Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 August 2021
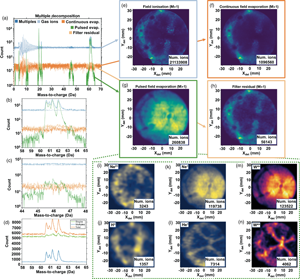
Atom probe tomography (APT) helps elucidate the link between the nanoscale chemical variations and physical properties, but it has a limited structural resolution. Field ion microscopy (FIM), a predecessor technique to APT, is capable of attaining atomic resolution along certain sets of crystallographic planes albeit at the expense of elemental identification. We demonstrate how two commercially available atom probe instruments, one with a straight flight path and one fitted with a reflectron lens, can be used to acquire time-of-flight mass spectrometry data concomitant with a FIM experiment. We outline various experimental protocols making the use of temporal and spatial correlations to best discriminate field-evaporated signals from the large field-ionized background signal, demonstrating an unsophisticated yet efficient data mining strategy to provide this discrimination. We discuss the remaining experimental challenges that need to be addressed, notably concerned with accurate detection and identification of individual field-evaporated ions contained within the high field-ionized flux that contributes to a FIM image. Our hybrid experimental approach can, in principle, exhibit true atomic resolution with elemental discrimination capabilities, neither of which atom probe nor FIM can individually fully deliver—thereby making this new approach, here broadly termed analytical field ion microscopy (aFIM), unique.
Current address: CEA Saclay Des/-Service de Recherches de Métallurgie Appliquée, Gif-sur-Yvette, France