No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 February 2015
The temperature dependence of yield stress and the associated dislocation dissociation in L12 intermetallic compounds are investigated in order to check the feasibility of the classification of L12 intermetallic compounds so far made in terms of the planarity of core structures of partial dislocations with b = 1/2<110> and 1/3<112> on {111} and {001} glide planes. In contrast to what is believed from the classification, the motion of APB-coupled dislocations is evidenced to give rise to the rapid decrease in yield stress at low temperatures for Pt3Al. In view of the fact that rapid decrease in yield stress at low temperatures is also observed in Co3(Al,W) and Co3Ti in which APB-coupled dislocations are responsible for deformation, the SISF-type dissociation is not a prerequisite for the rapidly decreasing CRSS for slip on (111) and the relative magnitudes of the APB energy on (111) and the SISF energy on (111) cannot be a primary factor that determines the type of the temperature dependence of CRSS for L12 compounds. The importance of the CSF energy as a factor determining the type of the temperature dependence of yield stress for L12 compounds through the changes in the planarity of the core structure of the APB-coupled partial dislocation with bp = ½[1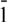 $\overline 1$0] is discussed in the light of experimental evidence obtained from Pt3Al.
$\overline 1$0] is discussed in the light of experimental evidence obtained from Pt3Al.