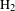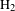Based on realistic numerical simulations of the three-dimensional
time-dependent Schrödinger equation describing a hydrogen
atom interacting with a strong electromagnetic field, the influence
of the magnetic component is studied. The same computational
techniques can be applied to the case of strong field
photoionization as well as to the case of ionization by an incident
relativistic heavy ion. One of the main consequences, in the
strong-laser-field case, is the presence of true even harmonics
of the incoming field. In the heavy ion impact, the asymmetry
of the wave function reveals the importance of the nondipole
nature of the interaction.
 $\text{H}_{2}$ in two-color laser fields
$\text{H}_{2}$ in two-color laser fields