No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 March 2021
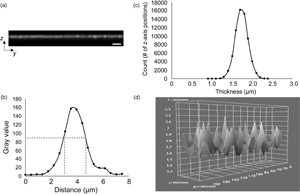
The ability to accurately and precisely measure the thickness of biomaterial constructs is critical for characterizing both specific dimensional features and related mechanical properties. However, in the absence of a standardized approach for thickness measurements, a variety of imaging modalities have been employed, which have been associated with varying limits of accuracy, particularly for ultrathin hydrated structures. Electron microscopy (EM), a commonly used modality, yields thickness values for extensively processed and nonhydrated constructs, potentially resulting in overestimated mechanical properties, including elastic modulus and ultimate tensile strength. Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) has often been used as a nondestructive imaging alternative. However, published CLSM-derived image analysis protocols use arbitrary signal intensity cutoffs and provide minimal information regarding thickness variability across imaged surfaces. To address the aforementioned limitations, we present a standardized, user-independent CLSM image acquisition and analysis approach developed as a custom ImageJ macro and validated with collagen-based scaffolds. In the process, we also quantify thickness discrepancies in collagen-based scaffolds between CLSM and EM techniques, further illustrating the need for improved strategies. Employing the same image acquisition protocol, we also demonstrate that this approach can be used to estimate the surface roughness of the same scaffolds without the use of specialized instrumentation.