Article contents
A Self-Normalized Central Limit Theorem for Markov Random Walks
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 January 2016
Abstract
Motivated by the study of the asymptotic normality of the least-squares estimator in the (autoregressive) AR(1) model under possibly infinite variance, in this paper we investigate a self-normalized central limit theorem for Markov random walks. That is, let {Xn, n ≥ 0} be a Markov chain on a general state space X with transition probability P and invariant measure π. Suppose that an additive component Sn takes values on the real line 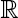 , and is adjoined to the chain such that {Sn, n ≥ 1} is a Markov random walk. Assume that Sn = ∑k=1nξk, and that {ξn, n ≥ 1} is a nondegenerate and stationary sequence under π that belongs to the domain of attraction of the normal law with zero mean and possibly infinite variance. By making use of an asymptotic variance formula of Sn / √n, we prove a self-normalized central limit theorem for Sn under some regularity conditions. An essential idea in our proof is to bound the covariance of the Markov random walk via a sequence of weight functions, which plays a crucial role in determining the moment condition and dependence structure of the Markov random walk. As illustrations, we apply our results to the finite-state Markov chain, the AR(1) model, and the linear state space model.
, and is adjoined to the chain such that {Sn, n ≥ 1} is a Markov random walk. Assume that Sn = ∑k=1nξk, and that {ξn, n ≥ 1} is a nondegenerate and stationary sequence under π that belongs to the domain of attraction of the normal law with zero mean and possibly infinite variance. By making use of an asymptotic variance formula of Sn / √n, we prove a self-normalized central limit theorem for Sn under some regularity conditions. An essential idea in our proof is to bound the covariance of the Markov random walk via a sequence of weight functions, which plays a crucial role in determining the moment condition and dependence structure of the Markov random walk. As illustrations, we apply our results to the finite-state Markov chain, the AR(1) model, and the linear state space model.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- General Applied Probability
- Information
- Copyright
- © Applied Probability Trust
References
- 1
- Cited by


