In situ liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (LC-TEM) is an innovative method for studying the processes involved in the formation of crystals in liquids. However, it is difficult to capture early stages of crystallization because of the small field of view and the unfavorable changes in sample composition resulting from electron-beam radiolysis. Nevertheless, if the radiolysis required to induce the crystallization of a sample could be controlled in LC-TEM, this would be advantageous for observing the crystallization process. Here, we examined this possibility by using a mixture of sodium chlorate (NaClO3) and acetone in the LC-TEM. The electron beam induced the formation of dendritic crystals in a saturated acetone solution of NaClO3; moreover, these crystals consisted of sodium chloride (NaCl), rather than NaClO3, suggesting that chloride ions (Cl−), which were not present in the initial solution, were generated by radiolysis of chlorate ions 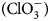 ${\rm ( ClO}_3^- )$. As a result, the solution then supersaturated with NaCl because its solubility in acetone is much lower than that of NaClO3. The combination of radiolysis and a solvent in which a solute is much less soluble is potentially useful for establishing crystallization conditions for materials that are difficult to crystallize directly in LC-TEM experiments.
${\rm ( ClO}_3^- )$. As a result, the solution then supersaturated with NaCl because its solubility in acetone is much lower than that of NaClO3. The combination of radiolysis and a solvent in which a solute is much less soluble is potentially useful for establishing crystallization conditions for materials that are difficult to crystallize directly in LC-TEM experiments.