Evidence for a possible role of early infant-feeding pattern in the development of asthma and allergic diseases is inconsistent. Early introduction of solid foods in infancy may not increase the risk of developing allergic diseases and asthma(Reference Tarini, Carroll and Sox1, Reference Zutavern, Brockow and Schaaf2). Previous studies suggest that early introduction of fish, fruits, vegetables, egg and milk may reduce the risk of atopy and allergic rhinitis(Reference Nafstad, Nystad and Magnus3–Reference Njå, Nystad and Lodrup Carlsen5).
In a series of prospective cohort studies, exclusive breastfeeding for at least 3 months has been linked to a reduced frequency of asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema compared with shorter breastfeeding(Reference Gdalevich, Mimouni and Mimouni6–Reference Gdalevich, Mimouni and David8). There are, however, prospective studies showing contrasting results(Reference Benn, Wohlfahrt and Aaby9, Reference Kramer and Kakuma10). Whether breastfeeding protects from allergies only in families with a known allergic propensity remains unclear(Reference Benn, Wohlfahrt and Aaby9, Reference Saarinen and Kajosaari11, Reference Rothenbacher, Weyermann and Beerman12). Breastfeeding may also increase the risk when maternal asthma is present(Reference Wills-Karp, Brandt and Morrow13). Various cytokines and the function of macrophages in breast milk of mothers whose infants later developed allergic disorders have been claimed to be the culprit(Reference Jarvinen and Suomalainen14).
We set out to assess how age at introduction of different main foods or food groups such as fruits and berries, roots, milk products and cereals as well as breastfeeding during the first year of life is related to the emergence of asthma and allergic rhinitis by the age of 5 years in a population-based cohort of young children with increased HLA-DQB1-conferred risk for type 1 diabetes. Our primary endpoints were assessed by an International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood type of questionnaire, where also the age at diagnosis of the diseases was inquired. In accordance with international guidelines(15, Reference Muraro, Dreborg and Halken16), Finnish families are advised to start solid foods in their offspring at the age of 4–6 months.
Experimental methods
Subjects
The Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Study is a multidisciplinary prospective population-based cohort study(Reference Kupila, Muona and Simell17). Newborn infants from the areas of three university hospitals in Finland are screened for HLA-DQB1-conferred susceptibility to type 1 diabetes using cord blood samples. Infants who have increased genetic susceptibility (HLA-DQB1*02/0302 heterozygous and DQB1*0302/x-positive subjects; x stands for homozygosity or neutral alleles) are monitored for diabetes-associated autoantibodies, growth and viral infections at 3–12 months intervals. HLA-DQB1 alleles were analysed as described previously(Reference Ilonen, Reijonen and Herva18). Procedures were approved by the local ethics committees.
The Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Nutrition Study falls within the framework of The Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Study(Reference Virtanen, Kenward and Erkkola19). The at-risk children born between 2 September 1996 and 31 March 2000 at Oulu University Hospital and between 20 October 1997 and 31 March 2000 at Tampere University Hospital, and who took part in the dietary follow-up, were invited to take part in the present study on asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema at the age of 5 years. All those children who attended the 5 year visit were invited to take part in the allergy study: 1302 out of the 1374 attending (94·8 %) participated. Among the children, 1293 had information on asthma status and 1288 on allergic rhinitis.
Dietary methods
Information on infant-feeding patterns was collected using a structured dietary questionnaire, which was completed when the child was 3, 6, 12 and 24 month old and in addition to the ‘age at introduction of new foods’ form. Trained study nurses checked the questionnaires during the visits (at 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 months). In the 3-month dietary questionnaire, the feeding in the delivery hospital was assessed in detail: whether the child was breastfed; had received banked breast milk; was exposed to infant formula and if so to which formula; and which of these was/were the main type of feed during the delivery hospital stay. The duration of breastfeeding and the age at introduction and brand names of all infant formulas, which the child had received, as well as the age at introduction of other cow's milk and sour milk products and foods and drinks containing cow's milk were requested in all questionnaires. The brand name of the infant formula was recorded and the formulas were later classified as regular cow's milk based, special (hydrolysed) or soya based. At the age of 3 months, all the food items the infant had so far received were carefully recorded in the questionnaire. During the first 2 years of life, the family was asked to complete at home continuously the age at introduction of new foods form, which was checked at every visit. The form included the following food groups: fruits and berries; potato; carrot; spinach or beetroot; turnip and swede; cabbages; lettuce; wheat; barley; oats; rye; maize, rice, millet or buckwheat; pork; beef; chicken; other meats; sausage; fish; egg; sour milk products; foods containing cow's milk; cow's milk and ice cream; soya products. In the analysis, the following food groupings were used: (1) fruits and berries; (2) roots: potato, carrot, turnip and swede; (3) wheat, barley, rye and oats; (4) other cereals: maize, rice, millet and buckwheat; (5) cabbages (cauliflower, broccoli, kale and Chinese, red and turnip cabbage); (6) milk products; (7) fish; (8) meat (pork, beef, chicken and other meat); (9) egg. In addition, wheat, barley, rye and oats were analysed separately. Exclusive breastfeeding was defined as the period during which the child received, in addition to breast milk, only water and/or vitamin/mineral supplements.
Asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema
The participating families completed a questionnaire on the child's possible history and symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema when the child was 5 year old. The questionnaire was modified from the validated International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood questionnaire(Reference Asher, Keil and Anderson20, Reference Remes, Korppi and Kajosaari21). For all outcomes, we added the question about the age of appearance of first symptoms. We used as endpoint of asthma persistent asthma: the child's asthma was diagnosed by a physician and he/she has either had wheezing or asthma medication during the previous 12 months. Allergic rhinitis was defined as: sneezing, nasal congestion or rhinitis other than with respiratory infection and together with the symptoms of rhinitis eye itching and tearing(Reference Asher, Keil and Anderson20). Parental asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema were considered in the analyses of the results. Also the presence of pets at home during the first year of the life was used as a covariate.
Sociodemographic and perinatal characteristics
Information on child's sex, maternal age and educational level and the number of siblings were recorded in a structured questionnaire completed by the parents after the delivery. Information on duration of gestation, mode of delivery, birth weight and height and maternal smoking during pregnancy was received from the Medical Birth Registries of the Oulu and Tampere University Hospitals (Table 1).
Table 1 Characteristics of the participating infants and hazard ratio (HR) and 95 % CI of development of persistent asthma and allergic rhinitis*
(HR and 95 % CI)

* Information on asthma status was available for 1293 children and information on allergic rhinitis for 1288 children. Altogether, there were 77 cases of asthma and 185 cases of allergic rhinitis. The age at onset of the disease information was available for 75 cases with asthma and 121 cases with allergic rhinitis.
† A Cox regression survival model was used in the analysis. Adjusted for all the variables in the table and for area (hospital) of birth: Oulu and Tampere University Hospitals. P values are indicated for terms that are significantly associated with the endpoint.
‡ At the time of the birth of the child.
Statistical methods
In order to use also the information on the age of onset of asthma and allergic rhinitis and to gain in statistical power in the analysis, survival analysis was used. Cox proportional hazards regression was selected to analyse the association between dietary variables and the disease endpoints. The assumption of proportionality was not strongly violated. All the final analyses were repeated with logistic regression, which identified the same significant associations (results not shown).
There were nine twin pairs and forty-four other sibling pairs. The sibling effect was taken into account in the analysis (clustering by family in STATA). The statistical significance of dietary variables was tested with the Wald test. The STATA 9.0 program (College Station, TX, USA) was used in the analysis. We used tertiles of the dietary variables to avoid ad hoc or outcome-dependent choices of categorisation (Tables 2 and 3). The exclusive and overall durations of breastfeeding were also used as continuous variables. The strategy of analysis when testing the associations of the dietary variables with the endpoints was the following: first, all dietary variables were tested separately in single variate models. Then, the least significant one/ones were removed from the multiple regression model and the possible confounding variables were included in the model, and this was repeated until all dietary variables remaining in the model were statistically significant at the 5 % level. Among the cereals, wheat, oats, rye and barley were all significantly associated with the asthma endpoint in single variate models. Due to high correlations between these variables, the strategy of analysis described was first applied to these cereals separately (Table 2).
Table 2 Unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and 95 % CI for persistent asthma related to age at introduction of different cereals*
(HR and 95 % CI)
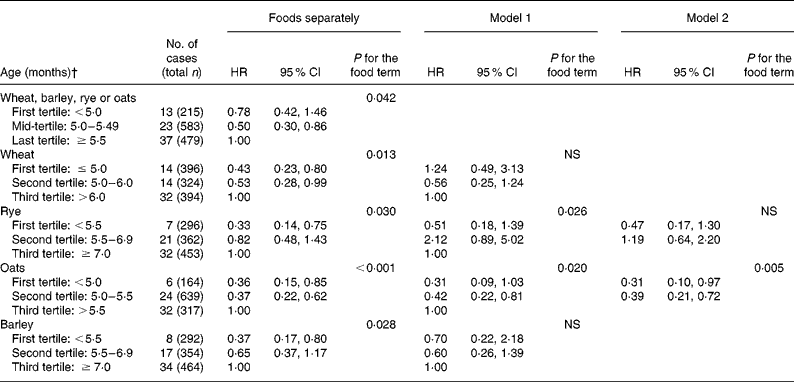
* Cox regression survival model was used in the analysis. Model 1 includes wheat, rye, oats and barley and model 2 includes rye and oats. In addition, both of the models are adjusted for parental asthma, rhinitis and atopic eczema, gestational age, maternal age and smoking during pregnancy, mode of delivery, child's sex, study area, presence of atopic eczema during the first 6 months of life, number of siblings and presence of pets at home during the first year of life.
† The variables were categorised into tertiles. In some cases, the same age was reported for many children, which resulted in categories unequal in size. The nearest cut point was always used.
Table 3 Unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and 95 % CI for persistent asthma related to age at introduction of different foods*
(HR and 95 % CI)

* Cox regression survival model was used in the analysis. Model 1 includes fish, egg and oats, model 2 includes fish and oats and model 3 includes oats. In addition, all the models 1–3 are adjusted for parental asthma, rhinitis and atopic eczema, gestational age, maternal age and smoking during pregnancy, mode of delivery, child's sex, study area, presence of atopic eczema during the first 6 months of life, number of siblings and presence of pets at home during the first year of life.
† The variables were categorised into tertiles. In some cases, the same age was reported for many children, which resulted in categories unequal in size. The nearest cut point was always used.
The present study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects/patients were approved by the Ethical Committee of Pirkanmaa Hospital District and the Ethical Committee of Pohjois-Pohjanmaa Hospital District. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects/patients.
Results
Among the children participating, 6·0 % (77 out of 1293) developed persistent asthma and 14·4 % (185 out of 1288) allergic rhinitis by the age of 5 years (Table 1). The age at onset information was not available for two cases with asthma and sixty-four cases with allergic rhinitis. Among the baseline characteristics of the study population, parental rhinitis and the presence of atopic eczema in the child during the first 6 months of life were related to increased risk of persistent asthma (Table 1). Parental asthma and atopic eczema, the presence of atopic eczema in the child during the first 6 months of life and male sex were associated with increased risk of allergic rhinitis and having had a pet in the family during the first year of the life of the child was associated with a reduced risk of allergic rhinitis (Table 1).
Age at introduction of wheat, rye, oats and barley
The age at introduction of wheat, rye, oats and barley was not differentiated during the first year of the study (September 1996–August 1997). Using the combined variable for the age at introduction of these cereals, the hazard ratios (HR) for persistent asthma were decreased (Table 2). When the cereals were studied separately, the age at introduction of oats showed up to be the most important one (Tables 2 and 3). There was no evidence that the introduction of oats during breastfeeding influenced the development of persistent asthma (results not shown).
Age at introduction of fish and egg
Early introduction of fish and egg was related to a decreased risk of persistent asthma (Table 3), but when age at introduction of fish, egg and oats together with potential confounders was introduced to the same model, only oats remained significant (Table 3).
Early introduction of fish was related to a decreased risk of allergic rhinitis (Table 4). Also early age at introduction of wheat, rye, oats or barley was related to the decreased risk of allergic rhinitis, but this association became non-significant after adjustment for fish and potential confounding variables (Table 4). Fish remained significant when adjusted for the before-mentioned cereals and the potential confounders (Table 4).
Table 4 Unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and 95 % CI for allergic rhinitis related to age at introduction of different foods*
(HR and 95 % CI)
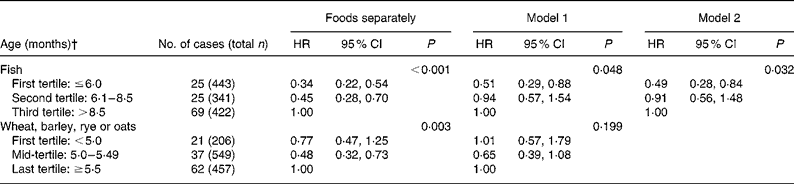
* Cox regression survival model was used in the analysis. Model 1 includes fish and combined cereals (wheat, barley, rye or oats) and model 2 includes fish. In addition, both of the models are adjusted for parental asthma, rhinitis and atopic eczema, gestational age, maternal age and smoking during pregnancy, mode of delivery, child's sex, study area, presence of atopic eczema during the first 6 months of life, number of siblings and presence of pets at home during the first year of life.
† The variables were categorised into tertiles. In some cases, the same age was reported for many children, which resulted in categories unequal in size. The nearest cut point was always used.
Duration of breastfeeding and age at introduction of cow's milk
Duration of total and exclusive breastfeeding was associated with neither asthma (HR (95 % CI) for the lowest and mid-tertiles compared with the highest was 1·35 (0·71, 2·55) and 1·30 (0·69, 2·45) for total breastfeeding, respectively, and 0·93 (0·53, 1·63) and 0·73 (0·38, 1·42) for exclusive breastfeeding, respectively) nor allergic rhinitis (HR (95 % CI) for the lowest and mid-tertiles compared with the highest was 1·10 (0·64, 1·88) and 1·08 (0·61, 1·63) for total breastfeeding, respectively, and 0·96 (0·57, 1·60) and 0·84 (0·48, 1·46) for exclusive breastfeeding, respectively), neither among infants from families with parental asthma, allergic rhinitis or atopic eczema (results not shown). The results regarding exclusive breastfeeding were similar when the information on feeding at the delivery hospital was taken into account (results not shown). Several measures of cow's milk exposure were used: any type of cow's milk exposure, exposure to cow's milk-based infant formulas (hydrolysed and soya-based formulas were excluded) and early exposure in the delivery hospital. The age at introduction of any of these exposures was unrelated to the endpoints.
Effects of parental asthma, allergic rhinitis or atopic eczema on infant feeding
Parental asthma and allergic rhinitis were associated with later introduction of some foods. For example, oats and fish were introduced to the child at the age of 5·8 v. 5·6 months (P = 0·214) and 8·8 v. 8·0 (P = 0·013) months in the families with and without parental asthma, respectively. The respective figures in the families with and without parental allergic rhinitis were 5·7 v. 5·4 months for oats (P = 0·020) and 8·4 v. 7·7 months for fish (P < 0·001). To take into account the possibility that parental asthma, allergic rhinitis or atopic eczema affected the way the parents fed their children, the final analyses were repeated for those families for whom one or both parents were affected by at least one of these three diseases. Among these ‘atopic’ families (n 836), the association between an early age at introduction of oats and a decreased risk of persistent asthma in the child remained significant (HR (95 % CI) for the first and mid-tertiles compared with the latest tertile was 0·31 (0·11, 0·90) and 0·39 (0·23, 0·69), respectively, P for the term = 0·002). Among families in which either or both of the parents had asthma (n 154), there was no significant association between early introduction of oats and development of persistent asthma (HR (95 % CI) for the first and mid-tertiles compared with the latest tertile was 0·28 (0·04, 2·30) and 0·48 (0·17, 1·36), respectively, P for the term = 0·251), although the direction of the association remained the same.
Among the ‘atopic’ families (n 890), an early age at introduction of fish remained significantly associated with a decreased risk of allergic rhinitis in the child (HR (95 % CI) for the first and mid-tertiles compared with the latest tertile was 0·34 (0·20, 0·56) and 0·38 (0·22, 0·64), respectively, P for the term < 0·0001). Among families in which either or both of the parents had allergic rhinitis (n 715), there was also a significant association between early introduction of fish and decreased development of allergic rhinitis (HR (95 % CI) for the first and mid-tertiles compared with the latest tertile 0·35 (0·20, 0·60) and 0·41 (0·23, 0·72), respectively, P for the term < 0·0001).
Discussion
The present findings suggest that early introduction of certain foods into the infant diet is associated with reduced development of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Specifically, early introduction of oats was associated with decreased risk of asthma and early introduction of fish with decreased risk of allergic rhinitis. The main virtues of the present study are a well-defined study population and basing endpoints on standardised and validated international questionnaire(Reference Asher, Keil and Anderson20) adapted for the Finnish situation(Reference Remes, Korppi and Kajosaari21).
In the present study, the collection of dietary data before the development of the endpoints excluded the possibility of differential bias in the selection of subjects or in the reporting of dietary habits. We chose to use predefined categories of the explanatory variables to avoid post hoc or outcome-dependent choices of categorisation. In contrast to previous analyses in similar studies, we have accommodated between-sibling dependence, i.e. taken into account that there were fifty-three sibling pairs from the same families in our series. The strength of the study is that it was not defined as an allergy study, nor an allergy prevention study, but rather as a study focusing on nutrition, diet and type 1 diabetes.
The time window for the first exposure is conspicuously narrow in Finland for some of the supplementary foods introduced in infancy, e.g. rye and oats. This reflects that most Finnish parents comply in this respect closely with the national recommendations on infant feeding conveyed by the staff at the well-baby clinics. The narrow age range would make the analyses less sensitive for detecting any risk or protective effects of early exposure to various foods in relation to asthma or allergic rhinitis.
The reason for the present findings might be reverse causation: the presence of allergic diseases and/or asthma in the family could have influenced infant feeding. Some foods (e.g. fish) were indeed introduced later in families with parental asthma or rhinitis. To exclude this, we first adjusted for parental asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema in the multivariate analysis. Second, we looked at the associations between feeding and the risk of persistent asthma and allergic rhinitis separately in atopic families; third, separately in families with parental asthma or parental allergic rhinitis. The findings remained consistent in all these comparisons. Neither did adjusting for the presence of eczema by 6 months of age change the results.
The present population comprised only children with increased HLA-conferred genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes (15 % of all newborn infants). The evidence concerning whether children with type 1 diabetes have less allergic diseases and asthma than other children is inconsistent(Reference Cardwell, Shields and Carson22, Reference Stene and Joner23). In previous Finnish studies, the prevalence of clinically diagnosed asthma in school-aged children was 4 % and that of allergic rhinitis 16 %, the figures being quite similar to the present findings(Reference Remes, Korppi and Kajosaari21, Reference Remes, Korppi and Remes24). Most importantly, it is quite unlikely a priori that the association between diet and allergic disease would differ between subjects genetically susceptible to type 1 diabetes and the general population.
The dietary exposures measured can act at least partly as proxies of other lifestyle characteristics. In industrialised countries, low educational attainment, young age, single marital status and smoking of the mother, low gestational age, Caesarean section, having a first baby, having a baby of male sex, high number of siblings, and urban environment are factors that associate inversely with total and exclusive durations of breastfeeding and with age at introduction of supplementary foods(Reference Virtanen, Kenward and Erkkola19, Reference Pande, Unwin and Haheim25–Reference Dubois and Girard28). Conversely, allergic diseases and asthma have been inconsistently linked to improved hygiene, decreased or changed exposure to common infections during infancy, small number of siblings, high educational level, Caesarean section, low birth order and day care non-attendance(Reference Strachan29–Reference Pekkanen, Remes and Kajosaari31). The adoption of hygiene practices is influenced to some degree by social, lifestyle and environmental factors(Reference Sherriff and Golding32). Adjustment for several putative confounding factors, however, had minor effects on the present results.
Primary prevention of allergic diseases has on occasion been a subject of heated debate(Reference Muraro, Dreborg and Halken16). Research has focused on high-risk families, i.e. those already including members with allergic diseases. Eliminating foods from maternal diet during pregnancy or lactation or infant diet has been the primary prevention method, combined with the promotion of breastfeeding. The European recommendation strongly advocates exclusive breastfeeding and avoidance of solids for the first 4–6 months of life. We could not demonstrate any association between long duration of total or exclusive breastfeeding and a decrease in the frequency of asthma or allergic rhinitis. This is in agreement with a systematic review concluding that exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months has not been shown to significantly reduce atopic eczema, asthma or other atopic outcome(Reference Kramer and Kakuma10).
There are two interesting observations in the present study. The first is the apparent association between early introduction of oats and protection against persistent asthma. Oats is a commonly used cereal in Finland, as porridge and bread. It is often grouped together with wheat, rye and barley, but it is not closely related to these; e.g. patients with coeliac disease cannot eat wheat, rye or barley, but can use oats(Reference Picarelli, Di Tola and Sabbatella33). Animal and cell experiments suggest that oats may have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties(Reference Boisnic, Branchet-Gumila and Coutanceau34, Reference Davis, Murphy and Brown35). The same is true for fish – the second interesting finding was that early introduction of fish associates with a reduced frequency of allergic rhinitis. Fish oils may modulate inflammatory responses and have inconsistently modified the risk of allergic diseases and asthma(Reference Devereux and Seaton36).
The present findings imply that delaying introduction of oats in infancy may increase the risk of asthma by the age of 5 years at least in children with genetic susceptibility for type 1 diabetes. As shown before, delaying introduction of fish may increase risk of allergic rhinitis. These observations need to be confirmed in other populations.
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the children and parents who participated. We thank The Diabetes Prediction and Prevention research nurses, doctors, nutritionists and laboratory staff for their excellent collaboration over the years. We are also grateful to Sirpa Pohjola and Ilona Kalliomäki for their skilful technical assistance.
Supported by the Academy of Finland (Grants 44 105, 48 724, 80 846, 201988 and 129492), the Finnish Pediatric Research Foundation, the Juho Vainio Foundation, the Yrjö Jahnsson Foundation, Medical Research Funds, Turku, Oulu and Tampere University Hospitals, JDRF, Novo Nordisk Foundation and EU Biomed 2 Program (BMH4-CT98-3314).
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest. The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Contribution of each author. S. M. V., M. K. and J. P. designed the present study. M. G. K. and S. M. V. planned the statistical analysis and S. M. V. analysed the data. S. M. V. wrote the manuscript. C. K.-K. and U. U. participated in preparing and interpreting the data. P. P. and T. H. participated in interpreting the data. O. S., J. I., R. V. and M. K. were responsible for the clinical study. All authors participated in drafting and revising of the manuscript, and approved the final version to be published.






