Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 September 2022
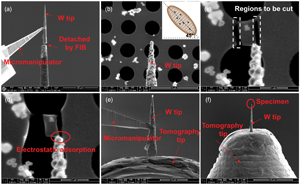
Electron tomography (ET) has gained increasing attention for the 3D characterization of nanoparticles. However, the missing wedge problem due to a limited tilt angle range is still the main challenge for accurate reconstruction in most experimental TEM setups. Advanced algorithms could in-paint or compensate to some extent the missing wedge artifacts, but cannot recover the missing structural information completely. 360° ET provides an option to solve this problem by tilting a needle-shaped specimen over the full tilt range and thus filling the missing information. However, sample preparation especially for fine powders to perform full-range ET is still challenging, thus limiting its application. In this work, we propose a new universal sample preparation method that enables the transfer of selected individual nanoparticle or a few separated nanoparticles by cutting a piece of carbon film supporting the specimen particles and mounting them onto the full-range tomography holder tip with the help of an easily prepared sharp tungsten tip. This method is demonstrated by 360° ET of Pt@TiO2 hollow cage catalyst showing high quality reconstruction without missing wedge.