The stochastic process {Xn} satisfying Xn+1 = max{Yn+1+ αβ Xn, βXn} where {Yn} is a stationary sequence of non-negative random variables and 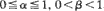 , 0<β <1, can be regarded as a simple thermal energy storage model with controlled input. Attention is mostly confined to the study of μ = EX where the random variable X has the stationary distribution for {Xn}. Even for special cases such as i.i.d. Yn or α = 0, little explicit information appears to be available on the distribution of X or μ . Accordingly, bounding techniques that have been exploited in queueing theory are used to study μ . The various bounds are illustrated numerically in a range of special cases.
, 0<β <1, can be regarded as a simple thermal energy storage model with controlled input. Attention is mostly confined to the study of μ = EX where the random variable X has the stationary distribution for {Xn}. Even for special cases such as i.i.d. Yn or α = 0, little explicit information appears to be available on the distribution of X or μ . Accordingly, bounding techniques that have been exploited in queueing theory are used to study μ . The various bounds are illustrated numerically in a range of special cases.

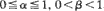 , 0<
, 0<