Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2016
The X-ray radiation from inverse Compton scattering of CMB photons by the relativistic electrons in ‘radio’ lobes provides a direct measure of their column density at a known energy, unlike synchrotron radiation which also depends on the unknown magnetic field. Thus by combining inverse Compton and radio data we can separately determine the particle energies and field strengths, rather than having to rely on uncertain estimates like minimum energy. The predicted flux is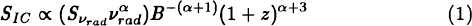 and strong IC signal requires high radio flux and low magnetic field, properties of giant radio galaxies. On the other hand the minimum detectable count rate, Imin , increases with the target size due to the larger background contribution. As a result the detectability of IC X-rays for ROSAT PSPC B measurements is roughly,
and strong IC signal requires high radio flux and low magnetic field, properties of giant radio galaxies. On the other hand the minimum detectable count rate, Imin , increases with the target size due to the larger background contribution. As a result the detectability of IC X-rays for ROSAT PSPC B measurements is roughly,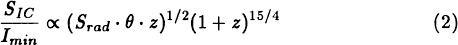 assuming a spectral index of 0.75. After making detailed prediction of SIC for a number of objects of the 3CR sample, the best candidates were 3C 236, 3C 326, and 4C 73.08.
assuming a spectral index of 0.75. After making detailed prediction of SIC for a number of objects of the 3CR sample, the best candidates were 3C 236, 3C 326, and 4C 73.08.