Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 November 2021
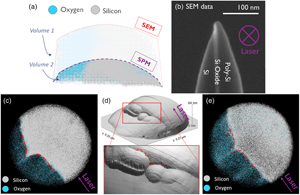
Reliable spatially resolved compositional analysis through atom probe tomography requires an accurate placement of the detected ions within the three-dimensional reconstruction. Unfortunately, for heterogeneous systems, traditional reconstruction protocols are prone to position some ions incorrectly. This stems from the use of simplified projection laws which treat the emitter apex as a spherical cap, although the actual shape may be far more complex. For instance, sampled materials with compositional heterogeneities are known to develop local variations in curvature across the emitter due to their material phase specific evaporation fields. This work provides three pivotal precursors to improve the spatial accuracy of the reconstructed volume in such cases. First, we show scanning probe microscopy enables the determination of the local curvature of heterogeneous emitters, thus providing the essential information for a more advanced reconstruction considering the actual shape. Second, we demonstrate the cyclability between scanning probe characterization and atom probe analysis. This is a key ingredient of more advanced reconstruction protocols whereby the characterization of the emitter topography is executed at multiple stages of the atom probe analysis. Third, we show advances in the development of an electrostatically driven reconstruction protocol which are expected to enable reconstruction based on experimental tip shapes.