Article contents
Self-Aligning Hot-Wire Probe
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 July 2016
Summary:—
This note describes how a single constant temperature hot wire may be used for measurements of direction, velocity and turbulence in a two-dimensional flow. The wire probe is rotated by a servo motor which automatically sets the wire with its axis either in the stream direction or normal to the flow. The accuracy of setting the wire in the direction of the stream is about 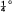 , and across the stream is about 1°. If the higher accuracy is demanded the velocity and turbulence measurements require a second setting of the probe, at 90° to the previous one. When less precision is acceptable, the angle, velocity and turbulence measurements may be taken at the single setting, normal to the stream.
, and across the stream is about 1°. If the higher accuracy is demanded the velocity and turbulence measurements require a second setting of the probe, at 90° to the previous one. When less precision is acceptable, the angle, velocity and turbulence measurements may be taken at the single setting, normal to the stream.
- Type
- Technical Notes
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Royal Aeronautical Society 1967
References
- 3
- Cited by


