Ground penetrating radar (GPR) has been extensively used in glaciology to infer glacier's ice thickness, liquid water content, water drainage pathways, and other properties. The interpretation of such GPR data is not always straightforward and for temperate glaciers, the signal is often affected by strong scattering and attenuation. It has often been suggested that such effects originate from englacial water inclusions, since water and ice have a large contrast in their di-electric permittivity. To investigate such effects quantitatively, we perform an extensive numerical modeling study of GPR signals. By exploring how different liquid water contents (LWC) and water-inclusions size affect the GPR signal, we show that their effects are much larger than the potential presence of a wet snowpack or a heterogeneous distribution of ice permittivity. In particularly, we show that the presence of such water inclusions is a necessary and sufficient condition for reproducing the typical characteristics of GPR data acquired in the field. Further, we find that for 25 MHz GPR antennas, a bulk LWC $\gtrsim$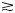 0.2%, associated with decimeters-scale water inclusions already limits bedrock detectability for ice thicknesses $\gtrsim 100$
0.2%, associated with decimeters-scale water inclusions already limits bedrock detectability for ice thicknesses $\gtrsim 100$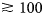 m. Since these values are typical for Alpine glaciers, they clarify why the quality of GPR data is often poor in such environments.
m. Since these values are typical for Alpine glaciers, they clarify why the quality of GPR data is often poor in such environments.