In this article I begin with an outline of the connection between theological concepts related to the person of the Gnostic Christian Saviour and the ritual practice of Gnostic Christian groups. After setting the scene in this general way, I look specifically at the Gospel of Philip, investigating the connection between the description of the rebirth of the Saviour at the Jordan and the rebirth of the Gnostic in the ritual of the bridal chamber.
The Nag Hammadi corpus, to which the Gospel of Philip belongs, contains many texts which may be identified as Gnostic Christian, partly because of the fact that, in these texts, the key figure of the Saviour or Revealer is identified as Jesus or Christ. The work that Jesus performs in the world for the Gnostics is revelation, for the most part, rather than redemption in the sense in which mainstream Christianity identified his activity. His revelation may involve imparting secret knowledge, especially during that time prior to his final ascent into the heavenly region of light (for those texts which are closely aligned with the mainstream Christian pattern of descent and several stages of ascent for Jesus), but it must be generally categorised as activity designed to awaken the Gnostic to the insight (gnosis) which this person already possesses.

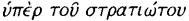 (p.330 Reiske). Markland is commonly reckoned the greatest critic of the eighteenth century apart from Bentley, and one would have supposed that editors of Juvenal would have thought that the very dust of his writings was gold. In fact, however, these annotations have never been published in their entirety, and it seems time that they should be. Some of the textual proposals have been made independently by other scholars; some, to the best of my knowledge, have never been made by anyone else and now see the light for the first time. Some, as one would expect, are brilliant and incisive; others are strikingly bad. One must remember that these are the thoughts which passed through his mind as he was reading Juvenal in a very second-rate edition, and no doubt he jotted them down for future consideration. No one will think the less of a critic because his marginalia and anecdota contain material which later reflection would have rejected.
(p.330 Reiske). Markland is commonly reckoned the greatest critic of the eighteenth century apart from Bentley, and one would have supposed that editors of Juvenal would have thought that the very dust of his writings was gold. In fact, however, these annotations have never been published in their entirety, and it seems time that they should be. Some of the textual proposals have been made independently by other scholars; some, to the best of my knowledge, have never been made by anyone else and now see the light for the first time. Some, as one would expect, are brilliant and incisive; others are strikingly bad. One must remember that these are the thoughts which passed through his mind as he was reading Juvenal in a very second-rate edition, and no doubt he jotted them down for future consideration. No one will think the less of a critic because his marginalia and anecdota contain material which later reflection would have rejected.