Animal adaptation, training protocol, diets, supplementation and collection (a). Rats were divided into eight groups (b). UC, untrained control diet; UK, untrained ketogenic diet; UCKa, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA; UKKa, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; TC, trained control diet; TK, trained ketogenic diet; TCKa, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA; TKKa, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA.
Table 1 Nutritional composition of diets (g/1000 g)
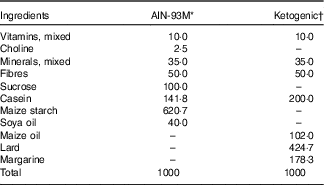
KAAA, keto analogues and amino acids.
* Standard/control diet AIN-93M( Reference Reeves, Nielsen and Fahey 21 ). Untrained control diet, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA, trained control diet, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA groups.
† Ketogenic diet( Reference Bough, Valiyil and Han 20 ). Untrained ketogenic diet, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA, trained ketogenic diet, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA groups.
To ensure the ketogenic effects, the amount of ketone bodies in urine was assessed every 3 d through ketonuria analysis with qualitative urinalysis reagent strips( Reference Mesa, Salcedo and Calle Hde 23 ). Body weight and feeding behaviour were measured weekly. Rats were divided into eight groups (Fig. 1(b)), but KAAA supplementation (Ketosteril®; Fresenius Kabi) was administered 3 d before testing in the following groups: UCKa, UKKa, TCKa and TKKa. The supplement was administered via gavage at 19.30 hours (±60 min) every day before training.
On the 80th day, all animals were fasted (about 10.00 hours), anaesthetised with isoflurane and euthanised via bleeding at the brachial plexus( Reference Rogero, Tirapegui and Pedrosa 24 ). Blood was immediately collected and centrifuged (14 000 g for 15 min) to obtain either plasma (in a vacuum tube with the anticoagulant EDTA for ammonia measurements) or serum (in a vacuum tube without anticoagulant for urea, urate, creatinine, glucose and lactate measurements), which was aliquoted and stored in liquid nitrogen for no more than 3 d before biochemical analysis. Analyses were performed using commercially available spectrophotometric assays (Labtest and Randox) using enzyme kinetic-based methods on a Dade Model Dimension RXL Automated Chemistry Analyzer (Dade Behring). Hepatic and muscle glycogen concentrations were examined in rats according to previously described methods( Reference Schlamowitz 25 , Reference Bowtell, Gelly and Jackman 26 ). In brief, tissue was sliced and homogenised in 5 % TCA. The homogenate was centrifuged at 14 000 g , and the supernatant was extracted with ethanol (1:1). The mixture was centrifuged at 14 000 g , the supernatant was mixed with acetic acid (1:1), and the mixture was centrifuged again. The supernatant was brought to pH 7·4 and analysed with a colorimetric glucose oxidase activity kit (Labtest Diagnostica).
Statistical analyses
Statistically significant differences in the data were assessed using one-way ANOVA and the post hoc Holm–Sidak test. Corresponding non-parametric tests were used to analyse data with non-normal distributions. A value of P<0·05 indicated statistical significance for all comparisons. Data are presented as the mean values with their standard errors. Statistical analyses were performed using SigmaStat version 3.5 for Windows (Systat Software Inc.). Sample size, Cohen’s d effect size and statistical power were calculated to analyse data and identify statistically significant differences in the concentrations of hepatic glycogen, skeletal muscle glycogen and blood ammonia and urate. In this case, the thresholds for small, medium and large effects were 0·20, 0·50 and 0·80, respectively. Sample size, Cohen’s f effect size and statistical power were also calculated to analyse data and identify statistically significant differences in blood urea, creatinine, glucose and lactate concentrations by performing a post hoc analysis (G*Power software version 3.1.9.2, University of Kiel). Here, the thresholds for small, medium and large effects were 0·10, 0·25 and 0·40, respectively( Reference Cohen 27 ). Complete sample statistical analyses are shown in the online Supplementary Material.
Results
The ketogenic diet group tested positive for ketosis after the 3rd day on the diet (data not shown). During exercise, both groups were maintained under controlled temperature conditions (approximately 31°C). The untrained and trained groups had similar times to exhaustion at the same exercise intensity (Fig. 2).
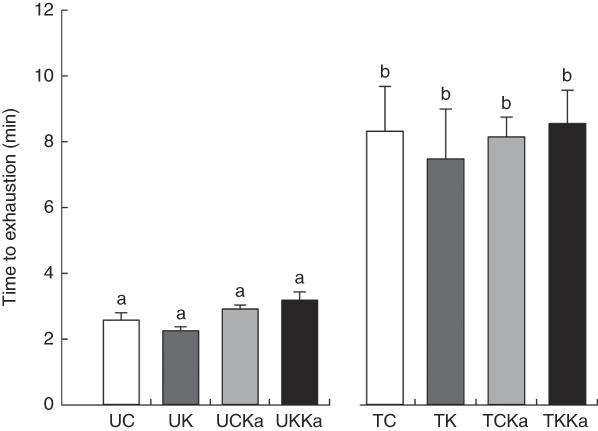
Fig. 2 Time to exhaustion after extenuating endurance exercise. Time to exhaustion in the last test is presented as mean values with their standard errors for all groups according to the experimental design. Untrained and trained groups are separated by a break. KAAA, keto analogues and amino acids, UC, untrained control diet; UK, untrained ketogenic diet; UCKa, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA; UKKa, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; TC, trained control diet; TK, trained ketogenic diet; TCKa, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA; TKKa, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
At rest, the hepatic glycogen concentration was 10·6 (se 0·2) µg/g. Significant differences between the untrained groups (UC v. UK) were not observed. However, KAAA supplementation reduced the hepatic glycogen concentration by approximately 30 % (UCKa v. UC; effect size=2·47; statistical power=0·99). Furthermore, the ketogenic diet plus KAAA supplementation decreased the glycogen concentration to approximately 50 % compared with the control diet (UKKa v. UC; effect size=3·97; statistical power=1·0). Extenuating endurance exercise did not reduce the hepatic glycogen concentration in rats fed the control diet (TC v. UC; effect size=0·07; statistical power=0·05). Compared with the untrained group, the trained group fed the ketogenic diet experienced a decrease in hepatic glycogen concentration by approximately 22 % (TK v. TC; effect size=1·35; statistical power=0·67). The KAAA supplementation in the trained groups led to lower hepatic glycogen concentrations in both groups (TCKa and TKKa) than in the trained control group (43 % for TCKa v. TC; effect size=1·86; statistical power=0·91; and 36 % for TKKa v. TC; effect size=1·75; statistical power=0·88) (Fig. 3(A)). The total hepatic glycogen concentration did not change in any of the groups (10·4 (se 0·4) µg/g).
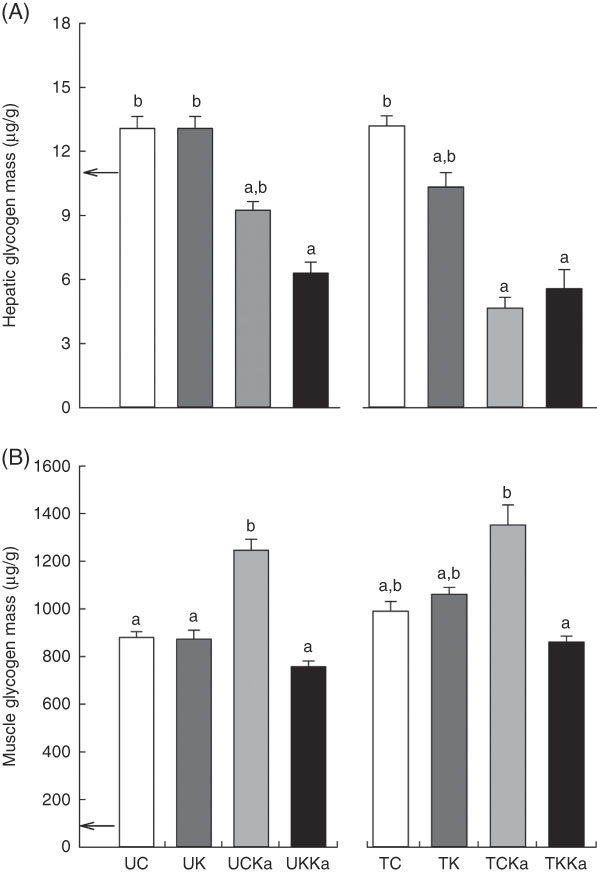
Fig. 3 Hepatic and muscle glycogen concentrations after extenuating endurance exercise presented as mean values with their standard errors. Hepatic (A) and muscle (B) glycogen concentrations. KAAA, keto analogues and amino acids, UC, untrained control diet; UK, untrained ketogenic diet; UCKa, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA; UKKa, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; TC, trained control diet; TK, trained ketogenic diet; TCKa, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA; TKKa, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; ![]() , mean basal hepatic and muscle glycogen concentrations. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
, mean basal hepatic and muscle glycogen concentrations. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
The skeletal muscle glycogen concentration was 42·7 (se 1·15) µg/g during rest but was reduced by the ketogenic diet. Diet manipulation in the untrained groups did not affect the skeletal muscle glycogen concentration in response to exercise. However, training did increase the skeletal muscle glycogen concentration by 12·5 % (TC v. UC; effect size=1·03; statistical power=0·53) and 22·8 % (TK v. UK; effect size=1·34; statistical power=0·72). In addition, KAAA supplementation plus the control diet increased the skeletal muscle glycogen concentration in untrained rats by 41 % (UCKa v. UC; effect size=3·15; statistical power=0·99) and in trained rats by 36 % (TCKa v. TC; effect size=1·44; statistical power=0·73) (Fig. 3(B)).
To investigate the effects of KAAA supplementation on ammonia metabolism, we measured blood ammonia concentrations after swimming. The blood ammonia concentration was 59·4 (se 21·4) µmol/l at baseline and decreased by 5 % in response to acute exercise after training in supplemented animals compared with untrained animals fed the same diet (TC v. UC; effect size=0·28; statistical power=0·07). The blood ammonia concentration was lower after exercise in the untrained group fed a ketogenic diet (approximately 20 %) than in the trained group fed the same diet (TK) (effect size=0·62; statistical power=0·19). There were no differences in the blood ammonia concentration between the untrained group supplemented with KAAA and the untrained group fed the control diet (UCKa v. UC; effect size=0·76; statistical power=0·29). Therefore, KAAA did not affect blood ammonia concentrations in untrained groups.
Interestingly, the blood ammonia concentration increased by 37 % in animals fed a ketogenic diet with KAAA supplementation compared with those fed the control diet (UKKa v. UC; effect size=1·14; statistical power=0·56). Diet did not affect the blood ammonia concentration in the untrained or trained groups (UC v. UK; effect size=0·31; statistical power=0·08; and TC v. TCKa; effect size=0·44; statistical power=0·08). In the trained groups, the ketogenic diet plus KAAA supplementation and extenuating endurance exercise increased the blood ammonia concentration by approximately 50 % compared with the control diet (TKKa v. TCKa; effect size=1·33; statistical power=0·50), suggesting that blood ammonia concentrations are higher after exercise and KAAA supplementation (Fig. 4(A)).
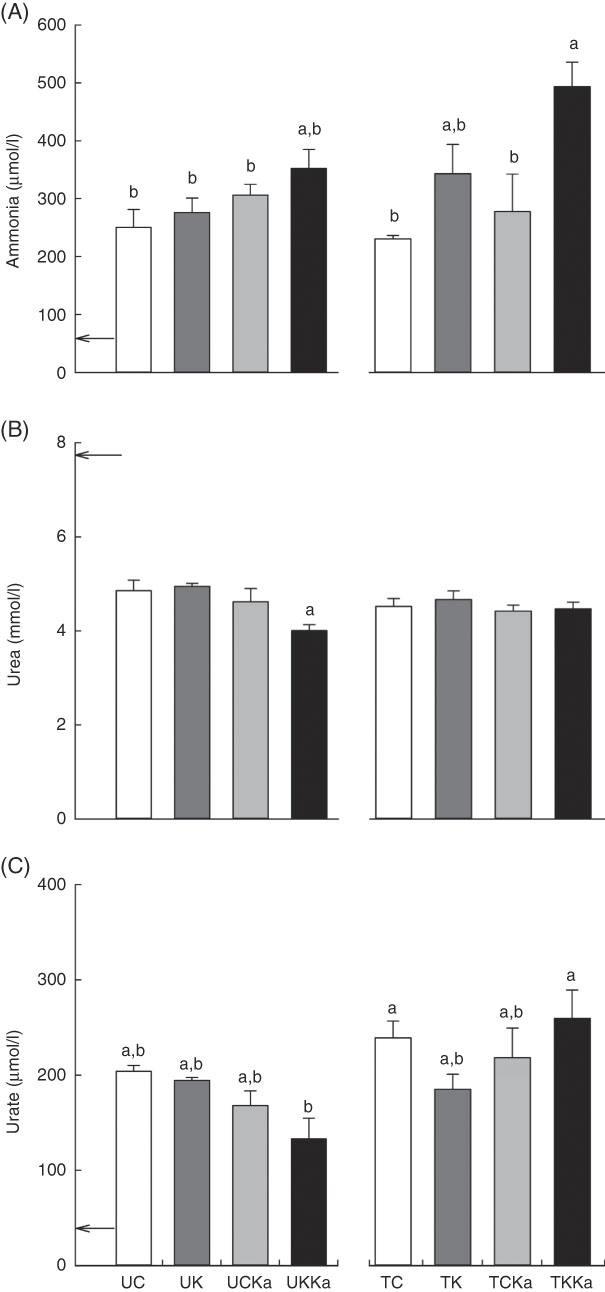
Fig. 4 Keto analogues and amino acids (KAAA) supplementation and a ketogenic diet increase blood ammonia and urate concentrations after extenuating endurance exercise presented as mean values with their standard errors. Blood ammonia (A), urea (B) and urate (C) concentrations. UC, untrained control diet; UK, untrained ketogenic diet; UCKa, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA; UKKa, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; TC, trained control diet; TK, trained ketogenic diet; TCKa, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA; TKKa, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; ![]() , mean basal metabolite levels. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
, mean basal metabolite levels. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
To evaluate the effect of KAAA supplementation on urea metabolism, we measured blood urea concentrations. The resting blood urea concentration was equivalent in all groups (7·8 (se 0·2) mmol/l) and did not differ between the two untrained groups fed either the control or ketogenic diet (UC v. UK). However, KAAA supplementation significantly deceased the blood urea concentration in the untrained group fed a ketogenic diet (effect size=0·50; statistical power=0·77). Differences were not observed between the trained groups (Fig. 4(B)).
To differentiate ammonia produced from AMP deamination from that produced from amino acid deamination, we measured blood urate concentrations. The basal blood urate concentration was 37·6 (se 1·8) µmol/l. Independent of training, KAAA supplementation significantly reduced the blood urate concentration (approximately 30 %) in the UKKa group compared with the UC group (effect size=1·26; statistical power=0·68). This effect in the supplemented group was enhanced after extenuating endurance exercise. The blood urate concentration was significantly higher in the TKKa group than in the TCKa group (effect size=0·60; statistical power=0·13) (Fig. 4(C)).
The basal blood creatinine concentration was 30·0 (se 1·5) mmol/l. Decreases in blood creatinine concentration were only observed in the UC and untrained groups. Despite decreases in the TC group, blood creatinine concentrations did not change in the TKKa, TCKa and TK groups (effect size=0·59; statistical power=0·92) (Fig. 5(A)).
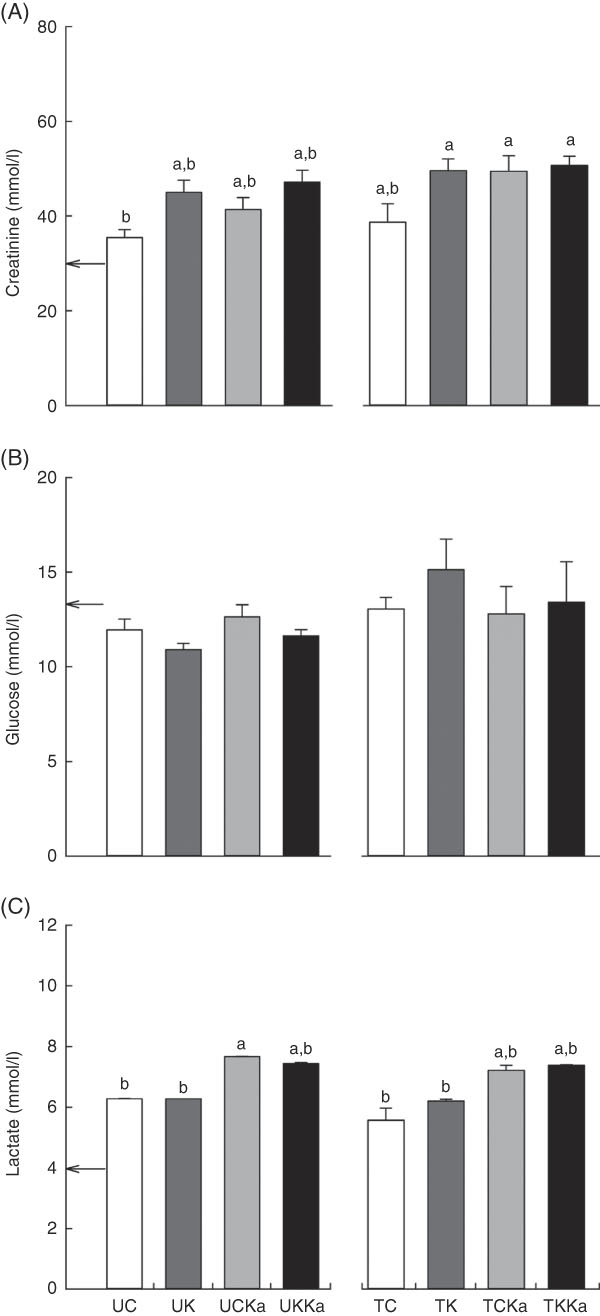
Fig. 5 Keto analogues and amino acids (KAAA) supplementation and a ketogenic diet affect blood lactate concentrations but not creatinine and glucose concentrations after extenuating endurance exercise. Results are presented as mean values with their standard errors. Blood creatinine (A), glucose (B) and lactate (C) concentrations. UC, untrained control diet; UK, untrained ketogenic diet; UCKa, untrained control diet supplemented with KAAA; UKKa, untrained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; TC, trained control diet; TK, trained ketogenic diet; TCKa, trained control diet supplemented with KAAA; TKKa, trained ketogenic diet supplemented with KAAA; ![]() , mean basal metabolite levels. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
, mean basal metabolite levels. a,b Mean values with unlike letters were significantly different (P<0·05).
To understand the effect of KAAA supplementation on glucose maintenance, we measured glucose concentrations in all of the groups. The basal glucose concentration was 9·1 (se 0·3) mmol/l, and we did not detect significant differences within the groups (effect size=0·39; statistical power=0·59) (Fig. 5(B)).
Blood lactate concentration is an indicator of glucose metabolism during exercise. The basal lactate concentration was 4·0 (se 0·3) mmol/l. Significant KAAA-induced differences were not observed between the TCKa (7·4 (se 0·01) mmol/l) and TKKa (7·4 (se 0·2) mmol/l) groups or between the UKKa (7·7 (se 0·7) mmol/l) and UCKa (7·4 (se 0·03) mmol/l) groups after extenuating endurance exercise. However, blood lactate concentration was increased in the groups supplemented with KAAA compared with the unsupplemented groups with or without a ketogenic diet after extenuating endurance exercise (effect size=0·87; statistical power=0·99) (Fig. 5(C)).
Discussion
The aim of this study was to investigate the acute effects of KAAA supplementation on ammonia metabolism during extenuating endurance exercise in rats fed a ketogenic diet. Here, we used a ketogenic diet and extenuating endurance exercise to decrease glycogen availability in liver and muscle, increasing the need for amino acids as an energy source and inducing hyperammonaemia( Reference Czarnowski, Langfort and Pilis 28 – Reference Greenhaff, Leiper and Ball 30 ). Our results indicated that KAAA supplementation reduced the blood ammonia concentration during extenuating endurance exercise in rats fed a balanced diet; however, the ammonia concentration was unaffected in rats fed a ketogenic diet.
The KAAA supplementation has been widely used to treat patients with chronic kidney disease and hepatic disorders, such as hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonaemia( Reference Walser 31 , Reference Maddrey, Weber and Coulter 32 ). However, it is also known that carbohydrate ingestion may attenuate blood ammonia concentrations during prolonged submaximal exercise by reducing amino acid degradation( Reference Wagenmakers, Beckers and Brouns 5 ). In addition, glycogen depletion in muscles could lead to a more rapid increase in blood ammonia concentration( Reference Snow, Carey and Stathis 33 ). In addition, high energy demand and protein catabolism can exacerbate exercise-induced hyperammonaemia in humans and animals( Reference Linnane, Bracken and Brooks 34 – Reference Halpin, Gunning and Yamamoto 36 ). Previous work from our lab demonstrated that during exercise, KAAA supplementation decreases the concentrations of ammonia, urea and urate in the plasma of humans fed a ketogenic diet( Reference Prado, de Rezende Neto and de Almeida 12 ) and rats fed a non-ketogenic diet( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ). The results of this study demonstrated that KAAA supplementation significantly reduced the blood ammonia concentration in trained rats fed the balanced control diet, which may have occurred by increasing the muscle glycogen concentration. We can explain this finding by a synergistic effect of carbohydrate ingestion and the use of KAAA for glycogen synthesis.
High-intensity exercise is known to increase ammonia production via AMP deamination( Reference Graham and MacLean 37 ). A previous study demonstrated that higher blood concentrations of catecholamines and IMP are produced when training exercise is continued until exhaustion( Reference Harmer, McKenna and Sutton 38 ). Furthermore, a low-carbohydrate diet has been found to increase the blood ammonia concentration and blood noradrenaline and adrenaline concentrations during exercise( Reference Langfort, Czarnowski and Zendzian-Piotrowska 6 ). The trained group fed the ketogenic diet had a lower muscle glycogen concentration than the trained group fed a balanced diet. Supplementation with KAAA did not decrease ammonaemia in the group fed a ketogenic diet. It is possible that these results are due to extenuating endurance exercise or to effects of environmental temperature during exercise( Reference Nybo 8 ).
In addition, exercise in hot conditions appears to exacerbate exercise-induced hyperammonaemia( Reference Linnane, Bracken and Brooks 34 ). The rats were subjected to a swimming protocol to the point of exhaustion in a hot environment (approximately 31°C). In humans, Mohr et al.( Reference Mohr, Rasmussen and Drust 39 ) demonstrated that blood ammonia concentrations were higher during intermittent exercise performed under heat stress conditions than under thermoneutral conditions. Increased intramuscular ammonia accumulation has been found to occur in both endurance-trained and untrained humans during heat stress. This accumulation is likely the result of an increasing concentration of IMP, a product of AMP deamination( Reference Febbraio 40 ). Furthermore, blood adrenaline and noradrenaline concentrations have been shown to be higher during exercise under heat stress conditions( Reference Morris, Nevill and Boobis 41 ). We previously showed that under thermoneutral conditions, blood ammonia concentrations decreased in rats fed a standard diet and supplemented with KAAA after resistance exercise( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ). In this study, the effects on blood ammonia concentration were greater under conditions of training at elevated temperature than at ambient temperature.
We measured blood urea concentrations to evaluate the effects of KAAA supplementation on urea metabolism in rats fed a ketogenic diet under extenuating endurance exercise. Although a previous study reported that a low protein diet and KAAA supplementation could reduce blood urea concentrations in patients with chronic renal failure disease without exercise( Reference Savica, Santoro and Ciolino 42 ), in our study, KAAA supplementation maintained uraemia after extenuating endurance exercise independent of diet. In addition, KAAA supplementation efficiently reduced uraemia in animals undergoing resistance exercise( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ). We can explain the discrepant results because the previous study was performed under fatiguing exercise conditions, not under extenuating endurance exercise.
Previous studies have reported that the ATP:ADP ratio decreases in muscle, leading to increased AMP deamination and ammonia production during low energetic states and extenuating exercise, such as in the current study( Reference Hellsten, Richter and Kiens 43 ). In the present study, we observed that KAAA administration reduced basal urataemia. In addition, KAAA supplementation delayed the increase in urate concentration in the blood after extenuating exercise in trained animals fed the control diet. However, urataemia increased after extenuating exercise in trained animals that received KAAA supplementation and the ketogenic diet. Our data suggest that the increase in the blood ammonia concentration observed after extenuating exercise in the KAAA-supplemented group fed a ketogenic diet was primarily because of AMP deamination and not amino acid catabolism. These data suggest that heat stress could exacerbate adenine degradation( Reference Linnane, Bracken and Brooks 34 , Reference Mohr, Rasmussen and Drust 39 , Reference Parkin, Carey and Zhao 44 ); however, the trained group fed a ketogenic diet had lower muscle glycogen concentrations than the trained group fed a balanced diet.
The KAAA supplementation has been used to treat patients with chronic kidney disease( Reference Walser 31 ). We evaluated blood creatinine concentrations in response to acute KAAA supplementation after extenuating exercise in rats fed different diets. Blood creatinine concentrations are influenced by diet and exercise( Reference Banfi, Colombini and Lombardi 45 ) and can be used to evaluate renal function( Reference Baum, Dichoso and Carlton 46 ). In this study, blood creatinine concentrations were similar in all of the groups supplemented with KAAA, suggesting similar kidney filtration rates across these groups. It is important to emphasise that we did not measure urinary creatinine in this study, but we demonstrated previously that KAAA supplementation increases creatinine clearance after resistance exercise( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ); however, these data were acquired under thermoneutral environmental conditions and not under heat as in the current study. Blood creatinine concentrations were similarly increased in the exercise groups with and without heat stress( Reference Li, Wang and Liu 35 ).
Consistent with our previous findings in humans( Reference Camerino, Lima and Franca 18 ), KAAA supplementation maintained similar blood glucose concentrations in all the studied groups, including the ketogenic and control diet groups, after extenuating exercise. The KAAA supplement is a mixture of ketogenic and glucogenic KAAA that can be used to produce glucose via gluconeogenesis during exercise under thermoneutral environmental conditions( Reference de Almeida, Prado and Llosa 9 ). In the current study, KAAA supplementation exacerbated blood lactate concentrations after extenuating exercise in the trained groups with and without a ketogenic diet compared with the unsupplemented control group. In humans, blood lactate levels were found to be significantly higher under heat stress conditions than under thermoneutral environmental conditions after 5 min of high-intensity exercise, although this increase was not observed at any other time points during exercise( Reference Linnane, Bracken and Brooks 34 ).
It is important to emphasise that body temperature was not measured in this study, and it may have limited our interpretations. Body temperature could have changed, and this parameter should be evaluated in similar studies in the future. This study demonstrated that extenuating endurance exercise and a ketogenic diet in combination with low glycogen stores and possibly heat stress exceed the protection offered by KAAA supplementation against hyperammonaemia under thermoneutral conditions.
In conclusion, we showed that KAAA supplementation could reduce blood ammonia concentrations in rats fed a control diet but not in rats fed a ketogenic diet after extenuating endurance exercise, which suggests that changes in ammonia metabolism differ under maximal voluntary effort and exhaustive exercise.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Comitê Olimpíco do Brasil; Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico; Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior; Federal University of Ouro Preto; Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos; Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro; Merck-Sigma-Aldrich; Universidade Federal do Estado do Rio de Janeiro and Waters Corporation.
L. C. C., M. L. P. and M. E. S. conceived and designed the experiment; R. T. F. and S. C. G. performed the experiment; M. L. P., M. E. S., A. B., W. S. C., E. S. P., A. M. d. M. and L. C. C. analysed the data; M. L. P. and M. E. S. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; W. S. C., E. S. P. and L. C. C. wrote the paper.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material/s referred to in this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114518001770









