No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 August 2014
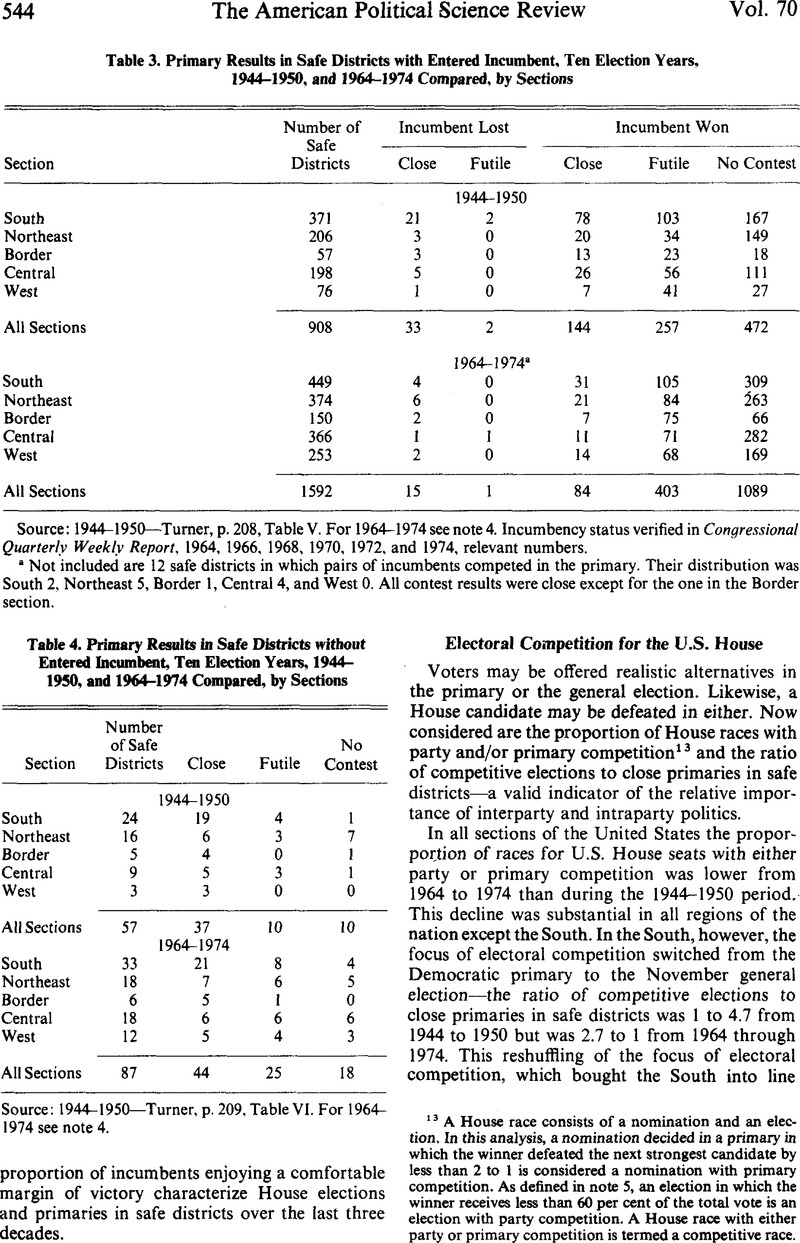
13 A House race consists of a nomination and an election. In this analysis, a nomination decided in a primary in which the winner defeated the next strongest candidate by less than 2 to 1 is considered a nomination with primary competition. As defined in note 5, an election in which the winner receives less than 60 per cent of the total vote is an election with party competition. A House race with either party or primary competition is termed a competitive race.
14 As in Key, V. O. Jr., “The Erosion of Sectionalism,” Virginia Quarterly Review, 31 (Spring, 1955), 161–179Google Scholar.
15 Schumpeter, p. 271. The comments of Milton C. Cummings, Jr., Alan J. Eade, Robert L. Peabody, Stephen V. Stephens, and two anonymous Review referees are gratefully acknowledged.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.