Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is a collective term for isomers of linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6) and the two main isomers are cis-9, trans-11 and trans-10, cis-12( Reference Diez, Menoyo and Pérez-Benavente 1 ). In mammals, CLA has been shown to exert potential health benefits related to its antioxidative, anticarcinogenic, immunomodulative and diabetes-modulator properties in addition to decreasing body fat deposition( Reference Belury 2 – Reference Makol, Torrecillas and Fernandez-Vaquero 4 ). In the last decade, studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of CLA on growth performance, liver lipid deposition, non-specific immunity as well as deposition of this fatty acid in a variety of freshwater fish species including channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus), tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco), and some euryhaline fish species, such as sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), yellow perch (Perca flavescens) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)( Reference Makol, Torrecillas and Fernandez-Vaquero 4 – Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ). It has been shown that fish are capable of accumulating high levels of CLA in their tissues when diets are supplemented with this particular fatty acid( Reference Valente, Bandarra and Figueiredo-Silva 12 ). However, as for growth performance and liver lipid deposition, results vary significantly among different fish species. It has been shown that growth performance is not significantly affected by the inclusion of CLA up to 1 % in juvenile sea bass( Reference Makol, Torrecillas and Fernandez-Vaquero 4 ) and Atlantic salmon( Reference Kennedy, Campbell and Porter 10 ), or 2 % in channel catfish( Reference Twibell and Wilson 7 ). However, growth performance was significantly decreased by CLA at the level of 1 % in hybrid striped bass (Morone saxatilis× Morone chrysops)( Reference Twibell, Watkins and Rogers 6 ) and yellow catfish( Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ), and by 2 % in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.)( Reference Diez, Menoyo and Pérez-Benavente 1 ) and tilapia( Reference Yasmin and Takeuchi 13 ). Growth-promoting effects by dietary CLA have also been reported, with weight gain of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and channel catfish increased by the level of 1 % CLA( Reference Choi, Kang, Ha, Xiong, Ho and Shahidi 14 , Reference Peterson, Manning and Li 15 ). Similar variation has been found in lipid deposition in response to increasing dietary CLA( Reference Bandarra, Nunes and Andrade 9 – Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ). Furthermore, little information is available about the effects of dietary CLA on non-specific immunity and antioxidant capacity in fish species( Reference Makol, Torrecillas and Fernandez-Vaquero 4 ).
Previously, mechanisms related to the physiological effects of CLA have not been completely elucidated in any animal models. In mammals, dietary CLA can decrease oxidative stress and over-inflammation through suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and TNF-α as well as phospholipid-derived hormones, for example, eicosanoids( Reference Byrne 16 – Reference Goodwin and Webb 19 ). CLA has also been found to exert physiological effects by modulating NF-κB, which controls important cell signalling, phosphorylates certain transcription factors and subsequently activates relevant gene expression( Reference Park and Pariza 20 – Reference Chung, Brown and Provo 22 ). However, to our knowledge, no information is available about the effects of dietary CLA on the expression of genes related to inflammation and fatty acid oxidation under a formulation with constant n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) and n-3:n-6 PUFA in any fish species. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a key biosynthetic enzyme in the synthesis of prostaglandins, such as PGE2. It has been shown that COX-2 is dramatically up-regulated during pathological conditions, such as inflammation and cancer( Reference Wun, McKnight and Tuscano 23 ). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α, are key regulators of the immune system that shapes innate and adaptive immune responses( Reference Chabalgoity, Baz and Rial 24 ). An adequate balance of the cytokine environment is critical to achieve protective immunity and to avoid immunopathology( Reference Chabalgoity, Baz and Rial 24 – Reference Montero, Mathlouthi and Tort 26 ).
PPARα, carnitine palmitoyl transferase I (CPT1) and acyl CoA oxidase (ACO) participate in fatty acid oxidation and their expression levels could reflect the oxidative stress inside cells to some extent( Reference Yang 27 ). Previous studies have investigated the relationship between the transcription of these genes and lipid metabolism( Reference Diez, Menoyo and Pérez-Benavente 1 , Reference Zhao, Wu and Tang 28 ). It was shown that transcription of PPARα could increase in the liver of the large yellow croaker as well as the muscle and adipose tissue of gilthead sea bream as dietary CLA increased from 0 to 4 %( Reference Diez, Menoyo and Pérez-Benavente 1 , Reference Zhao, Wu and Tang 28 ). However, little attention has been paid to the role of fatty acid oxidation-related genes in control of oxidative stress in fish species. Since inflammation, immune function and state of oxidative stress have been found to be closely correlated( Reference Furukawa, Meydani and Blumberg 29 , Reference Meydani, Barklund and Liu 30 ), there is great interest to investigate the mRNA expression of fatty acid-related genes (PPARα, CPT1 and ACO) in both the liver and kidney of large yellow croaker fed diets with graded levels of CLA.
The large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) is an important marine fish species that is widely cultured in southeast China. During the past few years, studies on the nutrition of this fish have been conducted intensively( Reference Ai, Mai and Zhang 31 – Reference Wang, Ai and Mai 35 ). However, as far we know, little information is available about the effects of fatty acid nutrition on immune function, antioxidant capacities and lipid deposition, especially mechanisms involved in these processes for this fish species. Thus, the present study was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary CLA on growth performance, selected immunological parameters, antioxidant capacity and lipid deposition as well as on the expression of inflammation- and fatty acid oxidation-related genes in the large yellow croaker.
Materials and methods
Feed ingredients and diet formulation
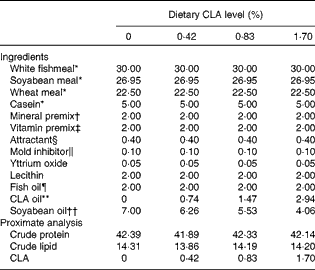
Four isoproteic (42 % crude protein) and isolipidic (12 % crude lipid) diets were formulated to contain graded levels of CLA (0, 0·42, 0·83 and 1·70 % dry diet) by adding different amounts of CLA-enriched oil (18 : 2 cis-9, trans-11: 38·86 % total fatty acids (TFA); 18 : 2 cis-10, trans-12: 32·91 % TFA; Aohai Biotechnology Co., Ltd). Then soyabean oil (China Oil and Foodstuffs Corp.) was added to a final amount of 7·0 % oil mixture of dry diet. The optimal n-3 HUFA level (about 0·8 % dry diet) was guaranteed by supplementing 30 % white fishmeal (crude protein 74·3 % DM, crude lipid 6·6 % DM; Great Seven Biotechnology Co., Ltd) and 2·0 % fish oil (arachidonic acid (ARA) content, 0·23 % TFA; EPA content, 13·34 % TFA; DHA content, 10·53 % TFA; Great Seven Biotechnology Co., Ltd) in each diet according to the results of our previous study( Reference Zuo, Ai and Mai 36 ). White fishmeal and soyabean meal (crude protein 49·4 % DM, crude lipid 0·9 % DM; Great Seven Biotechnology Co., Ltd) were included as the main protein sources. Ingredients and nutrient composition of the four experimental diets are given in detail in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1 Formulation and proximate analysis of the experimental diets (% dry weight)
CLA, conjugated linoleic acid; TFA, total fatty acids.
* White fishmeal: crude protein 74·3 % DM, crude lipid 6·6 % DM; soyabean meal: crude protein 49·4 % DM, crude lipid 0·9 % DM; wheat meal: crude protein 16·4 % DM, crude lipid 1·0 % DM (all supplied by Great Seven Biotechnology Co., Ltd). Casein: 93 % crude protein and 1 % crude lipid (Alfa Aesar, Avocado Research Chemicals Ltd).
† Mineral premix (mg or g/kg diet): CuSO4·5H2O, 10 mg; Na2SeO3 (1 %), 25 mg; ZnSO4.H2O, 50 mg; CoCl2·6H2O (1 %), 50 mg; MnSO4.H2O, 60 mg; FeSO4.H2O, 80 mg; Ca(IO3)2, 180 mg; MgSO4·7H2O, 1200 mg; zeolite, 18·35 g.
‡ Vitamin premix (mg or g/kg diet): vitamin D, 5 mg; vitamin K, 10 mg; vitamin B12, 10 mg; vitamin B6, 20 mg; folic acid, 20 mg; vitamin B1, 25 mg; vitamin A, 32 mg; vitamin B2, 45 mg; pantothenic acid, 60 mg; biotin, 60 mg; niacin acid, 200 mg; α-tocopherol, 240 mg; inositol, 800 mg; ascorbic acid, 2000 mg; microcrystalline cellulose, 16·47 g.
§ Attractant: glycine and betaine.
∥ Mold inhibitor: contained 50 % calcium propionic acid and 50 % fumaric acid.
¶ Fish oil: palmitic acid (16 : 0) content, 15·77 % TFA; oleic acid (18 : 1n-9) content, 3·29 % TFA; linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6) content, 2·12 % TFA; linolenic acid (18 : 3n-3) content, 0·42 % TFA; arachidonic acid content, 0·23 % TFA; EPA content, 13·34 % TFA; DHA content, 10·53 % TFA (Great Seven Biotechnology Co., Ltd).
** CLA oil: palmitic acid (16: 0) content, 3·17 % TFA; oleic acid (18 : 1n-9) content, 14·34 % TFA; linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6) content, 2·24 % TFA; 18 : 2 cis-9, trans-11 content, 38·86 % TFA; 18 : 2 cis-10, trans-12 content, 32·91 % TFA (Aohai Biotechnolgy Co., Ltd).
†† Soyabean oil: palmitic acid (16 : 0) content, 10·90 % TFA; oleic acid (18 : 1n-9) content, 16·18 % TFA; linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6) content, 51·22 % TFA; linolenic acid (18 : 3n-3) content, 6·12 % TFA (China Oil and Foodstuffs Corp.).
Table 2 Fatty acid composition (% total fatty acids) of the experimental diets with different levels of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)*
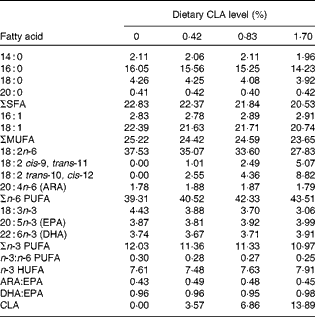
ARA, arachidonic acid; HUFA, highly unsaturated fatty acids (EPA + DHA).
* Some fatty acids, of which the contents are minor, in trace amounts or not detected (such as 22 : 0, 24 : 0, 14 : 1, 20 : 1n-9, 22 : 1n-11, 20 : 2n-6, 20 : 3n-6 and 22 : 5n-3), are not listed in the Table.
All ingredients were ground into fine powder so that they passed through a 246 μm screen. Ingredients of each diet were blended thoroughly first by hand and then mechanically. The oil mixture was then thoroughly mixed with all ingredients of each diet, after which water (200 g/kg) was added to make stiff dough. Pellets (4 × 5 mm and 5 × 5 mm) were made using an automatic pellet-producing machine (Weihai) and dried for about 12 h in a ventilated oven at 40°C. After drying, feeds were packed in double plastic bags and stored at − 20°C until used.
Fish rearing and sampling
Fish rearing and sampling were carried out according to the experimental procedures of the key laboratory of mariculture (Ministry of Education of China), Ocean University of China. Large yellow croaker were bought from a commercial farm in Xiangshan Bay, Ningbo, China. Before the start of the experiment, juveniles were reared in floating sea cages (3 × 3 × 3 m) and fed the control diet for 2 weeks to acclimatise to the experimental conditions and feeds.
At the start of the experiment, the fish were fasted for 24 h and weighed after being anaesthetised with eugenol (1:10 000) (Shanghai Reagent). Fish of similar sizes (7·56 (sem 0·60) g) were distributed into twelve sea cages (1 × 1 × 1·5 m), and each cage was stocked with sixty fish. Each diet was randomly allocated to triplicate cages of fish. Fish were hand-fed twice daily (05.00 and 17.00 hours) to apparent satiation. The feeding trial lasted for 70 d. During the experimental period, water temperature, salinity and dissolved O2 were measured daily. The water temperature ranged from 24 to 30°C, and salinity from 32 to 36‰. The dissolved O2 was approximately 7 mg/l.
At the termination of the experiment, fish were fasted for 24 h before harvest. Then, experimental fish in each cage were weighed one by one and final fish number was recorded after they were anaesthetised with eugenol as described above. After that, blood samples were obtained from the caudal vein of five fish from each cage with 27-gauge needles and 1 ml syringes and allowed to clot at room temperature for 4 h and then at 4°C for a further 6 h. The clot was removed and residual blood cells were separated from the straw-coloured serum by centrifugation (836 g ; 10 min; 4°C). The serum was frozen in liquid N2 and then stored at − 80°C for later analysis of lysozyme activity. Livers and kidneys from five fish in each cage were pooled into 1·5 ml tubes (RNAase-Free; Axygen), frozen in liquid N2 and then stored at − 80°C for later analysis of gene expression related to inflammation and fatty acid oxidation. Liver and muscle from another ten fish in each cage were pooled into 10 ml tubes, frozen in liquid N2 and then stored at − 80°C for the assay of fatty acid composition, moisture and crude lipids. Whole bodies of six fish in each cage were collected into plastic bags and then stored at − 20°C for the assay of moisture and crude lipids.
Biochemical analysis
Crude protein was determined by digestion using the Kjeldahl method (Kjeltec FOSS 2300; Tecator) and estimated by multiplying N by 6·25. Crude lipid was measured by ether extraction using the Soxhlet method (Soxhlet Extraction System B-811). Fatty acid profiles were analysed using the procedures described by Metcalfe et al. ( Reference Metcalfe, Schmitz and Pelka 37 ) with some modification( Reference Ai, Zhao and Mai 33 ). About 100 mg freeze-dried samples/50 μl oil were added into a 20 ml volumetric screwed tube with a cover. Then 3 ml potassium hydroxide methanol (1 m) were added and heated in a 72°C water-bath for 20 min. After that, 3 ml hydrogen chloride methanol (2 m) were added and the mixture was heated in a 72°C water-bath for another 20 min. Previous tests were conducted to make sure that all fatty acids could be esterified following the procedures above. Finally, 1 ml hexane was added into the mixture above, shaken vigorously for 1 min, and then allowed to separate into two layers. Fatty acid methyl esters were separated, and quantified by a HP6890 gas chromatograph (Agilent Technologies Inc.) with a fused silica capillary column (007-CW; Hewlett Packard) and a flame ionisation detector. The column temperature was programmed to rise from 150°C up to 200°C at a rate of 15°C/min, and from 200°C to 250°C at a rate of 2°C/min. Injector and detector temperatures were both 250°C.
Functional immune assays
Phagocytic index
Phagocytic index (PI) was measured according to the method of Pulsford et al. ( Reference Pulsford, Crampe and Langston 38 ) with some modification. Head kidneys of six fish per cage were removed, homogenised in the modified formula of L-15 culture medium (10 μg/ml heparin; 200 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin; 15 mm-HEPES; 1 % fetal bovine serum) and then filtered through a 100 μm nylon mesh. The resulting cell suspensions were enriched by centrifugation (836 g , 25 min, 4°C) on a 34 %/51 % Percoll (Pharmacia) density gradient. The cells were collected at the 34–51 % interface and washed twice using L-15 culture medium above. Then 100 μl cell suspensions were stained with 100 μl trypan blue (0·4 %; Sigma) at 23·5°C for 1 min, and then detected under a microscope (40 × ) to determine the cell concentration and viability. The cell viability was more than 95 % and final cell concentration was adjusted to approximately 1 × 107 leucocytes/ml. Then 100 μl cell suspensions of head kidney leucocytes and 100 μl yeast suspension (Bakers yeast, Type II, Sigma; 1 × 108 cells/ml) were mixed into a 2 ml-sized plastic tube and cultured at 23·5°C for 40 min. To calculate the PI, a sample of mixture was put into the blood cell counting plate (Shanghai Qiujing Biochemical Reagent and Apparatus Co., Ltd) and 200 cells were counted where the number of cells with ingested yeasts was recorded.
Respiratory burst activity
Production of intracellular superoxide anion (O2 −) for five fish from each cage was evaluated using nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) (Sigma) reduction following the method of Secombes( Reference Secombes, Stolen, Fletcher, Anderson, Robertsen and van Muiswinkel 39 ) with some modifications. A 100 μl cell suspension was stained with 100 μl NBT (1 mg/ml) and 100 μl phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; 1 μg/ml; Sigma) which was used as a trigger for O2 − production for 45 min. Absolute methanol was added to terminate the staining. Each tube was washed three times with 70 % methanol and air-dried. Then, 120 μl 2 m-KOH and 140 μl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were added and absorbance was measured at 630 nm with a spectrophotometer using KOH/DMSO as a blank.
Lysozyme activity
Lysozyme activity in serum was measured according to the method of Ellis( Reference Ellis, Stolen, Fletcher, Anderson, Robertsen and van Muiswinkel 40 ). Briefly, a sample of 0·05 ml serum was added to 1·4 ml of a suspension of Micrococcus lysodeikticus (Sigma) (0·2 mg/ml) in a 0·1 m-sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6·8). The reaction was carried out at 25°C and absorbance was measured at 530 nm after 0·5 and 4·5 min in a spectrophotometer. Each unit is defined as the amount of sample causing a decrease in absorbance of 0·001/min.
Hepatic antioxidative capacity assays
Liver samples were first ground into powder in liquid N2 and then homogenised in nine volumes of ice-cold phosphate solution (pH 7·4) and centrifuged at 4000 g for 10 min at 4°C. After that, the supernatant fraction was determined for soluble protein by the method of Bradford( Reference Bradford 41 ) using bovine serum albumin as standard and then stored at − 80°C until use.
Total antioxidative capacity
Total antioxidative capacity was assayed using a commercial kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bio-engineering Institute). Briefly, Fe3+ can be reduced to Fe2+ under some antioxidative enzyme systems and Fe2+ can combine with phenanthroline. Absorbance was read at 520 nm, with distilled water as blanks. Results are expressed in units of total antioxidative capacity per mg soluble protein and each unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that can increase the absorbance by 0·01 in 1 min at 37°C.
Catalase activity
Hepatic catalase (CAT) was assayed using a commercial kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bio-engineering Institute). CAT reacts with H2O2 for exactly 1 min and then ammonium molybdate was quickly added to stop the reaction( Reference Aebi 42 ). The remaining H2O2 can react with ammonium molybdate and generate a light-yellow complex. The CAT activity can be calculated by assaying the absorbance at 405 nm, with distilled water as blanks. Results are expressed in units of CAT per mg soluble protein and each unit is defined as the amount of enzyme necessary to resolve 1 μmol H2O2 in 1 s at 37°C.
Superoxide dismutase activity
Superoxide dismutase activity was measured spectrophotochemically by the ferricytochrome c method using xanthine/xanthine oxidase as the source of superoxide radicals. The reaction mixture consisted of 50 mm-potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7·8), 0·1 mm-EDTA, 0·1 mm-xanthine, 0·013 mm-cytochrome c and xanthine oxidase (0·024 IU/ml). The reaction was triggered by the addition of the xanthine oxidase. Results are expressed in units of superoxide dismutase per mg soluble protein and each unit is defined as the amount of enzyme necessary to produce 50 % inhibition of the ferricytochrome c reduction rate measured at 550 nm( Reference McCord and Fridovich 43 ).
Malondialdehyde content
Malondialdehyde (MDA) as one of the metabolites derived from lipid peroxidation was measured using the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bio-Engineering Institute). MDA reacts with TBA to produce a pink-coloured material that can readily be monitored by a spectrophotometer to give an overall indication of the level of lipid peroxidation( Reference Gavino, Miller and Ikharebha 44 ). Generally speaking, 100 μl supernatant fraction of liver homogenates in each replicate were incubated with 20 % TCA and 0·67 % TBA at 95°C for 40 min. Absorbance was read at 532 nm, with distilled water as blanks. Results were converted to nmol MDA per mg soluble protein using a standard sample of 10 nmol/ml malonaldehyde diethyl acetate.
RNA extraction and real-time quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the liver and kidneys using Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen) and electrophoresed on a 1·2 % denaturing agarose gel to test the integrity. The RNA was treated with RNA-Free DNase (Takara) to remove DNA and reverse transcribed to complementary DNA (cDNA) by a PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit (Takara) following the instructions. First-strand cDNA was diluted by four times using sterilised double-distilled water. Real-time quantitative PCR was carried out in a quantitative thermal cycler (Mastercycler® ep realplex; Eppendorf). The amplification was performed in a total volume of 25 μl, containing 1 μl of each primer (10 μm), 1 μl of the diluted first-strand cDNA product, 12·5 μl of 2 × SYBR® Premix Ex TaqTM II (Takara) and 9·5 μl of sterilised double-distilled water. The real-time PCR programme was as follows: 95°C for 2 min, followed by forty cycles of 95°C for 10 s, 58°C for 10 s, and 72°C for 20 s. The primer sequence for β-actin, COX-2, IL-1β, TNF-α, PPARα, CPT1 and ACO were designed following the published sequences for the large yellow croaker from GenBank or published papers( Reference Zhao, Wu and Tang 28 , Reference Xie, Zhang and Lin 45 , Reference Yao, Kong and Wang 46 ) and listed in Table 3. PCR fragments amplified by each pair of primers were sequenced, blasted and analysed to assure the specificity of each primer pair. At the end of each PCR reaction, melting curve analysis was performed to confirm that only one PCR product was present in these reactions. Standard curves were made with five different dilutions (in triplicate) of the cDNA samples and amplification efficiency was analysed according to the following equation E = 10( − 1/slope) – 1. The primer amplification efficiency was 1·020 for β-actin, 1·004 for COX-2, 0·9954 for IL-1β, 1·0188 for TNF-α, 0·9924 for PPARα, 1·1190 for CPT1 and 1·0813 for ACO. The absolute ΔCT (cycle threshold) values between the target gene and inner control gene were all close to zero and indicate that the ΔΔCT calculation for the relative quantification of target genes can be used. To calculate gene expression, the comparative CT method (2− ΔΔT method) was used as described by Yao et al. ( Reference Yao, Kong and Wang 46 ).
Table 3 Real-time quantitative PCR primers for inflammation- and fatty acid oxidation-related genes and β-actin of the large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea)

COX-2, cyclo-oxygenase-2; F, forward; R: reverse; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyl transferase I; ACO, acyl CoA oxidase.
Calculations and statistical analysis
Growth parameters were calculated as follows:
Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS 16.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc.). All data were subjected to a one-way ANOVA and differences between the means were tested by Tukey's multiple-range test. The level of significance was set at P< 0·05 and the results are presented as mean values with their standard errors.
Results
Survival rate, growth performance and somatic indices
Survival rate of large yellow croaker for all dietary treatments was above 91·0 % and there were no significant differences among dietary treatments in the present study (P>0·05). No statistical differences were detected in feed intake among dietary treatments (19·11–20·74 g/kg average body weight per d) (P>0·05). As dietary CLA increased from 0 to 0·42 %, weight gain rate increased significantly from 499·30 to 572·52 % (P< 0·01), and then decreased to 444·21 % with dietary CLA increasing from 0·42 to 1·70 % (P< 0·05). No significance was detected in the feed efficiency ratio of experimental fish among dietary treatments (P>0·05). The viserosomatic index of fish fed the 0·42 % CLA diet (6·79 %) was significantly higher than that of fish in the control (6·06 %) and 1·70 % CLA treatment (6·27 %) groups (P< 0·05). Hepatosomatic index significantly increased from 1·40 to 1·93 % with the increase of dietary CLA (P< 0·05) (Table 4).
Table 4 Effects of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on growth, survival and selected body parameters of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets (Mean values with their standard errors for three determinations)
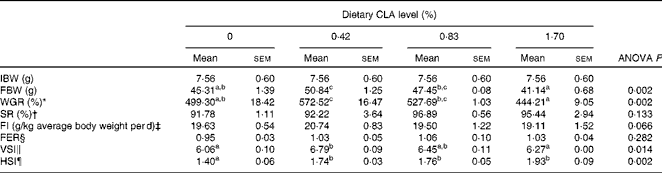
IBW, initial mean body weight; FBW, final mean body weight; WGR, weight gain rate; SR, survival rate; FI, feed intake; FER, feed efficiency ratio; VSI, viserosomatic index; HSI, hepatosomatic index.
a,b,cMean values within a row with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
* WGR (%) = 100 × ((FBW − IBW)/IBW).
† SR (%) = 100 × final fish number/initial fish number.
‡ FI (g/kg average body weight per d) = feed consumed (g)/((IBW+FBW)/2/1000 (kg))/d.
§ FER = wet weight gain (g)/dry feed consumed (g).
∥ VSI (%) = 100 × (visceral weight/body weight).
¶ HSI (%) = 100 × (liver weight/body weight).
Immunological and hepatic antioxidative parameters
As dietary CLA increased from 0 to 0·42 %, PI increased significantly from 17·9 to 34·7 %, and then decreased to 24·7 % with dietary CLA increasing from 0·42 to 1·70 % (P< 0·05). Respiratory burst activity (value of optical density (OD) 630) showed a similar trend to PI as dietary CLA increased. Respiratory burst activity was significantly increased by 0·83 % CLA (OD630 = 0·50) compared with the control (OD630 = 0·34) and 1·70 % CLA treatment (OD630 = 0·42) groups (P< 0·05). However, no significant differences were observed in this parameter between the control and the 1·70 % CLA groups (P>0·05). There were no statistical differences in serum lysozyme activity among four dietary treatments (P>0·05) (Table 5).
Table 5 Effects of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on selected immunological and hepatic antioxidative parameters of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets (Mean values with their standard errors for three determinations)
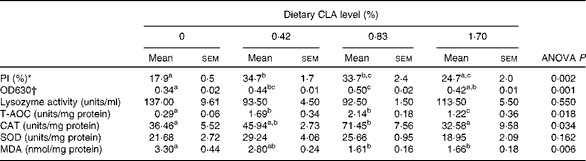
PI, phagocytic index; OD, optical density; T-AOC, total antioxidative capacity; CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; MDA, malondialdehyde.
a,b,cMean values within a row with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
* PI (%) = leucocytes with ingested yeast/200 observed leucocytes under the microscope.
† OD630, respiratory burst of activity.
Total antioxidative capacity increased significantly from 0·29 to 2·14 units/mg protein as dietary CLA increased from 0 to 0·83 %, and then decreased significantly to 1·22 units/mg protein with further increase of CLA (P< 0·05). Hepatic CAT increased significantly from 36·46 to 71·45 units/mg protein as dietary CLA increased from 0 to 0·83 %, and then decreased significantly to 32·58 units/mg protein with further increase of CLA (P< 0·05). Superoxide dismutase activity in the liver increased from 21·68 to 29·64 units/mg protein as dietary CLA increased from 0 to 0·42 % and then decreased to 18·95 units/mg protein with further increase of this fatty acid (P>0·05). MDA content in the liver decreased significantly from 3·30 to 1·66 nmol/mg protein with the increase of dietary CLA (P< 0·05) (Table 5).
Proximate composition of whole body, muscle and liver
No significant difference was detected in moisture content of the whole body, liver and muscle (P>0·05). The lipid content of the whole body and muscle increased significantly with the increase of dietary CLA (P< 0·05). The whole body lipid content of fish fed the diets with 1·70 % CLA (8·51 % wet weight) was significantly higher compared with the control (7·44 % wet weight) and 0·42 % CLA treatment (7·38 % wet weight) groups (P< 0·05). The muscle lipid content of fish fed the diets with 0·83 % CLA (7·26 % wet weight) was significantly higher compared with the control (5·97 % wet weight) and 0·42 % CLA treatment (5·47 % wet weight) groups (P< 0·05). There were no significant differences in liver lipid concentration among dietary treatments (P>0·05) (Table 6).
Table 6 Effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on composition of the whole body, liver and muscle (% of live weight) of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets (Mean values with their standard errors for three determinations)
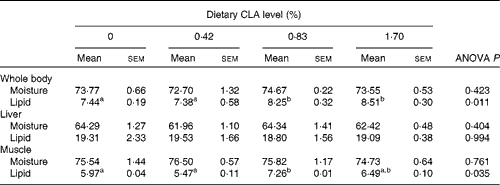
a,bMean values within a row with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
Liver and muscle fatty acid profiles
Deposition of CLA isomers, 18 : 2 cis-9, trans-11 and 18 : 2 trans-10, cis-12, were increased with the increase of dietary CLA (P< 0·05). Dietary CLA modified significantly the retention of SFA, MUFA and ARA in the liver. The total percentage of SFA, mainly 14 : 0, 16 : 0 and 18 : 0, increased with dietary CLA increasing to 0·42 %, and then decreased with further increase of CLA. The hepatic concentration of 16 : 0 in the 0·83 % CLA treatment group (18·97 % TFA) was significantly higher than that in the control (16·78 % TFA) and 1·70 % CLA treatment (16·43 % TFA) groups (P< 0·05). Hepatic 18 : 0 content in the 0·42 % CLA treatment group (10·64 % TFA) was significantly higher than that in the control group (4·92 % TFA) (P< 0·05). MUFA percentage in the liver decreased by a reduction in 16 : 1n-9 and 18 : 1n-9 as dietary CLA increased (P< 0·05). The percentage of ARA increased significantly from 1·64 to 2·72 % TFA as dietary CLA increased. The ARA:EPA ratio increased significantly from 1·11 to 2·79 with the increase in dietary CLA. There were no significant differences in the content of n-3 HUFA or the ratio of DHA:EPA among dietary treatments (P>0·05) (Table 7).
Table 7 Fatty acid composition (% total fatty acids) in the liver of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed diets with graded levels of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)* (Mean values with their standard errors for three determinations)
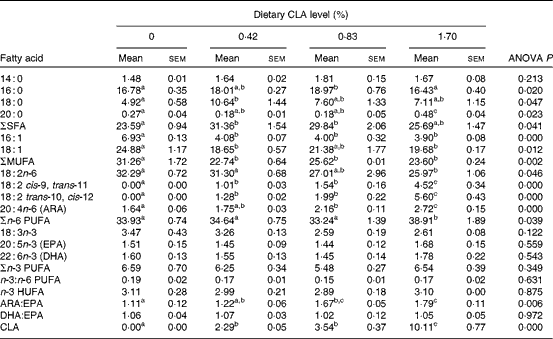
ARA, arachidonic acid; HUFA, highly unsaturated fatty acids (EPA + DHA).
a,b,cMean values within a row with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
* Some fatty acids, of which the contents are minor, in trace amounts or not detected (such as 22 : 0, 24 : 0, 14 : 1, 20 : 1n-9, 22 : 1n-11, 20 : 2n-6, 20 : 3n-6 and 22 : 5n-3), are not listed in the Table.
For muscle, the concentration of biologically active isomers, 18 : 2 cis-9, trans-11 and 18 : 2 trans-10, cis-12, increased significantly with increasing dietary inclusion of CLA (P< 0·05). The content of SFA in muscle increased, while MUFA decreased as dietary CLA increased (P< 0·05). The 18 : 0 content of muscle in the 0·83 % CLA treatment group (8·01 % TFA) was comparable with that in the 0·42 % CLA (6·40 % TFA) and 1·70 % CLA (6·70 % TFA) treatment groups, but significantly higher than that in the control treatment group (4·64 % TFA) (P< 0·05). ARA increased significantly from 1·93 to 2·61 % TFA as dietary CLA increased. The ARA:EPA ratio increased significantly from 0·65 to 0·87 with the increase in dietary CLA. No significant differences were detected in the concentration of n-3 HUFA or the DHA:EPA ratio among dietary treatments (P>0·05) (Table 8).
Table 8 Fatty acid composition (% total fatty acids) in the muscle of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed diets with graded levels of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)* (Mean values with their standard errors for three determinations)
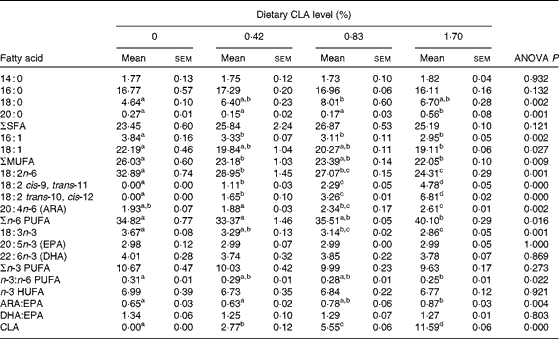
ARA, arachidonic acid; HUFA, highly unsaturated fatty acids (EPA + DHA).
a,b,c,dMean values within a row with unlike superscript letters were significantly different (P< 0·05).
* Some fatty acids, of which the contents are minor, in trace amounts or not detected (such as 22 : 0, 24 : 0, 14 : 1, 20 : 1n-9, 22 : 1n-11, 20 : 2n-6, 20 : 3n-6 and 22 : 5n-3), are not listed in the Table.
Expression of inflammation- and fatty acid oxidation-related genes
The transcriptional levels of COX-2 and IL-1β in the liver and kidney decreased significantly with increasing dietary CLA. Hepatic COX-2 mRNA expression level was significantly decreased by approximately 0·30-fold, 0·67-fold and 0·72-fold in the 0·42, 0·83 and 1·70 % CLA treatment groups, respectively (P< 0·05) (Fig. 1(A)). The kidney COX-2 mRNA transcriptional level was significantly decreased by about 0·60-fold, 0·70-fold and 0·85-fold in the 0·42, 0·83 and 1·70 % CLA treatment groups than that in the control group, respectively (P< 0·05) (Fig. 1(B)). IL-1β mRNA levels of fish fed diets with 0·83 and 1·70 % CLA were significantly decreased by about 0·90-fold in the liver and 0·60-fold in the kidney compared with the control group, respectively (P< 0·05) (Fig. 1(A) and (B)). There were no significant differences in the transcription of TNF-α in the liver and kidney among dietary treatments (P>0·05) (Fig. 1(A) and (B)).
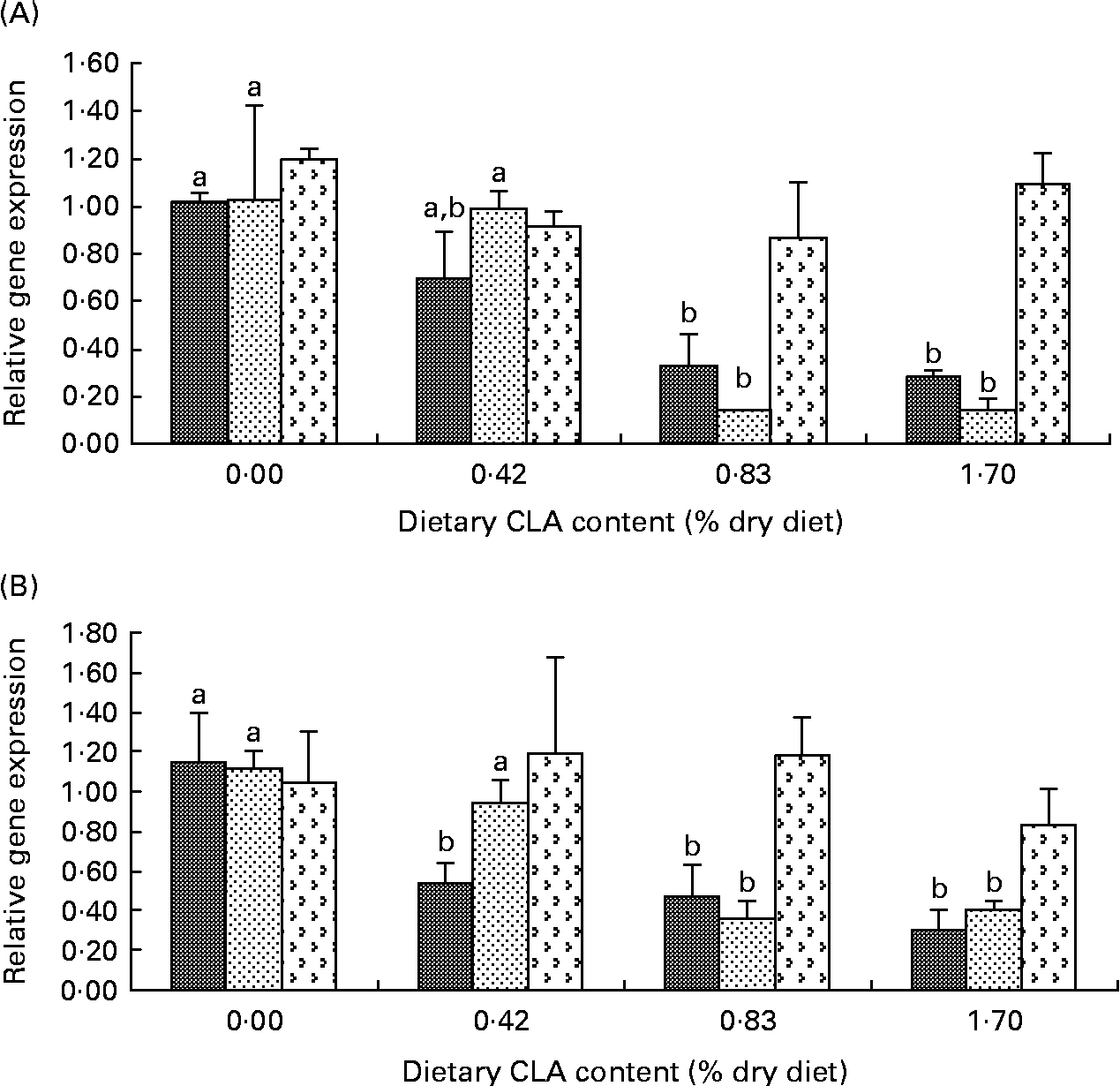
Fig. 1 Effects of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on relative mRNA expression of inflammation-related genes (cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2; ![]() ), IL-1β (
), IL-1β (![]() ) and TNF-α (
) and TNF-α (![]() )) in the liver (A) and kidneys (B) of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets. Values are means (n 3), with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. a,bMean values for the same gene with unlike letters were significantly different (P< 0·05; Tukey's test).
)) in the liver (A) and kidneys (B) of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets. Values are means (n 3), with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. a,bMean values for the same gene with unlike letters were significantly different (P< 0·05; Tukey's test).
Hepatic PPARα transcriptional levels increased significantly to the maximum levels with dietary CLA increasing from 0 to 0·42 %, and thereafter decreased significantly with further increase of dietary CLA (P< 0·05). mRNA expression levels of PPARα were increased by 0·89-fold in the 0·42 % CLA treatment group while they decreased by 0·1-fold and 0·4-fold in the 0·73 and 1·70 % dietary CLA treatment groups compared with the control treatment. The hepatic transcriptional levels of CPT1 in the 0·83 and 1·70 % CLA treatment groups were about 1·40-fold higher than those of the control and 0·42 % CLA treatment groups. The ACO transcriptional levels in the liver of fish fed diets with equal to or above 0·42 % CLA were decreased by more than 0·50-fold compared with the control group (Fig. 2(A)).
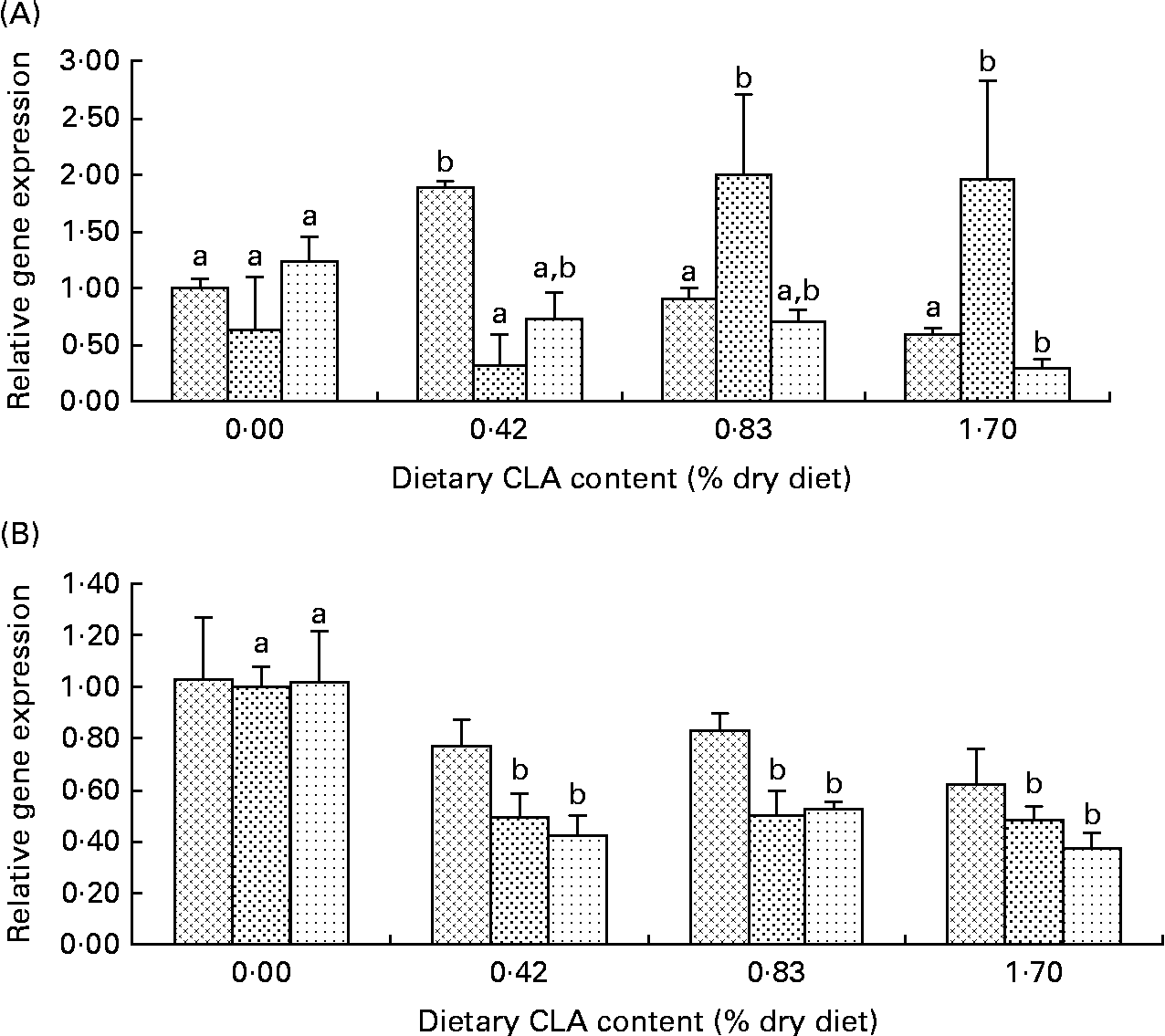
Fig. 2 Effects of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on relative mRNA expression of fatty acid oxidation-related genes (PPARα (![]() ), carnitine palmitoyl transferase I (CPT1;
), carnitine palmitoyl transferase I (CPT1;![]() ) and acyl CoA oxidase (ACO;
) and acyl CoA oxidase (ACO; ![]() )) in the liver (A) and kidneys (B) of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets. Values are means (n 3), with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. a,bMean values for the same gene with unlike letters were significantly different (P< 0·05; Tukey's test).
)) in the liver (A) and kidneys (B) of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oil-based diets. Values are means (n 3), with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. a,bMean values for the same gene with unlike letters were significantly different (P< 0·05; Tukey's test).
There was no significant difference in kidney PPARα mRNA expression among dietary treatments, though a decreasing trend was observed as dietary CLA increased (P>0·05). The transcription levels of CPT1 and ACO in the kidney decreased significantly as dietary CLA increased. CPT1 transcriptional levels in the kidney of fish fed diets with equal to or above 0·42 % CLA were significantly decreased by about 0·50-fold compared with the control treatment group (P< 0·05). ACO transcriptional levels in the kidney were decreased by 0·58-fold, 0·47-fold and 0·63-fold in the 0·42, 0·83 and 1·70 % CLA treatment groups, respectively (Fig. 2(B)).
Discussion
In the present study, the growth of fish was significantly enhanced by moderate inclusion of CLA (0·42 %), but decreased when the level of this particular fatty acid was equal to or above 0·83 %. The growth-promoting effects of a moderate level of CLA are consistent with the findings in common carp( Reference Choi, Kang, Ha, Xiong, Ho and Shahidi 14 ), Pacific white shrimp( Reference Zhong, Zhang and Li 47 ) and channel catfish( Reference Peterson, Manning and Li 15 ). On the contrary, some studies have reported the deleterious effects of CLA on the growth performance of fish( Reference Twibell, Watkins and Rogers 6 , Reference Yasmin, Takeuchi and Hayashi 8 , Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ). Thus, it can be concluded that the effect of CLA on growth performance varies significantly among different species, and this is probably due to different physiological responses to dietary CLA inclusion for different species( Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 , Reference Valente, Bandarra and Figueiredo-Silva 12 ).
The two non-specific immune parameters, PI and respiratory burst, were significantly higher in fish fed diets with 0·42 and 0·83 % CLA compared with the control and other groups. The poor non-specific immunity of fish fed the control and the highest-CLA diet (1·70 %) could be due to a too high or low inflammation level of the fish body( Reference Chabalgoity, Baz and Rial 24 , Reference Alfano and Poli 25 ). In the present study, mRNA levels of COX-2 and IL-1β were significantly higher in the liver and kidney of fish fed the control diet with a high amount of linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6). High inclusion of dietary n-6 fatty acids have been found to exert deleterious effects on the health of gilthead sea bream by influencing fatty acid composition of immune cells with a high deposition of linoleic acid, altering eicosanoid production, and even chronically increasing the basal expression of certain inflammation-related genes( Reference Montero, Mathlouthi and Tort 26 , Reference Montero, Kalinowski and Obach 48 – Reference Montero, Grasso and Izquierdo 51 ). Thus, the relatively higher level of inflammation could account for the low non-specific immunological parameters of fish fed the control diet in the present investigation. Moderate dietary CLA (0·42–0·83 %) could benefit the immunity of fish through modulating inflammation, which is characterised by transcriptional levels of COX-2 and IL-1β, to a relatively optimum level. However, cytokines are key regulators of the immune system that shape innate and adaptive immune responses( Reference Chabalgoity, Baz and Rial 24 ). Scarce expression of COX-2 and IL-1β could be responsible for the relatively worse fish immunity in treatments with the higher level of CLA. Since a positive control (100 % fish oil-containing diet) was not included in the present study, it is still unknown whether dietary CLA can attenuate inflammation as strongly as fish oil does or whether dietary CLA can improve immune potential. However, it should be admitted that CLA could enhance non-specific immunity by ameliorating high inflammation (COX-2 and IL-1β) caused by high n-6 fatty acids at least from the results of the present study.
In the present study, no significance was detected in the transcription of TNF-α among dietary treatments. This was inconsistent with the findings of Montero et al. ( Reference Montero, Mathlouthi and Tort 26 ) who found that transcription of TNF-α was significantly higher in fish fed diets with 100 % soyabean oil compared with those fed diets with 100 % fish oil, 70 % linseed oil or 70 % soyabean oil. However, it should be noted that transcription of TNF-α was detected at different time points (1 d, 3 d and 7 d) after exposure to a sub-lethal dose of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida in that study. Increased expression of TNF-α and IL-1β after exposure to pathogens has been reported in several fish species( Reference Montero, Mathlouthi and Tort 26 , Reference Xie, Zhang and Lin 45 ). Thus, it is possible that TNF-α was less sensitive than IL-1β to dietary CLA without pathogen challenge. Furthermore, different fish species and diet formulation could also account for the inconsistent results.
On the other hand, the immune enhancement by moderate dietary CLA may benefit from its antioxidant capacity. The antioxidant effect of CLA has been observed in many studies of rodents and human subjects( Reference Hayek, Han and Wu 52 – Reference Bergamo, Maurano and Rossi 54 ). In the present study, mRNA expression of fatty acid oxidation-related genes in the liver and kidney declined while hepatic antioxidant capacity increased as dietary CLA level increased to 0·83 %. This means that CLA could function as a kind of antioxidant nutrient in the large yellow croaker. Intervention with antioxidant nutrients (vitamin E, vitamin C, β-carotene and carotenoids) has been shown to enhance the immune response in several fish species( Reference Ai, Mai and Zhang 31 , Reference Lin and Shiau 55 – Reference Amar, Kiron and Akutsu 59 ). Antioxidant nutrients are proposed to exert their immune-enhancing effects through suppression of lipid peroxide and/or PGE2 production according to the findings in mammals( Reference Furukawa, Meydani and Blumberg 29 , Reference Meydani, Barklund and Liu 30 ). In the present study, the expression of COX-2 and IL-1β generally paralleled well with the transcription of fatty acid oxidation-related genes while showing an antagonistic tendency with hepatic antioxidant capacity as dietary CLA increased. However, hepatic antioxidant capacity was not further enhanced in fish fed the diet with the highest level of CLA, which was in accordance with PI and respiratory burst activity. Reactive oxygen species exert a critical role in bacterial killing after bacteria are ingested by phagocytes( Reference Sharp, Nagelkeke and Secombes 60 , Reference Sharp and Secombes 61 ). When fatty acid oxidation was inhibited to a very low level, the normal respiratory burst activity (reactive oxygen species production) could be unavoidably damaged.
In the present study, fish fed the control diet were subject to serious inflammation, characterised by a relatively higher transcription of COX-2 and IL-1β, higher expression of fatty acid oxidation-related genes (PPARα, CPT-I and ACO) and MDA production, as well as significantly lower antioxidant capacity. In accordance, the hepatosomatic index and viserosomatic index were significantly lower in fish fed the control diet. This implies that fish fed the diets without CLA (the control) may suffer hepatic injury and toxicity from serious oxidative stress and inflammation. Indeed, hepatic disease caused by inflammation and oxidative stress has been reported in considerable studies on rodents( Reference Byrne 16 ) and male Japanese medaka( Reference Yang 27 ). However, no direct evidence was obtained in the present study, and investigations are needed to verify this hypothesis in further studies.
An increasing lipid content of the whole body and muscle was observed as dietary CLA level increased in the present study. This could result from decreasing fatty acid oxidation, which is reflected by reduced transcription of PPARα, CPT1 and ACO, in response to increasing dietary CLA. However, there were no significant differences in liver lipid concentration among dietary treatments. The present results are in accordance with the findings of Kennedy et al. ( Reference Kennedy, Campbell and Porter 10 ) who found that muscle lipid content of Atlantic salmon increased as dietary CLA increased and support the fact that dietary CLA had no significant effect on the liver lipid content of catfish( Reference Twibell and Wilson 7 ), Atlantic salmon( Reference Kennedy, Campbell and Porter 10 ) or rainbow trout juveniles( Reference Bandarra, Nunes and Andrade 9 ). In contrast, decreased lipid concentration in the whole body or liver was observed in some other studies( Reference Twibell, Watkins and Brown 5 , Reference Twibell, Watkins and Rogers 6 , Reference Bandarra, Nunes and Andrade 9 , Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ). The different physiological effects of CLA observed in the present study and other reports may be attributed to differences in metabolic rate, administered dose of CLA, relative proportion of each isomer in a dietary CLA mixture, or duration of the feeding period, as pointed out by Terpstra( Reference Terpstra 62 ). Furthermore, different diet formulations may be one important cause for the discrepancies in the effects of dietary CLA on lipid deposition. In the present investigation, soyabean oil was used to balance the total amount of oil mixture, with almost equal amount of n-3 HUFA and ratio of n-3:n-6 PUFA among the four diets. However, in most previous studies, fish oil was used to acquire equal lipid content, and thus n-3 HUFA and ratio of n-3:n-6 PUFA were decreased as dietary CLA increased. The lipid concentration of the whole fish body increased with the increase of dietary n-3 HUFA in gilthead sea bream( Reference Kalogeropoulos, Alexis and Henderson 63 ) and large yellow croaker (RT Zuo, QH Ai, KS Mai and W Xu, unpublished results). As dietary n-3:n-6 PUFA increased, body lipid also increased in gilthead sea bream( Reference Robaina, Izquierdo and Moyano 64 ) and juvenile yellow catfish( Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 65 ). Evidence above indicated that lipid-decreasing effects caused by dietary CLA could be attributed to decreased dietary n-3 HUFA level or n-3:n-6 PUFA in some previous studies.
In the present study, the total percentages of the main fatty acids were strongly affected by the dietary inclusion of CLA. A significant increase of SFA and decrease of MUFA was observed in the liver and muscle of fish fed diets with increasing amounts of CLA. This was similar to the findings of some previous studies on other fish species( Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 , Reference Dos Santos, Furuya and da Silva 66 ). Since SFA and MUFA concentrations were equal among experimental diets in the present study, the increased SFA and decreased MUFA in the liver and muscle could be attributed to a low conversion of SFA to MUFA. Indeed, reduced activity of Δ9 desaturase, a rate-limiting enzyme converting SFA to MUFA, has been found to be suppressed by dietary CLA as pointed out by Valente et al. ( Reference Valente, Bandarra and Figueiredo-Silva 12 ). EPA and DHA profiles in selected tissues of the present experiment showed no significant differences among dietary treatments. This was consistent with the findings of studies by Makol et al. ( Reference Makol, Torrecillas and Fernandez-Vaquero 4 ) and Tan et al. ( Reference Tan, Luo and Xie 11 ), but inconsistent with the results of some other studies where increased EPA and DHA levels were found as dietary CLA increased( Reference Twibell, Watkins and Rogers 6 , Reference Valente, Bandarra and Figueiredo-Silva 12 , Reference Manning, Li and Robinson 67 ). Increased deposition of n-3 HUFA could result from a higher expression of Δ5 and Δ6 desaturases that play critical roles in HUFA biosynthesis( Reference Bandarra, Nunes and Andrade 9 , Reference Pereira, Leonard and Mukerji 68 ). In the present study, hepatic ARA concentration increased while COX-2 expression decreased significantly with the increase in dietary CLA. It was possible that more ARA in the liver of fish fed the control diet participated in eicosanoid production catalysed by COX-2 and this resulted in the lower ARA deposition in the control treatment. Although PGE2 concentration was not assayed in serum or other tissues, it is usually believed that PGE2 content parallels well with COX-2 transcriptional levels to a large extent( Reference Schuligoi, Ulcar and Peskar 69 – Reference Dhillon, Su and Liu 72 ).
To conclude, a moderate level of dietary CLA could be beneficial for fish growth performance, non-specific immunity and hepatic antioxidant capacity. In the large yellow croaker, dietary CLA may exert beneficial effects through modulating the mRNA expression of inflammation-related genes (COX-2 and IL-1β) and fatty acid oxidation-related genes (PPARα, CPT1 and ACO). Future studies are needed to investigate the effects of this particular fatty acid on other metabolism processes such as lipid transportation and distribution in the large yellow croaker.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Foundation of China (grant no. 30871930 and 31172425).
We thank H. Asino, Q. Y. Duan, J. K. Shentu, Y. W. Luo, R. J. Sun, X. W. Yi and L. Wang for their selfless help during the samplings, Y. F. Zheng for his supplying of essential facilities during the tests of immunological parameters, and X. J. Dong for her help in cloning the core region of ACO.
R. Z. designed all experiments, carried out most of experimental work and wrote the manuscript under the direction of project leader Q. A.; K. M. assisted in the experimental design and manuscript revision; W. X. provided all fatty acid composition data.
There are no conflicts of interest to report.












