After many years of systematic experimental investigations, it is now possible to quantify the conditions for optimum fertility to melt production of most common crustal rock types as functions of temperature and 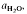 to about 30 kbar pressure. Quartzo-feldspathic melting produces steady increases in melt proportion with increasing temperature. The exact melt fraction depends on the mineral mode relative to quartz-feldspar eutectics and the temperatures of mica dehydration melting reactions. Mica melting consumes SiO2 from residual quartz during the formation of refractory Al2SiO5, orthopyroxene, garnet or cordierite.
to about 30 kbar pressure. Quartzo-feldspathic melting produces steady increases in melt proportion with increasing temperature. The exact melt fraction depends on the mineral mode relative to quartz-feldspar eutectics and the temperatures of mica dehydration melting reactions. Mica melting consumes SiO2 from residual quartz during the formation of refractory Al2SiO5, orthopyroxene, garnet or cordierite.
A simple graphical interpretation of experimental results allows a deduction of the proportions of mica and feldspar leading to optimum fertility. In effect, the mica dehydration melting reactions, at specific pressure and 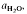 are superimposed on quartz-feldspar melting relations projected onto Ab-An-Or. Fertility to melt production varies with the mica to feldspar ratio and pressure. Pelites are more fertile than psammites at low pressures (e.g. 5 kbar), especially if they contain An40 to An50 plagioclase. At higher pressure (e.g. 10-20 kbar) and for rocks containing albitic plagioclase, psammites are more fertile than pelites. For a typical pelite (e.g. with An25 at 20 kbar), the cotectic with muscovite lies at higher
are superimposed on quartz-feldspar melting relations projected onto Ab-An-Or. Fertility to melt production varies with the mica to feldspar ratio and pressure. Pelites are more fertile than psammites at low pressures (e.g. 5 kbar), especially if they contain An40 to An50 plagioclase. At higher pressure (e.g. 10-20 kbar) and for rocks containing albitic plagioclase, psammites are more fertile than pelites. For a typical pelite (e.g. with An25 at 20 kbar), the cotectic with muscovite lies at higher 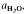 (≍·) and XAb (≍0·42) than with biotite
(≍·) and XAb (≍0·42) than with biotite 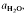 :≍0·35; XAb(≍·), thus dehydration melting of muscovite requires 10% more plagioclase for fertility than does biotite.
:≍0·35; XAb(≍·), thus dehydration melting of muscovite requires 10% more plagioclase for fertility than does biotite.
The first melts from dehydration melting of muscovite (with Plg + Qtz) are more sodic and form at lower temperatures than the first melts from Bio + Plg + Qtz. With increasing pressure, to at least 30 kbar, granite minimum and mica dehydration melts become more sodic. This indicates that 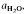 of such melts is greater than 0·3.
of such melts is greater than 0·3.