No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
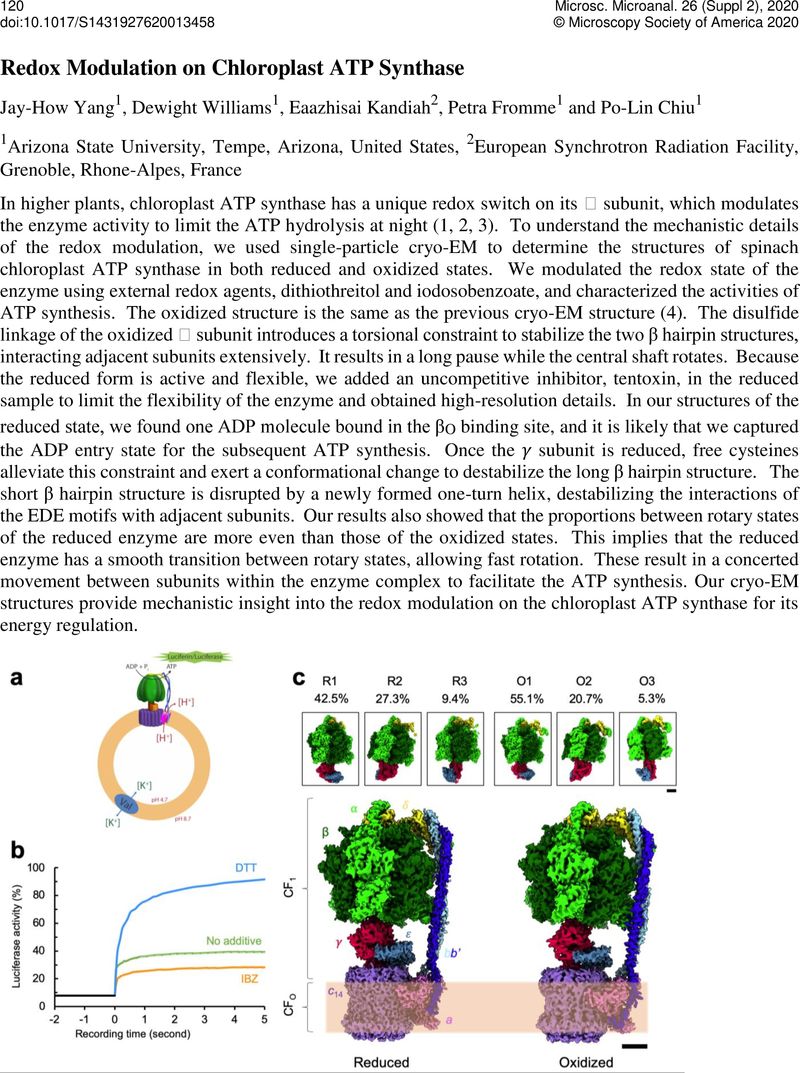
Redox Modulation on Chloroplast ATP Synthase
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 July 2020
Abstract
An abstract is not available for this content so a preview has been provided. As you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
- Type
- 3D Structures: From Macromolecular Assemblies to Whole Cells (3DEM FIG)
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America 2020
References
Nalin, C. M. & McCarty, R. E. Role of a disulfide bond in the γ subunit in activation of the ATPase of chloroplast coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem 259, 7275-7280 (1984).Google ScholarPubMed
Hisabori, T., Sunamura, E.-I., Kim, Y. & Konno, H. The chloroplast ATP synthase features the characteristic redox regulation machinery. Antioxid Redox Sign 19, 1846-1854 (2013).10.1089/ars.2012.5044CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
Hisabori, T., Ueoka-Nakanishi, H., Konno, H. & Koyama, F. Molecular evolution of the modulator of chloroplast ATP synthase: origin of the conformational change dependent regulation. FEBS Lett 545, 71-75 (2003).10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00395-8CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed
Hahn, A., Vonck, J., Mills, D. J., Meier, T. & Kühlbrandt, W. Structure, mechanism, and regulation of the chloroplast ATP synthase. Science 360 (2018).10.1126/science.aat4318CrossRefGoogle ScholarPubMed



