Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is a persistent concern in the United States, with an estimated ∼462,000 cases in 2017. Reference Guh, Mu and Winston1 The rates of CDI recurrence and community-associated CDI remained steady over the last decade despite decreases in the rates of healthcare-associated CDI and CDI-related mortality. Reference Guh, Mu and Winston1 Moreover, ∼25% of all patients with an initial episode of CDI experience recurrent CDI (rCDI), and ∼50% of patients who develop rCDI go on to suffer a future episode. Reference Smits, Lyras, Lacy, Wilcox and Kuijper2,Reference Lessa, Mu and Bamberg3 The impact of CDI is not solely on the digestive tract; it is associated with increased rates of subsequent sepsis, colectomy, and a psychiatric burden. Reference Feuerstadt, Boules and Stong4,Reference Lurienne, Bandinelli, Galvain, Coursel, Oneto and Feuerstadt5
The elderly population has a higher incidence of CDI than the younger population, with ∼500 cases per 100,000 persons in patients aged ≥ 65 years, compared to ∼90 cases per 100,000 persons among all adults in the United States. Reference Pechal, Lin, Allen and Reveles6,Reference Balsells, Shi and Leese7 Advanced age (≥65 years) is considered one of the most important nonmodifiable risk factors for CDI, with adults ≥65 years having a 63% higher risk of recurrence than younger persons, and each additional year of age increases the risk. Reference Deshpande, Pasupuleti and Thota8,Reference Nour Abou Chakra and Pepin9 The elderly are 3 times more likely to develop complicated CDI (eg, fulminant colitis, intensive care unit admission, CDI complication) than younger patients. Reference Nour Abou Chakra and Pepin9
Real-world data are more applicable to practicing clinicians in comparison to clinical trial data; however, studies evaluating clinical outcomes for elderly patients with CDI and rCDI based on actual claims data are limited. Additionally, clinical data from randomized controlled trials evaluating outcomes of older patients with CDI and rCDI are lacking. Reference Tariq, Hayat, Pardi and Khanna10,Reference Feuerstadt, Aroniadis and Svedlund11 Real-world data on outcomes of CDI and rCDI in a younger cohort have recently been reported utilizing commercial health insurance claims, showing a substantial burden of cost and clinical complications. Reference Feuerstadt, Boules and Stong4,Reference Feuerstadt, Stong, Dahdal, Sacks, Lang and Nelson12 In a previous study of the 2008–2010 Medicare 5% sample, patients who suffered CDI had higher baseline comorbidity scores, rates of hospitalizations, and antibiotic use than a propensity-matched group. Reference Shorr, Zilberberg, Wang, Baser and Yu13 However, little is known about the relative clinical experiences of older adults who suffer only a primary CDI event versus those who suffer 1 or multiple recurrences. In this study, we focused on an elderly population using 100% sample of Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) data covering a broad national population with robust longitudinal follow-up to describe 12-month recurrence rates, treatments, complications, and procedures in patients with primary and recurrent CDI.
Methods
Study design and patient identification
A retrospective, descriptive, cohort study was conducted to assess treatment patterns, healthcare resource utilization, and selected clinical outcomes for patients with CDI and rCDI using data from the 100% Medicare FFS claims database between January 1, 2009, through December 31, 2017.
The study included patients who were ≥ 65 years of age and had a first (index) CDI diagnosis (corresponding to disease onset) during the study identification period from January 1, 2010, to December 31, 2016, and continuous enrollment in Medicare Parts A, B, and D during 12 months before and 12 months after the index period. By definition, patients did not have any CDI claims within the 12 months prior to the index CDI episode. An episode of CDI was identified based on either an inpatient stay attributed to a CDI diagnosis code (Supplementary Table 1) or an outpatient medical claim with a CDI diagnosis code plus confirmation of an appropriate CDI treatment including vancomycin, fidaxomicin, metronidazole, rifaximin, bezlotoxumab, or fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) (Supplementary Table 1). Patients who died or changed enrollment from FFS to a Medicare Advantage plan during the follow-up period could not contribute a full 12 months of observation and therefore were not included in the study cohorts. The clinical experience of patients who died is expected to be distinctly different than that of patients who survived and, as such, a separate study with a different analytical design will be published on that cohort of patients with CDI.
To standardize the start date of events across cases, a CDI episode began on the date of the first CDI medical claim and included consecutive medical claims with a diagnosis of CDI and prescription fills for medications commonly used to treat CDI. A CDI episode end date was defined as the last day of a 14-day CDI claim-free period (eg, 14 days after the last CDI prescription dose was administered (Fig. 1). An episode of rCDI was defined as a second or subsequent episode of CDI, using the same criteria for the index CDI episode, that started within an 8-week window following the 14-day CDI-claim-free period (Fig. 1). Multiple rCDI episodes could be captured up to 12 months following the index CDI date. CDI events that occurred later than each 8-week window after the claim-free period were not counted as rCDI (in accordance with rCDI definition from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 14 ) but as new infections, and these were not included in this analysis to avoid misclassification.
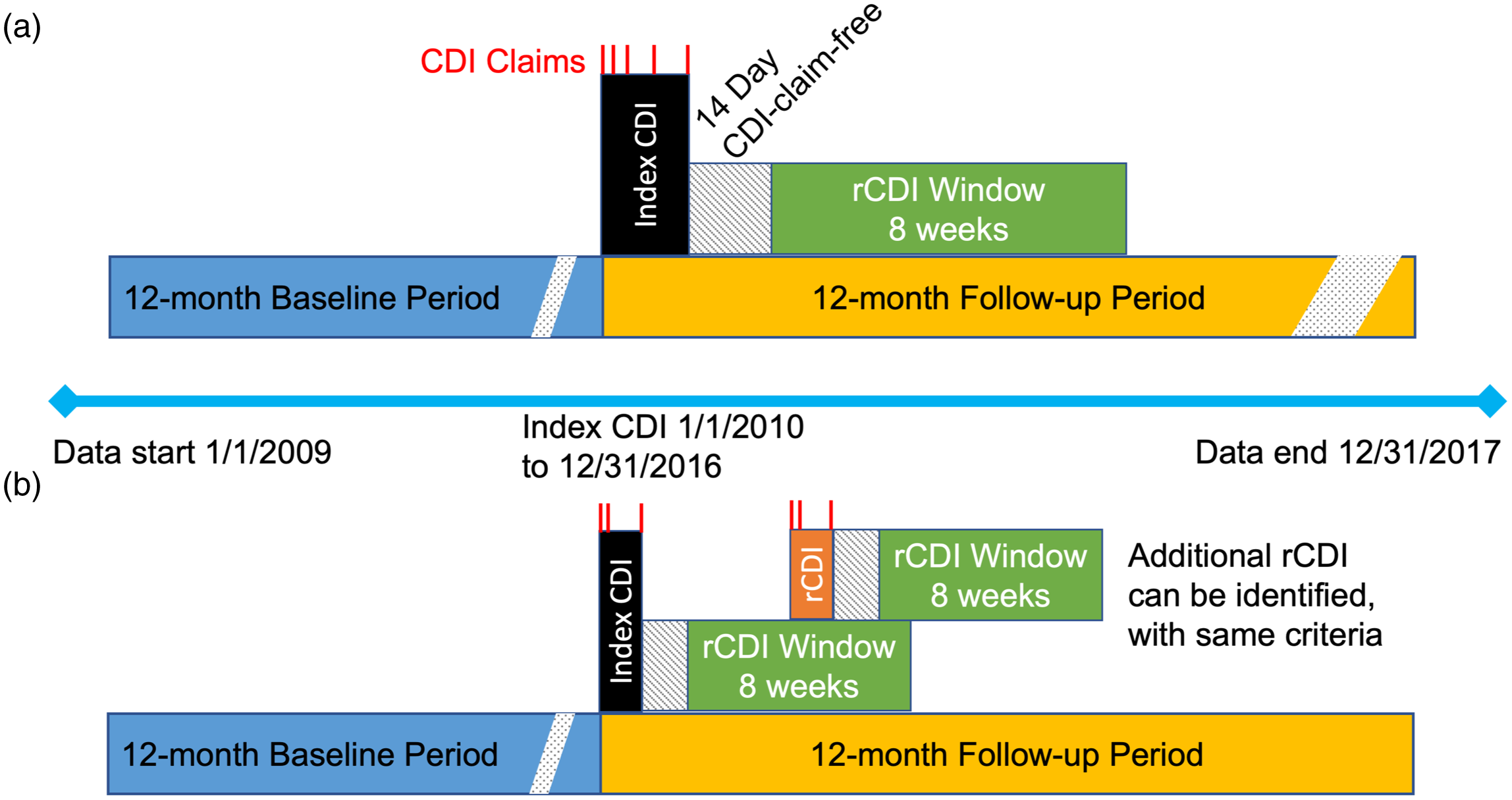
Fig. 1. Study design. (a) Definition of index CDI episode, including CDI claims (red), the 14-day CDI claim-free period after last CDI claim, and 8-week period to identify rCDI. (b) Definition of rCDI episodes. The rCDI episode (orange) indicates a hypothetical point at which the first rCDI episode occurs during the 8-week window after the index CDI claim-free period. Following this first rCDI episode, a new 14-day claim-free period occurs plus a new window for a subsequent rCDI episode. Multiple rCDI could occur after an index CDI event in this manner, until 12 months following the index CDI date.
Demographic and baseline clinical characteristics were evaluated for each individual, including age, sex, geographical region, Charlson comorbidity index (CCI), comorbid conditions, medication exposure (ie, any use of gastric acid-suppressing agents, antimicrobials, or immunosuppressant agents), and medical procedures and treatments (eg, transplants, gastrointestinal surgery, enteral feeding, or chemotherapy).
Data sources
Data sources were (1) the 100% Medicare FFS claims database, containing health service utilization data (inpatient, outpatient, demographic, and enrollment information) for Medicare beneficiaries with traditional Medicare FFS whose providers were paid directly by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and (2) the 100% Prescription Drug Event data set, which includes prescription drug claims for Medicare Part D (see the Supplementary Material for details).
Pre-index period
Healthcare resource utilization (HRU) for the pre-index period was quantified, including all-cause hospitalizations, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient visits. HRU for the 12-month pre-index period was separately reported as 0–6 months pre-index (ie, the 6 months immediately prior to the index CDI) and 7–12 months pre-index. The 0–6 months pre-index period captured the precipitating healthcare encounters of CDI, while the 7–12 months pre-index period represented the baseline health characteristics of the cohorts. To serve as a benchmark reference, select baseline and demographic data (ie, age, sex, census region, and select medical comorbidities) for the national Medicare population were extracted for all beneficiaries who were enrolled in Medicare FFS with medical and pharmacy benefits for at least 6 months in 2016.
Post-index outcomes
The number of CDI and rCDI episodes, surgical procedures (eg, subtotal colectomy or diverting loop ileostomy), and all-cause complications (eg, sepsis or incident psychiatric condition) were observed over the 12-month follow-up period, and the data were stratified by cohorts representing the total number of rCDI episodes (ie, no rCDI, 1 rCDI, 2 rCDI, or ≥3 rCDI). The timing of the first surgical procedure and all sepsis instances with respect to the recurrence time window were reported.
Data analysis
Descriptive analyses of the demographic characteristics and clinical outcomes data were performed. For categorical variables, counts and percentages were used. For continuous variables, measures of central tendency were calculated, reported as mean (standard deviation, SD). All analyses were conducted with SAS version 9.4 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Results
Demographics
In total, 268,762 patients with an index CDI were included (Table 1). Of this group, 65.3% had no rCDI; 14.2% had 1 rCDI; 8.5% had 2 rCDI; and 12.0% had ≥3 rCDI. The mean age of patients with CDI was 78.3 years (SD, 7.96), 69.0% were female, and the mean CCI was 5.1 (SD, 3.4). As a benchmark, in the national Medicare cohort of 4.8 million beneficiaries (including the CDI subgroup), the mean age was 75.4 years, 59.1% were female, and the mean CCI was 4.0 (SD, 3.8).
Table 1. Patient Characteristics, CDI-specific Risk Factors, and Healthcare Resource Utilization During 12-month Pre-index Period

Note. CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CVD, cerebrovascular disease; ED, emergency department; GI, gastrointestinal; PVD, peripheral vascular disease; SD, standard deviation.
a Select reference data were obtained from the entire population of patients who were enrolled in Medicare FFS with medical and pharmacy benefits for at least 6 months between January 1, 2016 and December 31, 2016.
Recurrences
Of the entire CDI cohort of 268,763 patients, 93,208 (34.7%) had at least 1 recurrence. Of those who experienced 1 recurrence, 59.1% had a second recurrence (55,045 of 93,208 patients). Of those who had 2 recurrences, 58.4% had ≥3 recurrences (32,147 of 55,045 patients). Among patients in the study cohort who had a CDI event after the index episode that was outside a recurrence window (classified as having another CDI occurrence), 21.2% (57,071) had 1 occurrence, 12.1% (32,435) had 2 occurrences, and 30.2% (81,273) had ≥3 occurrences. Recurrences and occurrences were counted separately, and a patient who had 1 recurrence could have, at a later date, experienced an occurrence that fell outside the recurrence window.
Across the entire study population, the mean time from the index CDI to first recurrence was 30.3 (SD, 14.0) days. Mean time to the next recurrences were slightly longer, with 36.9 (SD, 15.1) days between the first rCDI to the second rCDI, and 44.0 (SD, 14.7) days between the second rCDI to the third rCDI.
Pre-index exposures
In the 12 months prior to the index episode of CDI, >83% of patients in the rCDI cohorts received antimicrobials for other indications besides CDI, and more than half received gastric acid suppressing medications (Table 1). Antimicrobial use was high across all cohorts, approaching 90% in the ≥3 rCDI cohort. The proportion of patients with pre-index transplants (solid organ or hematopoietic stem cell) in the ≥3 rCDI cohort was 4 times higher than in the 2 rCDI cohort and 9 times higher than in the no-rCDI cohort.
Healthcare resource utilization (HRU) was higher during the 6 months immediately before the CDI index episode compared to 7–12 months before the index episode (Table 1). Comparing the 7–12 month pre-index period with the 0–6 month pre-index period, we detected trends for a higher proportion of patients with ≥1 hospital admission (55.1% vs. 27.5%), ≥1 ED visit (41.3% vs 27.4%), and ≥4 outpatient visits (86.2% vs 78.0%). In the 0–6 month pre-index period, the highest rates of inpatient admission and ED visits occurred in the ≥3 rCDI cohort, with 44.8% having at least 1 ED visit.
Post-index procedures
In total, 6.0% of patients with rCDI underwent all-cause subtotal colectomy and 1.1% of patients underwent all-cause diverting loop ileostomy during the 12-month follow-up period. Among the first bowel surgeries observed after a CDI episode, 51.4% of subtotal colectomies and 65.9% of diverting loop ileostomies occurred after the first or subsequent rCDI episode, with the remaining surgeries occurring after the index CDI (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2. Timing of the first bowel surgery. All-cause subtotal colectomy was performed on 6.0% of all patients with CDI and was most commonly performed after the index CDI episode. All-cause diverting loop ileostomy was performed on 1.1% of all patients with CDI and was most commonly performed after the fourth or subsequent rCDI episode.
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) was performed in 1.1% of the overall study population including 0.4% (n = 638) of those in the no rCDI cohort, 1.1% (437) of the 1 rCDI cohort, 2.1% (492) of the 2 rCDI cohort, and 4.5% (1,454) of the ≥3 rCDI cohort. Multiple FMT were performed in 326 (10.8%) of 3,021 patients.
Post-index clinical complications
Incident psychiatric conditions were diagnosed in a notable proportion of patients with CDI or rCDI, ranging from 16.2% to 18.2% of each rCDI cohort, with most of these patients showing a new diagnosis for anxiety, delirium, or depression (Table 2).
Table 2. All-Cause Procedures and Complications During 12-Month Post-Index Follow-up

Note. rCDI, recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection.
a Incident diagnosis: no prior claim for the condition in the 12-month pre-index window.
During the 12-month follow-up, 80,502 patients (30.0%) with CDI or rCDI experienced 1 or more all-cause sepsis episodes, and sepsis occurred in 27.0% of patients with no recurrence, compared to 35.5% of patients with ≥1 recurrence (Table 2). Sepsis was also evaluated by timing, with all instances captured after each CDI episode. After each CDI episode, ∼1 in 5 patients had a documented sepsis event (Fig. 3).

Fig. 3. Proportion of patients experiencing sepsis, by recurrence cohort. During the 12-month follow-up, 80,502 patients (30.0%) with CDI or rCDI experienced sepsis. All instances of sepsis were counted and, therefore, 1 patient could have had multiple sepsis events during follow-up. Sepsis events after the fourth or later CDI recurrence were not reported.
Discussion
More than one-third of elderly patients with CDI in this 100% Medicare FFS population had at least 1 recurrence after an initial episode, and ∼58% of patients with 1 or 2 rCDIs had an additional recurrence(s). The high recurrence rates were likely due to the older age of the population, other patient risk factors associated with older age such as comorbid conditions and recent medical treatments and procedures, the data source reflecting a broad range of care settings, and a long follow-up window to tally recurrence(s) versus a shorter 30-day window used in other analyses. The time to recurrence across all 3 rCDI cohorts was ∼1 month in our study, similar to data reported elsewhere. Reference Feuerstadt, Stong, Dahdal, Sacks, Lang and Nelson12,Reference Kelly15 This 4-week period presents a known “window of vulnerability” when it is hypothesized that the gut microbiome is reconstituting and ideally fighting off the infection, and when modifiable underlying risk factors for recurrence can be altered.
The rates of organ, tissue, and/or blood cell transplantation prior to the initial episode of CDI trended higher in those with more recurrences. In a retrospective study of patients receiving solid-organ or hematopoietic stem cell transplants, ∼15%–20% developed CDI after transplantation, with most infections occurring within 30 days of the transplant (median follow-up, 1.9 years). Reference Ilett, Helleberg and Reekie16 In patients receiving a liver transplant, CDI was associated with higher in-hospital mortality than those not developing this infection (5.5% vs 3.2%, P < .001). Reference Ali, Ananthakrishnan, Ahmad, Kumar, Kumar and Saeian17 CDI carried a 2-fold increased risk of graft loss in solid-organ transplantation, compared with patients who did not develop this infection. Reference Cusini, Béguelin and Stampf18,Reference Li, Trac, Husain, Famure, Li and Kim19 After organ transplantation, patients are at increased risk for developing CDI; this complication remarkably increases the risk for poor outcomes including mortality and loss of the transplanted organ.
Sepsis is more common in older adults, likely due to age-related changes that leave the elderly more susceptible to infection, and it is a common complication of CDI. Reference Feuerstadt, Boules and Stong4,Reference Rowe and McKoy20,Reference Lee, Hsu and Lee21 During follow-up of our elderly population, 35% of patients with rCDI experienced all-cause sepsis. In a retrospective, multicenter study of 440 patients hospitalized for CDI (mean age, 74 years), the 30-day mortality rate for patients with CDI who developed bloodstream infections was 38.9%. Reference Falcone, Russo and Iraci22 In a separate study, patients who had an initial hospitalization for CDI had a 10.7% adjusted probability of 90-day readmission for sepsis, compared with a 4.1% probability in patients who had an initial hospitalization for noninfectious reasons. Reference Prescott, Dickson, Rogers, Langa and Iwashyna23 Among Medicare FFS beneficiaries with sepsis, 6-month mortality rates were 35%–60%, depending on the severity of illness and complications. Reference Buchman, Simpson and Sciarretta24 Sepsis in the elderly population is also associated with substantial morbidity, including cognitive impairment and reduced ability to carry out activities of daily living. Reference Rowe and McKoy20 From this claims analysis, we were unable to determine whether CDI was the cause of sepsis. Despite a clear association between CDI and sepsis, the mechanisms have not been elucidated. Proposed mechanisms include the disruption of the microbiota, and the breakdown of the epithelial barrier after exposure to CDI toxins. Reference Baggs, Jernigan, Halpin, Epstein, Hatfield and McDonald25 As a result of the high mortality rates associated with sepsis and our exclusion of any patient who died for any reason during 12-month follow-up, our rates of CDI and rCDI may have been underestimated.
In patients with the most severe forms of CDI, surgical intervention is needed as a life-saving measure. In our cohort, subtotal colectomy or diverting loop ileostomy was performed on a small but notable proportion of patients, with some performed after the index CDI episode. As a result of the severity of the CDI that requires surgical intervention and the morbidity surrounding these surgical procedures, mortality following partial or total colectomy is known to be high, averaging ∼50% and ranging from 30% to 80%, depending on the patient population and the healthcare setting. Reference Kulaylat, Kassam, Hollenbeak and Stewart26,Reference Chan, Kelly, Helme, Gossage, Modarai and Forshaw27 Individuals aged >80 years had a significantly higher risk of 30-day mortality following colectomy for CDI. Reference Kulaylat, Kassam, Hollenbeak and Stewart26 Increased patient medical comorbidity is also a significant predictor of worse outcomes, including 30-day mortality, morbidity, and severe morbidity, after colectomy following CDI. Reference Venkat, Pandit, Telemi, Trofymenko, Pandian and Nfonsam28
The burden of CDI on patients is not just physical. A survey of 350 patients self-reporting CDI showed that 15% of those with current CDI and 20% of those with past CDI reported depression, and of those patients with past CDI who reported depression, 91.3% reported that CDI increased the activity or severity of their depression. Reference Lurienne, Bandinelli, Galvain, Coursel, Oneto and Feuerstadt5 A multinational health and wellness survey including 2,410 individuals with CDI showed those with past CDI had significantly lower scores for mental health compared to those with no CDI, and those with current CDI had significantly lower mental health scores than those with past CDI. Reference Heinrich, Harnett, Vietri, Chambers, Yu and Zilberberg29 This impact was also seen in our study; 16%–18% of the cohorts had newly occurring psychiatric diagnoses and related visits following index CDI. This finding emphasizes that CDI affects patients in many ways, including a significant emotional burden. The rates described in our study may be underestimates because many psychiatric illnesses in elderly individuals remain undiagnosed. Reference Park and Unützer30,Reference Bor31 An interplay between gut dysbiosis and changes in neurological function may play a role in psychiatric illness seen after CDI. Reference Rogers, Keating, Young, Wong, Licinio and Wesselingh32 CDI may be only a marker of dysbiosis and not be causally related to mental illness. Alternatively, rCDI may precipitate a posttraumatic stress disorder, with a fear of recurrence and future antimicrobial needs. Given the complicated interplay between so many variables, additional research to establish the connection between psychiatric disease and CDI is required.
FMT is a guideline-recommended therapeutic for patients with multiple CDI recurrences who have failed antibiotic interventions. Reference McDonald, Gerding and Johnson33,Reference Kelly, Fischer and Allegretti34 Since 2013, use of FMT for CDI has also been enabled by an enforcement discretion from the FDA. 35 Medicare provides coverage for FMT, but the level of reimbursement appears to be insufficient. Reference Joseph, Saha and Greenberg-Worisek36,37 FMT was performed in 1.1% of all patients with CDI in the study, reflecting the policy impact of the prevailing science, the US regulatory body, and the primary payer. Our study revealed that 80.7% of the first FMT procedures were performed after a recurrent episode. A previous study of commercial claims in the United States showed that 0.7% of adults <65 years with CDI received FMT. Reference Feuerstadt, Boules and Stong4 The use of FMT earlier in the treatment paradigm would likely decrease the downstream costs associated with future recurrence and burden of disease.
We designed our analysis to collect outcomes data using a full 12-month follow-up to ensure we can depict the clinical burden clearly, and we therefore did not include patients who died or changed enrollment from FFS to a Medicare Advantage plan during the follow-up period. The clinical experience of patients who died is expected to be distinctly different than that of patients who survived and, as such, a separate study with a different analytical design will be published on that cohort of patients with CDI. Patients who died within the recurrence window after an initial CDI episode did not have the chance to experience an rCDI, which may have led to underestimation of the true rates of CDI and rCDI in this study. Medicare’s coverage policy is narrower than that of commercial insurance; therefore, a range of services not covered by Medicare could have been provided and paid for by the patient or supplemental insurance, which would not be accounted for in our analysis. During the study period, Medicare FFS included >70% of all Medicare beneficiaries. Reference Jacobson, Freed, Damico and Neuman38 Although the data are generalizable to the Medicare FFS population, some Medicare beneficiaries self-select to join a Medicare Advantage plan and our study findings may not fully represent that cohort. For example, previous studies have shown that beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans were more likely female, Hispanic, less educated, and have fewer chronic health conditions than beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare FFS. Reference Miller, Decker and Parker39 Finally, the question of whether patients are experiencing a recurrence of the same infection versus a new “reinfection” when they represent is always considered. In clinical practice, we are unable to differentiate these 2 scenarios; here, we assumed that any patient re-presenting clinically with CDI within 8-weeks of completion of therapy has a “recurrence,” thereby following the clinical norms of practice.
The strengths of our study include the use of a large, representative sample of elderly patients with CDI and rCDI in the United States from 100% Medicare claims data that include medical and prescription claims from all settings of patient care. In this population, health insurance coverage is not employment related, thus leading to a robust longitudinal follow-up and allowing for a 12-month pre-index period to observe the very different healthcare usage during the 6 months immediately prior to the primary CDI compared with earlier (baseline) health status.
Patients with CDI and rCDI experience a significant clinical burden, which could lead to a poor quality of life. These results may inform future cost–benefit analyses of older patients who experience CDI and survive. Future studies could be conducted to explore statistical associations between the CDI cohort and the national Medicare population, or between those who experienced only the primary CDI versus those who experienced a recurrence. One of the best strategies to mitigate the deleterious effects of CDI in older individuals is to focus on CDI prevention. Reference Rauseo, Olsen, Reske and Dubberke40 Reduction of rCDI is an important step to reduce the burden of this disease and its related complications in older adults.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/ash.2022.2
Acknowledgments
Medical writing and editorial support were provided by Agnella Izzo Matic, PhD, CMPP (AIM Biomedical, LLC). The authors thank Alexis Parente, Takara A. Scott, Mena Boules, Laura Stong and Sudhir Unni for their contribution to study design and analysis.
Financial support
The study was funded by Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
Conflicts of interest
Drs. Nelson and Dahdal were employees of Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc at the time of the study. Dr. Teigland is an employee of Avalere Health and provided consulting services to Ferring Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Feuerstadt has served on the speaker’s bureau for Merck and Co, and he has served as a consultant for Ferring Pharmaceuticals, SERES Therapeutics, and Roche Pharmaceuticals.







