Article contents
An Algorithm for the Description of White and Characteristic Tube Spectra (11 ≤ Z ≤ 83, 10keV ≤ Eo ≤ 50keV)
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 March 2019
Extract
Kramers described the cross section of electron interaction with target atoms of atomic number Z by
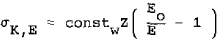
where Eo is the kinetic energy of impinging electrons, and E o S) the energy of x-ray photons of the continuum, Smith et al modified this equation, introducing an exponent x, so that
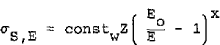
We applied the cross-section σS, E to the evaluation of experimental results. The evaluation of the measured spectral responses of the x-ray signals nE was performed by
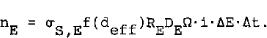
where f(deff) describes the absorption of x-rays of energy E in the target, RE accounts for backscattering of electrons, DE quantifies the efficiency of x-ray detection within the solid angle Ω.
- Type
- X. Mathematical Methods in X-Ray Spectrometry (XRS)
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © International Centre for Diffraction Data 1991
References
- 2
- Cited by


