No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2016
We compare the results of a spherical, steady-state cooling-flow model with gas loss with the observed X-ray emission profiles and temperatures for five bright elliptical galaxies in Virgo and Fornax. We adopt a “thermal-instability” mass-loss prescription (following Sarazin & Ashe 1989) and refer to galaxy models constrained by radially extended stellar dynamical data (Saglia et al. 1992). Our cooling-flow models are specified by three free parameters: the mass accretion rate 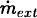 and the pressure pext at some external radius rext , and a dimensionless constant q, which regulates the mass deposition rate along the flow. We find that models with confining pressures of pext ≃ 4 ÷ 14 × 103K cm–3 and significant accretion rates of external material, up to 4M⊙/yr, provide emission and temperature profiles in good agreement with present-day data. The trend shown in the right frame of the lower panel in the Figure suggests a possible correlation between LX/LB and the iron abundance in the gas inside ellipticals. A full account of this work, together with all the relevant references, is given in Bertin & Toniazzo (1995); here below, we add a comparison of the models with some recent ASCA data (Loewenstein et al. 1994; Mushotzky et al. 1994).
and the pressure pext at some external radius rext , and a dimensionless constant q, which regulates the mass deposition rate along the flow. We find that models with confining pressures of pext ≃ 4 ÷ 14 × 103K cm–3 and significant accretion rates of external material, up to 4M⊙/yr, provide emission and temperature profiles in good agreement with present-day data. The trend shown in the right frame of the lower panel in the Figure suggests a possible correlation between LX/LB and the iron abundance in the gas inside ellipticals. A full account of this work, together with all the relevant references, is given in Bertin & Toniazzo (1995); here below, we add a comparison of the models with some recent ASCA data (Loewenstein et al. 1994; Mushotzky et al. 1994).
This work was partially supported by ASI (under contract 94RS94-202/3 FAE) of Italy.