Background
Suicidal behaviour is a significant public health issue worldwide, resulting in an estimated 16 million suicide attempts and 800 000 suicides per year.1 For every person who dies by suicide, more than 20 others make a non-fatal attempt,2 and many more have serious thoughts about ending their life.Reference May and Klonsky3 Suicidal ideation and suicidal behaviour (including both fatal and non-fatal suicide attempts) thus constitute a substantial disease burden. This underlines the importance of suicide prevention.Reference Nock, Borges, Bromet, Alonso, Angermeyer and Beautrais4
There is an increasing body of evidence in support of several psychological treatments for suicide prevention, including cognitive–behavioural therapy and dialectical behaviour therapy.Reference Mann, Apter, Bertolote, Beautrais, Currier and Haas5,Reference Zalsman, Hawton, Wasserman, van Heeringen, Arensman and Sarchiapone6 In recent years, brief interventions, defined as up to three encounters between a patient and (para-)professional, have also been linked to reduced risks of suicidal behaviour.Reference McCabe, Garside, Backhouse and Xanthopoulou7,Reference Doupnik, Rudd, Schmutte, Worsley, Bowden and McCarthy8
Safety planning-type interventions
One group of brief interventions consists of safety planning-type interventions (SPTIs). The technique in SPTIs is called safety planning, and is derived from cognitive therapy and cognitive–behavioural therapy for suicide prevention.Reference Brown, Ten Have, Henriques, Xie, Hollander and Beck9,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brent, Wells, Poling and Curry10 The goal of safety planning is to reduce the imminent risk of suicidal behaviour by constructing a predetermined set of coping strategies and sources of support in a plan.Reference Stanley, Brown, Brent, Wells, Poling and Curry10,Reference Stanley and Brown11 During a crisis, an individual may use these strategies to avert their thoughts about suicide and manage their suicidal urges.Reference Stanley and Brown11 Since its introduction, safety planning has become an integral part of standard clinical care for people at risk of suicide, and it is being used as a brief standalone intervention.Reference Stanley and Brown11
The plan that is constructed in safety planning has been referred to in a number of ways, including ‘safety plan’,Reference Stanley and Brown11 ‘crisis response plan’Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12 and ‘coping card’,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13 but in essence they all cover the same psychological technique. The current review uses the term SPTIs to summarise the entire range of brief interventions in which safety planning is applied. The strategies and sources of support are embedded in what we will call a safety plan.
Interventions of the safety planning type are recommended as best practice by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg133) in the UK, and the Suicide Prevention Resource Center (www.sprc.org) in the USA. Historically, the use of safety plans in clinical practice seems to be based on clinicians’ beliefs about their effectiveness,Reference Chesin, Stanley, Haigh, Chaudhury, Pontoski and Knox14,Reference Setkowski, van Balkom, Dongelmans and Gilissen15 rather than on empirical evidence.Reference Kayman, Goldstein, Wilsnack and Goodman16 Individual trials on the effectiveness of SPTIs have yielded conflicting results,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 whereas meta-analyses of studies that included SPTIs have focused on brief interventions more broadly.Reference McCabe, Garside, Backhouse and Xanthopoulou7,Reference Doupnik, Rudd, Schmutte, Worsley, Bowden and McCarthy8 Although the latter have made an important contribution to the literature, they did not include all published trials on SPTIs, and did not report on the effectiveness of SPTIs specifically.Reference McCabe, Garside, Backhouse and Xanthopoulou7,Reference Doupnik, Rudd, Schmutte, Worsley, Bowden and McCarthy8
Aims
The purpose of this study was to conduct a meta-analysis to assess whether SPTIs for suicide prevention are linked to reductions in first, suicidal behaviour (fatal and non-fatal suicide attempts), and second, suicidal ideation.
Method
Before study commencement, the study protocol was registered in the international Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews at the University of York (PROSPERO; registration number CRD42020129185). We modified the protocol in two respects. First, to more accurately reflect the focus of the study, we chose to use the term ‘safety planning-type’ instead of ‘crisis management’. Safety planning-type is a better description of a personalised plan. Second, to facilitate interpretation, we calculated relative risks instead of odds ratios. As the underpinning calculation is similar to that for an odds ratio, the use of relative risks should not alter the findings. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines were followed for reporting the meta-analysis;Reference Moher19 the PRISMA checklist is reproduced in Supplementary Appendix 1 available at https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2021.50.
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was developed and performed in collaboration with a librarian. We searched the following databases from their inception to 9 December 2019: Medline (PubMed.com), EMBASE (embase.com), PsycINFO (EBSCO), Web of Science (Clarivate) and Scopus (Elsevier). The search strategy included MeSH terms and free-text terms relating to suicide, safety management, crisis intervention and prevention. The actual terms used in the search strategy for PubMed are listed in Supplementary Appendix 2; these were subsequently adapted for other databases. We additionally conducted hand searches of reference lists in identified publications and consulted experts in the field to identify additional publications (C.N.).
Selection of studies
The following inclusion criteria were applied: (a) a brief standalone intervention based on safety planning for suicide prevention was delivered; (b) the safety plan contained, as a minimum, personalised coping strategies and sources of support; (c) the safety plan was the primary element of the intervention; (d) a control condition was applied (including treatment as usual (TAU) or another treatment) and (e) the study reported on at least one of the outcomes of suicidal behaviour, suicide attempts, suicides or suicidal ideation. The outcome ‘suicidal behaviour’ (suicide attempts, fatal suicides or both combined) was defined as the number of participants who engaged in suicidal behaviour as defined by the original authors of the included studies. As a result, suicide attempts were either identified from medical records, identified from clinical notes (recorded by a clinician or gatekeeper) or reported by patients (via questionnaires or during interviews). Suicidal ideation was reported by patients and assessed on the basis of questionnaires or clinical interviews. There were no restrictions on study participants in terms of age or disorder, as long as they were at risk of suicide (on the basis of current suicidal ideation or a recent suicide attempt). Studies were excluded if they were not written in English or not peer-reviewed.
All identified studies were exported to EndNote X9 for Windows (Clarivate, Boston, USA; see https://endnote.com/), where duplicates were removed. The studies were subsequently imported into Covidence software for Windows (covidence, Melbourne, Australia; see https://www.covidence.org/) for managing the meta-analysis. To determine study eligibility, all titles and abstracts were screened independently by two researchers (C.N. and W.v.B.), who also conducted the second full-text screening independently. Disagreements or uncertainties were discussed with the senior researcher supervising the project (H.R.).
Data extraction
We started data extraction on 4 February 2020. A data extraction sheet was used to collect information regarding setting, participants, design, intervention and control group. Intention-to-treat data were extracted when possible. The data were extracted independently by two authors (C.N. and D.J.). In the event of disagreement, a third author was consulted (W.v.B.). The corresponding authors were contacted if studies did not list the necessary data to conduct the quantitative analyses. If no additional data were available, the study was omitted from further analyses.
Statistical analysis
For our primary outcome of suicidal behaviour measured as the combined rate of suicide attempts and suicide deaths, effect sizes were calculated based on the number of participants in the intervention and control condition who had engaged in suicidal behaviour during the follow-up period. Effects were based on relative risk and its 95% confidence interval, calculated as the ratio of the probability of suicidal behaviour in the intervention condition to its probability in the control condition. A relative risk lower than 1 would indicate that persons receiving an SPTI had lower risks of suicidal behaviour than controls, whereas a relative risk higher than 1 would indicate a higher risk and a relative risk of 1 would indicate a similar risk for the two groups.
For the secondary outcome of suicidal ideation, we extracted mean (s.d.) scores and presented them as standardised effect sizes, using Hedges’ g. Hedges’ g was calculated by subtracting the average score at follow-up for suicidal ideation by persons receiving the intervention from the average score of those in the control condition, and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation. An effect size of 0.8 was considered a large effect, 0.5 was considered moderate and 0.2 was considered small.Reference Cohen20
To further quantify effects, the number needed to treat (NNT), which summarises the number of patients who would need to be treated in order for one additional patient not to engage in suicidal behaviour, was calculated if a significant outcome effect supported this.Reference Mendes, Alves and Batel-Marques21
To account for differences between study populations, interventions and control conditions, we performed a random-effects meta-analysis. In studies where multiple intervention conditions were investigated, the control condition was split into two or more subgroups, dividing the number of control participants by the number of intervention conditions.
Outliers were evaluated by examining whether the 95% confidence intervals of individual studies overlapped with the 95% confidence interval of the pooled effect size. In the absence of an overlap, the study would be identified as an outlier. Publication bias was assessed by visually examining the funnel plots of the outcome measures.Reference Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins and Rothstein22 We used Egger's linear regression test of the intercept to examine whether bias captured by the funnel plot was significant, and performed Duval and Tweedie's trim-and-fill procedure to assess for potential publication bias.Reference Egger, Smith, Schneider and Minder23,Reference Duval and Tweedie24
As a test of homogeneity of effect sizes, we calculated the I² statistic, an indicator of variation between studies. No observed heterogeneity is shown as 0%, and larger values suggest an increasing level of heterogeneity, with 25% as low, 50% as moderate and 75% as high.Reference Higgins25 We further estimated the 95% confidence interval around I², using the non-central χ²-based approach within the heterogi module in Stata for Windows version 16.0.Reference Ioannidis, Patsopoulos and Evangelou26,Reference Orsini, Bottai, Higgins and Buchan27 Factors that may have introduced heterogeneity in individual studies were investigated with subgroup analyses. Based on study characteristics of the included studies, subgroup analyses were performed with the following potential moderators: methodological quality, setting and population.
Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. All of these analyses were conducted with the software Comprehensive Meta-Analysis for Windows version 3.3.070 (Comprehensive Meta-Analysis, Englewood, USA; see https://www.meta-analysis.com/), except for the heterogeneity (I²) and its confidence interval, for which we used Stata.Reference Ioannidis, Patsopoulos and Evangelou26,Reference Orsini, Bottai, Higgins and Buchan27
Quality assessment
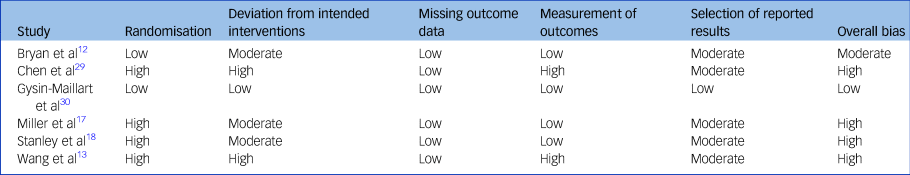
The methodological quality was determined with the Cochrane Collaboration's Risk-of-Bias Tool 2,Reference Sterne, Savović, Page, Elbers, Blencowe and Boutron28 which considers risk of bias across five domains: the randomisation process, deviations from the intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of outcome and selection of the reported results. The risk of bias for each domain was scored as low, moderate or high. The overall bias was considered high when one of the domains was scored as high. The risk of bias assessment was performed independently by two authors (C.N. and D.J.), with a third author (W.v.B.) consulted in case of disagreement.
Results
Study selection
The systematic search identified 3463 studies, and one additional study was added after the hand-searching of relevant journals. After removal of duplicates, 1816 studies remained. After evaluation of titles and abstracts against the inclusion criteria, 1782 studies were deemed not eligible. We retrieved 34 full-text articles for further review, from which 6 studies were ultimately included in the meta-analysis (see PRISMA flow chart in Fig. 1). Corresponding authors of four studies were contacted to retrieve additional information necessary for our meta-analysis, of which two authors replied.
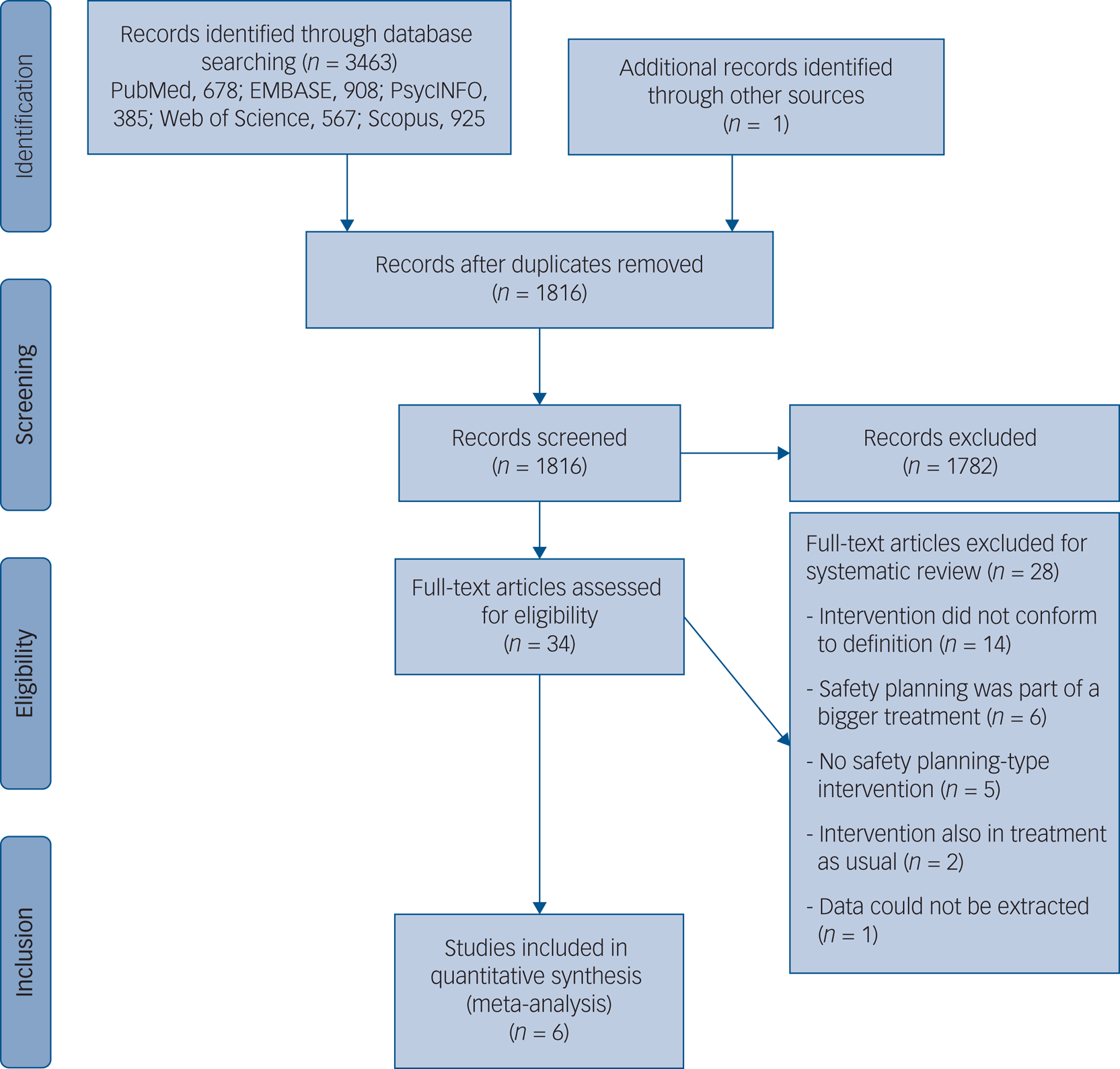
Fig. 1 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis flow chart of study selection process.
Study characteristics
The six studies were conducted in three different countries (USA, n = 3; Taiwan, n = 2; Switzerland, n = 1) and published between 2013 and 2018 (Table 1).Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 All studies reported rates for suicide attempts and suicides. Three studies additionally reported on suicidal ideation.Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 Intention-to-treat data could be extracted from five studies,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 and one study had only study completers’ data available.Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29
Table 1 Characteristics of studies
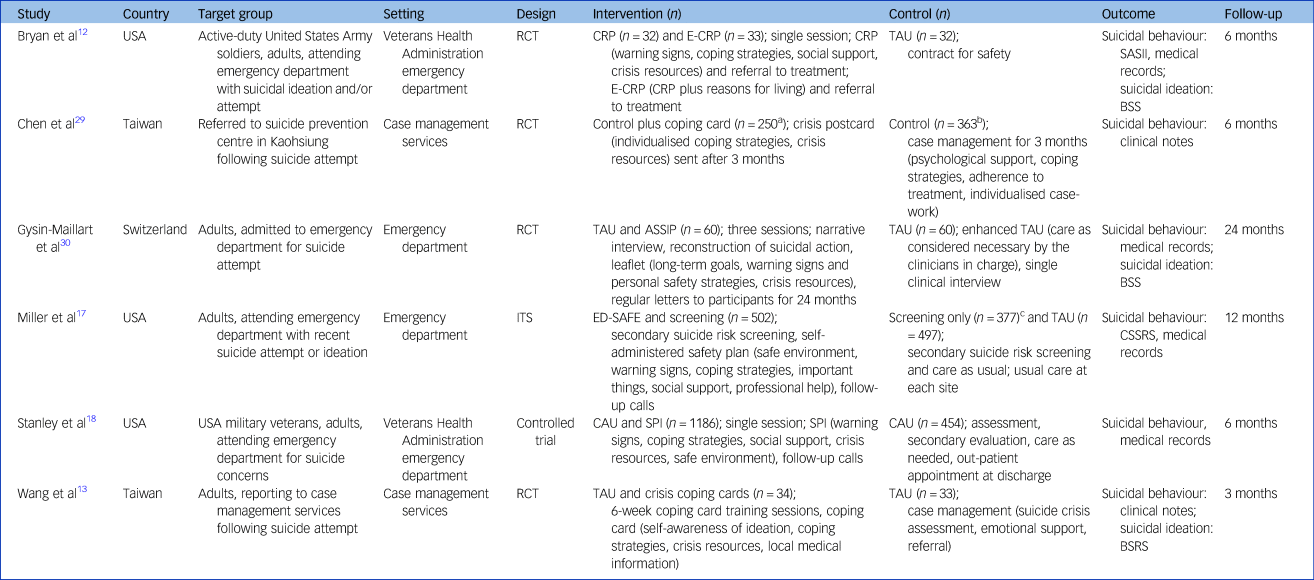
RCT, randomised controlled trial; CRP, Crisis Response Plan; E-CRP, Enhanced Crisis Response Plan; TAU, treatment as usual; SASII, Suicide Attempt Self-Injury Interview; BSS, Beck Scale for Suicide Ideation; ASSIP, Attempted Suicide Short Intervention Program; ITS, interrupted time series design; ED-SAFE, Emergency Department Safety Assessment and Follow-up Evaluation; CSSRS, Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale; CAU, care as usual; SPI, Safety Planning Intervention; BSRS, Brief Symptom Rating Scale.
a. Participants who read their crisis postcard.
b. Participants who received full case management for 3 months.
c. Screening-only condition was not included in the meta-analysis.
The meta-analysis included four randomised controlled trials,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 a non-randomised controlled trialReference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 and one study with an interrupted time-series design.Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17 In four studies, safety planning was assessed as an add-on to TAU.Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 Two studies compared a safety plan as a standalone intervention to TAU and included two intervention arms.Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17 One of those studies used a safety plan in both conditions,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12 and the other in only one condition.Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17 Here, the intervention condition without the safety plan was omitted from the meta-analysis. This yielded a total of seven comparisons in the current meta-analysis.
In all, 3536 participants (n = 2096 in intervention conditions; n = 1440 in control conditions) aged ≥18 years (average age range of 26–48 years) were enrolled in the studies. More male (63.2%) than female participants were included, and half of the participants (50.2%) had attempted suicide at least once before enrolment. Not all studies reported on participants’ mental health,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29 but depression,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 affective disordersReference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 and adjustment disordersReference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12 were mentioned as predominant comorbid disorders in other studies.
Suicidal behaviour was measured via interviews,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17 medical recordsReference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 and clinical notes (i.e. recorded by a gatekeeper or clinician).Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29 In some studies, participants had all previously attempted suicide (n = 3)Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 or were experiencing suicidal ideation and/or a recent suicide attempt (n = 2),Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17 whereas the participants in one study were reported to have visited a hospital for suicide-related concerns.Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 In two studies, professional groups (soldiers and military veterans) were involved,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 and the other studies comprised participants from the general population.Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 Settings varied between general hospitals (n = 2),Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 military hospitals (n = 2)Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18 and case management services (n = 2).Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29 Participants of one study were in-patients,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 whereas all others were out-patients.Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29
All interventions were provided face to face by a clinician, and consisted of comparable safety plans. See Table 1 for an overview of safety planning components included in the interventions. In addition to coping strategies and sources of support, four studies included personal warning signs of an impending suicidal crisis.Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 The safety plan was generally provided in person and on paper,Reference Bryan, Mintz, Clemans, Leeson, Burch and Williams12,Reference Wang, Hsieh, Wang, Chou, Huang and Ko13,Reference Miller, Camargo, Arias, Sullivan, Allen and Goldstein17,Reference Stanley, Brown, Brenner, Galfalvy, Currier and Knox18,Reference Gysin-Maillart, Schwab, Soravia, Megert and Michel30 although in one study it was sent to participants by post.Reference Chen, Ho, Shyu, Chen, Lin and Chou29
Primary outcome: suicidal behaviour
Of the 3536 included participants, 348 engaged in suicidal behaviour during the follow-up period (n = 150 in the intervention condition; n = 198 in the control condition). The incidence of suicidal behaviour ranged from 0 to 18.3% in intervention conditions, and 5.3 to 26.7% in control conditions (see Supplementary Appendix 3).
The relative risk of suicidal behaviour for participants who received an SPTI was 0.57 compared with TAU (95% CI 0.41–0.80, P = 0.001; I 2 = 32.51%, 95% CI 0–71%; NNT = 16), indicating that the risk of suicidal behaviour was significantly reduced by 43% in the intervention condition (Fig. 2). A visual inspection of the forest plot indicated no outliers, as the effect sizes overlapped with the 95% confidence interval of the pooled effect size (see Fig. 2).
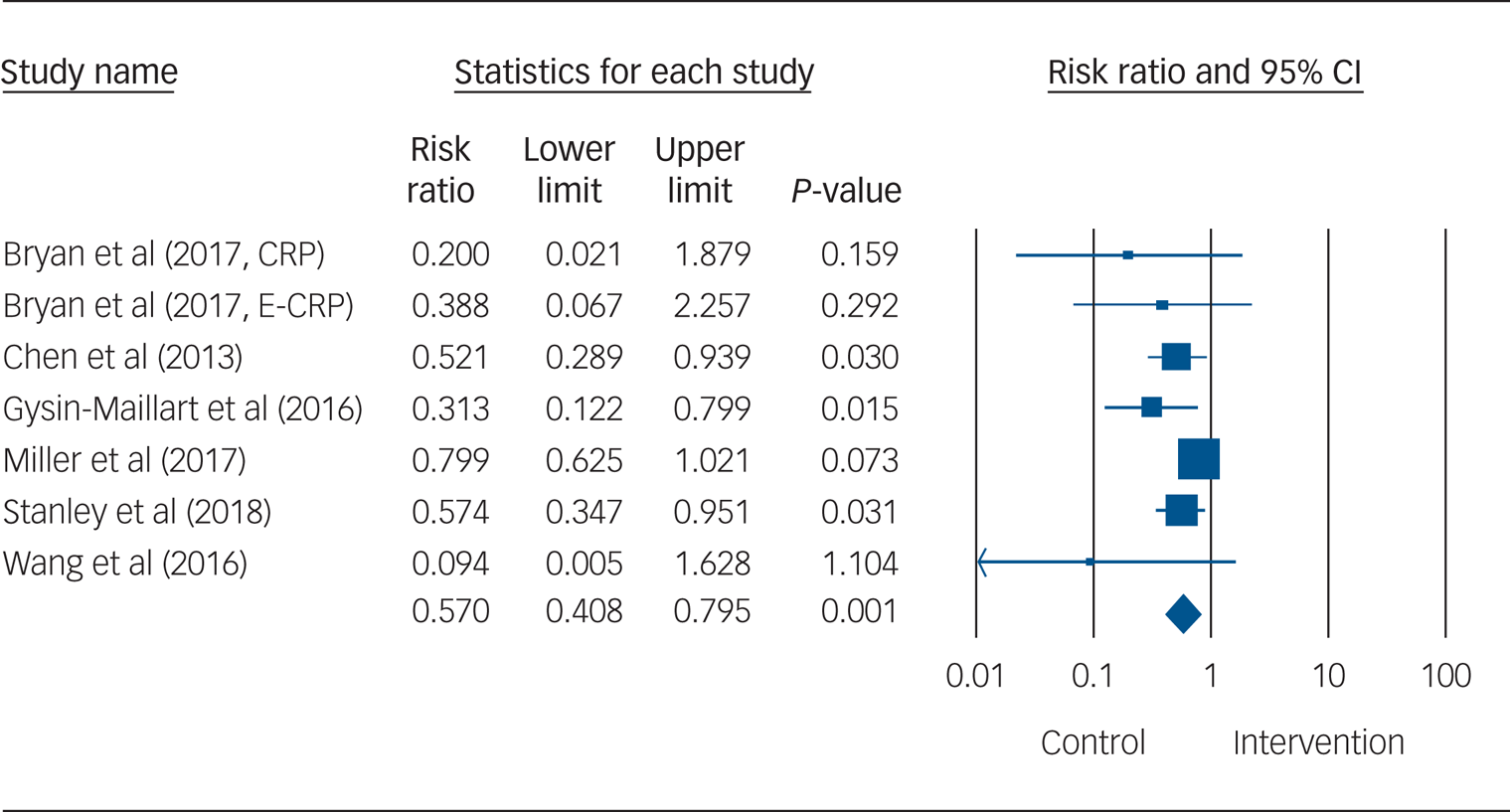
Fig. 2 Forest plot for suicidal behaviour. CRP, standard crisis response plan; E-CRP, enhanced crisis response plan.
Secondary outcome: suicidal ideation
The mean effect size of the three studies examining the effects of SPTIs on suicide ideation (combined N = 283) was non-significant (g = 0.69, 95% CI −0.04 to 1.42, P = 0.06; I 2 = 87.60%) (see Fig. 3 and Supplementary Appendix 3).Reference Stanley, Brown, Brent, Wells, Poling and Curry10,Reference Cohen20,Reference Ioannidis, Patsopoulos and Evangelou26
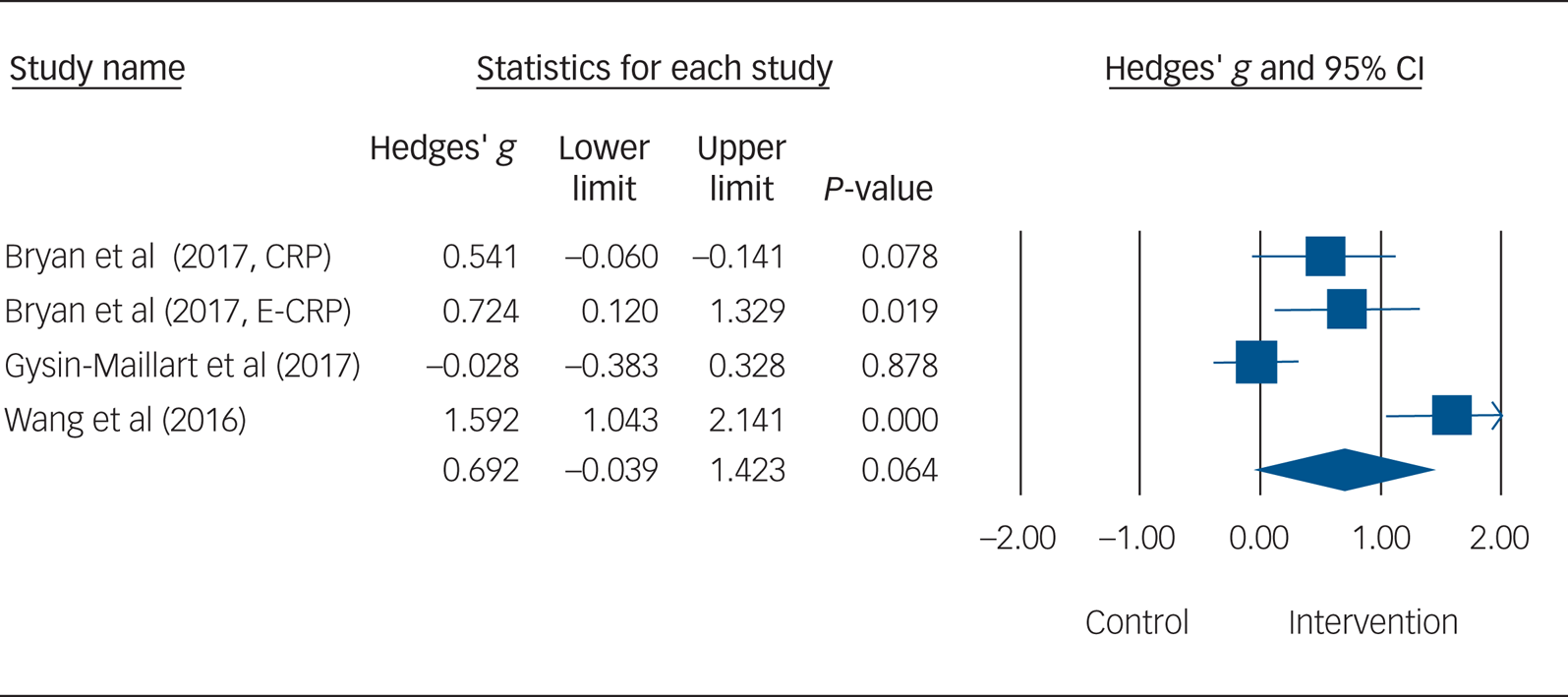
Fig. 3 Forest plot for suicidal ideation. CRP, standard crisis response plan; E-CRP, enhanced crisis response plan.
Methodological quality
In terms of methodological quality, participants in two studies were not randomised, and in two other studies, the randomisation was based on a national identification number. Hence, results of these four studies were considered to be at high risk of bias (Table 2). In five studies, deviations from the intended interventions (such as problems in recruitment or in delivering the intervention) were reported. All studies apparently handled incomplete outcome data correctly. In two studies, no description was given of the assessments and assessors, hence bias in outcome measurement was evaluated to be high. Five studies were considered at moderate risk of bias in their selection of the reported outcome measures. Overall, one study was considered to be at low risk of bias, one at moderate risk of bias and four at high risk of bias.
Table 2 Risk of bias within studies
Publication bias
The inspection of the funnel plot suggested publication bias (Fig. 4), and that was supported by a significant Egger's test of the intercept (P = 0.001). Duval and Tweedie's trim-and-fill procedure suggested that three studies in favour of TAU, with a smaller s.e., might be missing from the research literature. With those studies imputed, the relative risk for engagement in suicidal behaviour came to 0.71 (95% CI 0.59–0.86), implying that the relative risk for patients who received an SPTI would be closer to 1, as compared with TAU, but would remain significant.
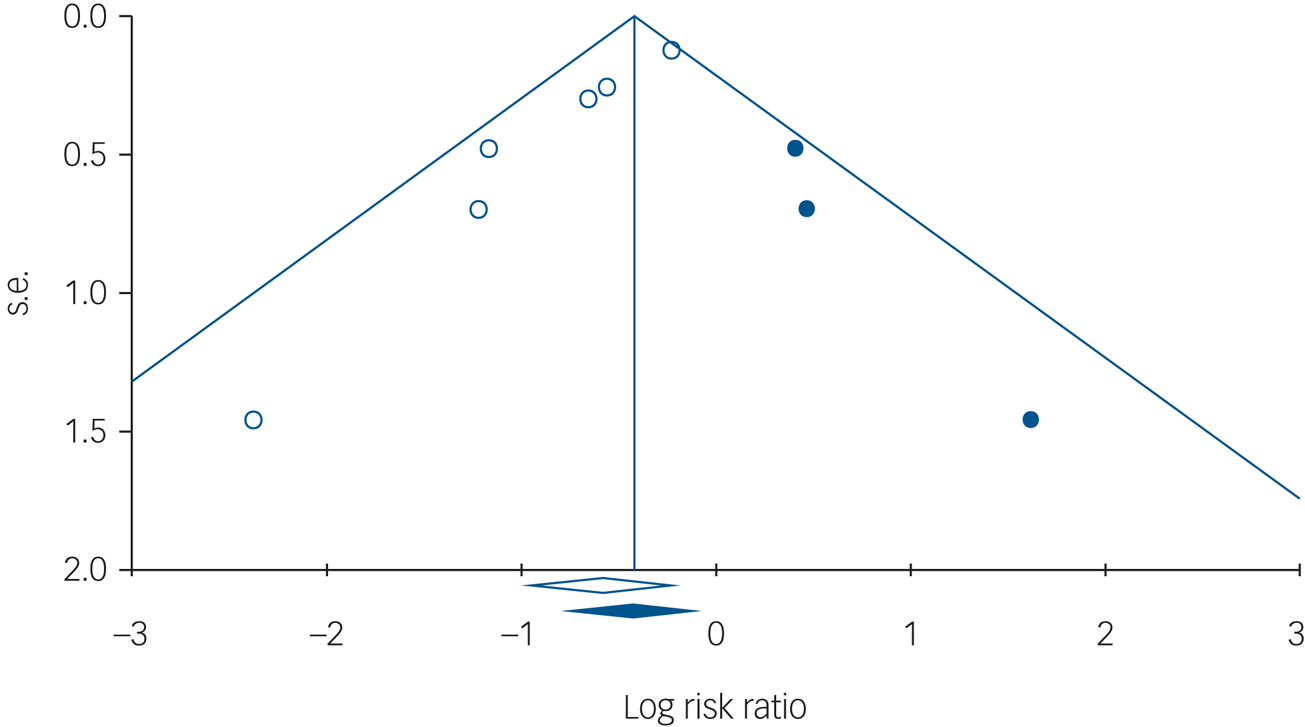
Fig. 4 Funnel plot of s.e., by log risk ratio.
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
We assessed possible sources of the heterogeneity, using methodological quality, setting and population as potential moderators in subgroup analyses, but found no significant differences between groups (Table 3).
Table 3 Subgroup analyses of associations between effect sizes and study characteristics
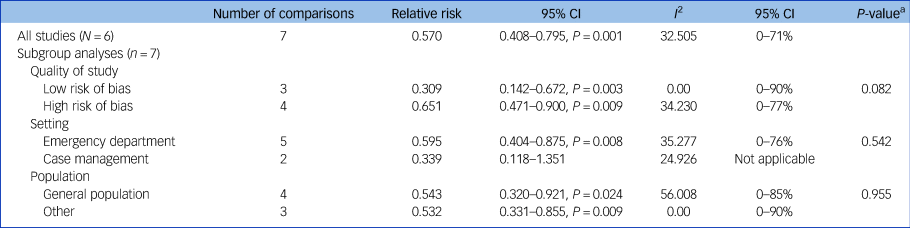
a. The P-values in this column indicate whether the difference between the effect sizes in the subgroups is significant.
We tested the robustness of the effect on suicidal behaviour in additional sensitivity analyses, yet the pooled relative risk remained significant after exclusion of the studies with the highest or lowest relative risk (relative risk 0.481, P = 0.000 versus relative risk 0.598, P = 0.001). A significant pooled relative risk was also found when we distinguished between studies with large samples (N > 500) and smaller samples (large samples: relative risk 0.688, P = 0.006; small samples: relative risk 0.285, P = 0.001), and between studies with and without randomisation (randomised: relative risk 0.414, P = 0.000; not randomised: relative risk 0.713, P = 0.032).
Discussion
This meta-analysis found that SPTIs for suicide prevention were associated with reductions in suicidal behaviour, but no effect was identified on suicidal ideation. Overall, six studies were included for analysis. SPTIs were associated with a risk of engagement in suicidal behaviour that was 0.57 times the risk of patients without such an intervention. This means that the risk of suicidal behaviour was reduced by 43% (NNT = 16) for patients who were utilising an SPTI. The findings from sensitivity analyses supported a robust effect. The observed effect is in line with the hypothesis that safety plans reduce the imminent risk of engagement in suicidal behaviour by presenting alternative coping strategies and sources of support.Reference Stanley, Brown, Brent, Wells, Poling and Curry10,Reference Stanley and Brown11 The outcome also appears consistent with clinicians’ beliefs in the effectiveness of safety planning.Reference Chesin, Stanley, Haigh, Chaudhury, Pontoski and Knox14,Reference Setkowski, van Balkom, Dongelmans and Gilissen15 However, other interventions may be needed to reduce suicidal ideation.
The lack of an effect from SPTIs on suicidal ideation might be explained by the fact that suicidal ideation was not directly targeted by this type of intervention. Such a supposition is supported by a recent systematic review by McCabe et al on brief psychological interventions for suicide prevention, which suggested that such interventions may alter behaviours of individuals at risk of suicide, but their level of cognitive distress remains unaffected.Reference McCabe, Garside, Backhouse and Xanthopoulou7 Another explanation for the lack of effect on suicidal ideation may lie in the fact that suicidal thoughts are known to fluctuate over time;Reference Czyz, King and Biermann31 hence, possible initial effects might have abated by the end of follow-up. Psychotherapeutic interventions that are known to be effective in reducing suicidal ideation include cognitive–behavioural therapy and dialectical behaviour therapy.Reference Mann, Apter, Bertolote, Beautrais, Currier and Haas5,Reference Zalsman, Hawton, Wasserman, van Heeringen, Arensman and Sarchiapone6
Strengths and limitations
To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first to report a meta-analysis on SPTIs for suicide prevention. Our meta-analysis was adequately powered and supported by sensitivity analyses. Nonetheless, our results should be interpreted with caution because of several limitations. First, the field of SPTIs is relatively new, thus only a few controlled studies could be included in the analyses. Second, not all of the included studies were randomised, implying limited comparability. Third, our findings cannot be generalised to adolescents and children, as only adults were included in the analyses. Fourth, we did not include the term ‘self-harm’ in our search string because the known SPTIs were developed specifically as suicide prevention tools. However, in response to a reviewer, we have run a post hoc search including self-harm as a search term, and this did not yield any additional studies meeting our inclusion criteria. Another limitation is the low methodological quality of the studies, which may have affected outcomes. On the other hand, our use of a single bias risk assessment tool for all studies could have distorted results from non-randomised controlled studies. Furthermore, the studies varied amongst themselves, including differences in the measurement of ‘suicide attempt' and in the length of follow-up. That said, variations in terms of quality, settings and included populations did not explain the heterogeneity in this meta-analysis. Other differences between studies might offer explanations; for example, in terms of inclusion criteria or the content of TAU (such as possible variations in the care needed in different countries). Moreover, since the studies implemented safety planning in different ways, future research is required to determine the active ingredients of SPTIs, and to assess whether follow-up telephone calls play a role.
Implications for the future
From a clinical point of view, the present study has important implications. SPTIs are already widely implemented, and they are identified as best practice for suicide prevention by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the Suicide Prevention Resource Center. So far, implementation has been largely based on clinicians’ beliefs about the value of the interventions,Reference Chesin, Stanley, Haigh, Chaudhury, Pontoski and Knox14,Reference Setkowski, van Balkom, Dongelmans and Gilissen15 but our study has now demonstrated their effectiveness in reducing suicidal behaviour. This suggests that safety planning should continue to be identified as best practice for the prevention of suicidal behaviour in individuals at risk of suicide, and should be strongly recommended in clinical practice and guidelines for suicide prevention.
Higher-quality, randomised controlled studies on the effectiveness of SPTIs will be needed to replicate the results of the current meta-analysis. For now, SPTIs appear to be an effective strategy to reduce suicidal behaviour.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2021.50.
Data availability
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
Acknowledgements
We thank Caroline Planting for performing the literature search, and Michael Dallas for editing the manuscript in preparation for submission.
Author contributions
C.N. had full access to all data in the study and takes responsibility for integrity of the data and accuracy of data analyses. C.N., W.v.B. and H.R. were responsible for the study concept and design. C.N., W.v.B. and D.J. contributed to the collecting and processing of the data. C.N. analysed the data and discussed the results and interpretation, with W.v.B. and H.R.. C.N. drafted the manuscript. C.N., W.v.B., D.d.B., D.J., A.E., G.P., R.C.O., J.H.S., A.K. and H.R. critically revised the manuscript.
Funding
This study is funded by ZonMw (Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development), project number 537001008.
Declaration of interest
None.











eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.