Introduction
Despite the advances in dental care, edentulous cases remain a significant issue, especially among elderly individuals. According to the Brazilian Oral Health Survey, 45% of elderly persons need to use complete dentures (Soares et al., Reference Soares, Freire and Reis2018). Denture-related stomatitis is considered the most common disease to afflict denture wearers and it has been shown to affect approximately 50% of this specific population (Figueiral et al., Reference Figueiral, Fonseca, Lopes, Pinto, Pereira-Leite and Sampaio-Maia2015). The long-term use of dentures, associated with poor oral and prosthesis hygiene, increases the risk of development of stomatitis, which is characterized as an inflammatory disorder of the palatal mucosa usually caused by the proliferation of Candida spp., mainly Candida albicans (Thilakumara et al., Reference Thilakumara, Jayatilake, Pallegama and Ellepola2017). The competence of C. albicans to colonize the mouth mucosa and, subsequently, to induce a successful infectious process is closely related to the production of several virulence factors, including surface adhesins, extracellular enzymes and biofilm formation (Mello et al., Reference Mello, Ramos, Braga-Silva, Branquinha and Santos2017; Schaller et al., Reference Schaller, Borelli, Korting and Hube2005; Willaert, Reference Willaert2018), as well as the host immune status (Swidergall, Reference Swidergall2019).
Objectives
In the present study, we have investigated the antifungal susceptibility profiles as well as the production of potential virulence attributes in oral isolates of Candida albicans recovered from denture-related stomatitis of elderly patients attended at the dentistry clinic of a Brazilian University (Universidade Vale do Rio Doce – UNIVALE, Minas Gerais State, Brazil).
Methods
Study design and ethics
The present study was approved by the ethics committee (CAAE-39005514.5.0000.5157) and conducted at the dentistry clinic of UNIVALE, including elderly individuals (>60 years-old), denture wearers, functionally independent and non-institutionalized.
Sample collection and Candida identification
Denture-related stomatitis diagnosis was defined by clinicians and samples were collected directly from oral lesions using a sterile swab (O’Donnell et al., Reference O’Donnell, Robertson, Nile, Cross, Riggio, Sherriff, Bradshaw, Lambert, Malcolm, Buijs, Zaura, Crielaard, Brandt and Ramage2015). Yeasts were morphologically identified by CHROMagar Candida®(HiMedia-Laboratories, India), phenotypically by VITEK®2 (bioMérieux, France) and molecularly by sequencing the ITS1–5.8S-ITS2 gene. Candida albicans ATCC 10231 was used as reference strain.
Virulence attributes
Biofilm formation on polystyrene surface and production of extracellular enzymes (aspartic protease, caseinase, phospholipase, esterase, phytase and hemolysin) were evaluated as previously described (Ziccardi et al., Reference Ziccardi, Souza, Gandra, Galdino, Baptista, Nunes, Ribeiro, Branquinha and Santos2015). Two biofilm parameters were analyzed: biomass (measured in methanol-fixed biofilm using crystal violet dye) and metabolic activity (measured in non-fixed biofilm by metabolization of 2,3-bis (2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-5-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-2H-tetrazolium hydroxidemetabolization). The enzymatic activity was expressed as Pz value, which was calculated by the ratio of the diameter of colony per the diameter of colony plus precipitation zone.
Antifungal susceptibility
Antifungal susceptibility of planktonic-growing yeasts was conducted following the standard microdilution method published by Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (documents M27-A3/M27-S3/M27-S4). The effect of antifungals on biofilm-forming cells was determined by a microtiter-based assay (Ziccardi et al., Reference Ziccardi, Souza, Gandra, Galdino, Baptista, Nunes, Ribeiro, Branquinha and Santos2015).
Statistics
All experiments were performed in triplicate, in three independent experimental sets, and, when appropriated, the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
Results
Fifty-two patients fitted our inclusion criteria and 4 (7.7%) of them presented denture-associated stomatitis, being selected to the next experiments. Demographic data, dental history and oral hygiene habits were summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Demographic and oral characteristics of studied patients.
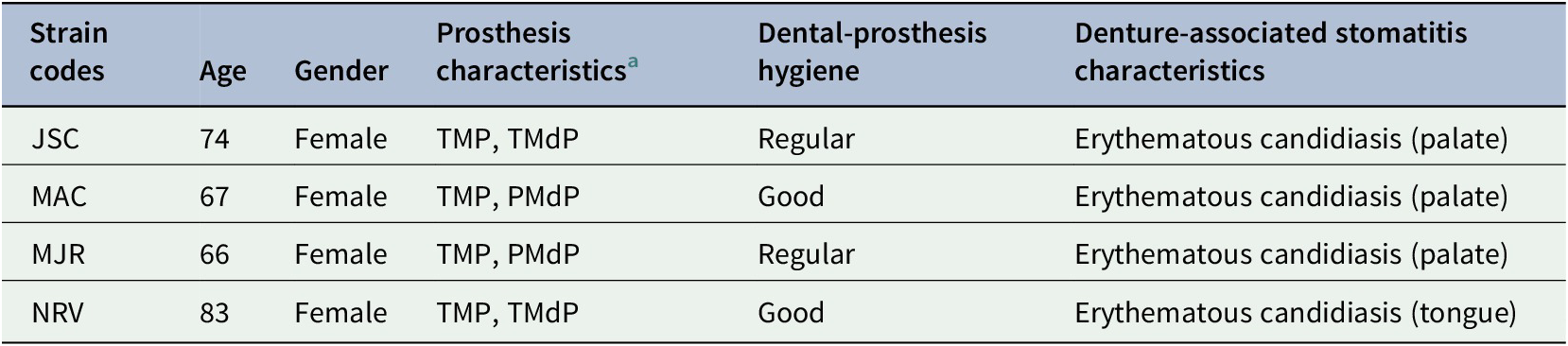
a TMP, total maxillary prosthesis; TMdP, total mandibular prosthesis; PMdP, partial mandibular prosthesis.
Candida was isolated from the lesions of patients with denture-related stomatitis. Morphological (green colonies in CHROMagar Candida), biochemical (carbohydrate assimilation/metabolic enzymatic profiles evaluated by VITEK®2 presented probability of identity to 98%) and genetic (ITS sequencing alignment scores revealed 100% identity with reference isolates deposited in GenBank) analyses identified the fungal isolates as C. albicans.
Phenotypic assays showed that all C. albicans isolates produced esterase, being classified as good producers as suggested by the Pz values, besides aspartic protease and hemolysin (weak producers). However, no fungal isolate with the ability to produce phospholipase and caseinase was detected (Table 2). Biofilm on a polystyrene surface was detected as judged by the measurement of two classical parameters: biomass and metabolic activity (viability) (Table 2).
Table 2. Hydrolytic enzyme production and biofilm formation by oral isolates of Candida albicans recovered from denture-related stomatitis.

a The enzymatic activities were measured by the formation of a clear halo around the colony and expressed as Pz value as previously proposed by Price et al. (Reference Price, Wilkinson and Gentry1982). The Pz value was scored into four categories: Pz of 1.0 was evaluated as negative (n); high Pz between 0.999 and 0.700 represents weak enzymatic activity (w); moderate Pz between 0.699 and 0.400 represents good enzymatic activity (g); low Pz between 0.399 and 0.100 represents excellent enzymatic activity. The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experimental sets.
Planktonic cells of all C. albicans isolates were susceptible to amphotericin B (a polyene antifungal) and caspofungin (an echinocandin antifungal), while the susceptibility pattern to azoles varied from susceptible to resistant depending on both isolate and antifungal (Table 3). Impressively, biofilm-growing C. albicans cells exhibited a remarkable resistance profile to all tested antifungal agents (Table 3).
Table 3. Susceptibility profiles of both planktonic- and biofilm-forming cells of oral isolates of Candida albicans recovered from denture-related stomatitis to different classical antifungals.
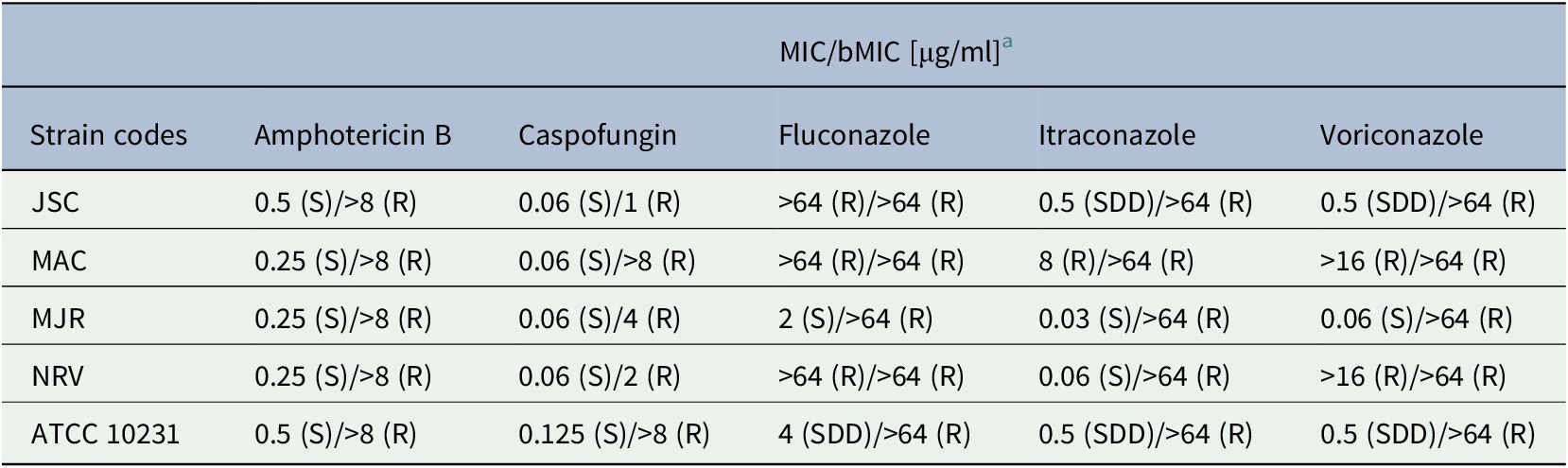
a MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration for planktonic cells; bMIC, minimum inhibitory concentration for biofilm-forming cells; R, resistant; S, susceptible; SDD, susceptible-dose dependent.
Discussion
Denture-associated stomatitis is related to both exogenous and endogenous factors, which can lead to differences in prevalence and clinical manifestations’ severity (Thilakumara et al., Reference Thilakumara, Jayatilake, Pallegama and Ellepola2017). In this context, published works reported a broad range of stomatitis prevalence in middle aged or elderly, varying from 10 to 85%, with females being affected slightly more commonly than males (Bianchi et al., Reference Bianchi, Bianchi, Tadano, Paula, Holffmann-Santos, Leite and Hahn2016; Rivera et al., Reference Rivera, Droguett and Márquez2017). Our study revealed a low prevalence (7.7%) of denture-related stomatitis and these selected patients were all female (mean age 70.5 ± 7.9 years-old). Our Dentistry sector has a small flow of patients attended at the University clinic. However, this small flow of patients has a positive impact in our studies permitting us to follow each patient more close. The socioeconomic conditions as well as the good oral hygiene are possible hypothesis to justify the small number of denture-associated stomatitis detected in our patients.
C. albicans was isolated from all stomatitis patients, being able to produce biofilm and hydrolytic enzymes, two well-known virulence attributes. Biofilm is a physical barrier that prevents the penetration of antimicrobials and host defenses (Mello et al., Reference Mello, Ramos, Braga-Silva, Branquinha and Santos2017). In a general way, hydrolytic enzymes are capable in destroying cell/tissue structures, including proteins and lipids, and humoral defense molecules, like antibodies, complement system proteins and antimicrobial peptides (Schaller et al., Reference Schaller, Borelli, Korting and Hube2005).
Conclusions
In our clinical samples, oral isolates of C. albicans resistant to azoles, including fluconazole that is commonly used to treat denture-associated stomatitis, were detected. The isolation of C. albicans able to form biofilm is a veritable problem, because it is one of the main causes of antifungal treatment failure. Moreover, the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes able to destroy host tissues/cells can increase the local inflammatory response, aggravating the clinical manifestations and the disease progression. So, it is urgently necessary to consider new treatment options to combat infections caused by resistant isolates of C. albicans. In this context, new drugs with anti-C. albicans action and novel compounds able to block the expression of virulence factors should be discovered to improve the antifungal armamentarium to be used in clinical settings.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Denise Rocha de Souza, who is supported by FAPERJ scholarships, for her technical assistance.
Funding Information
This work was supported by grants from Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES – Financial code 001).
Disclosure statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions
LVNFS, ACMG, MHB, HMSC and ALSS conceived and designed the study. LVNFS, CDOM, ISC, JMP, LCRA, MFV, MBM, TSP, LOPS, ACMG performed the experiments. LVNFS, ACMG and ALSS compile the data. LVNFS, ACMG, MHB, HMSC and ALSS wrote the article. All authors have read and agree to the submitted version of the manuscript.
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Ethics statement
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.





Comments
Comments to the Author: Swab method is not appropriate as we showed in this manuscript “Laboratory‐Based Investigation of Denture Sonication Method in Patients with Candida‐Associated Denture Stomatitis”. Please, stress the limitation of the study and add this manuscript as reference.