Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zhang, Yu
Rong, Wei
Wu, Yujuan
Peng, Liming
Nie, Jian-Feng
and
Birbilis, Nick
2018.
A comparative study of the role of Ag in microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd and Mg-Y alloys.
Materials Science and Engineering: A,
Vol. 731,
Issue. ,
p.
609.
Zhang, Yu
Gore, Poorwa
Rong, Wei
Wu, Yujuan
Yan, Yuanming
Zhang, Ruifeng
Peng, Liming
Nie, Jian-Feng
and
Birbilis, Nick
2018.
Quasi-in-situ STEM-EDS insight into the role of Ag in the corrosion behaviour of Mg-Gd-Zr alloys.
Corrosion Science,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
106.
Zheng, Jingxu Kent
Luo, Ruichun
Zeng, Xiaoqin
and
Chen, Bin
2018.
Nano-scale precipitation and phase growth in Mg-Gd binary alloy: An atomic-scale investigation using HAADF-STEM.
Materials & Design,
Vol. 137,
Issue. ,
p.
316.
Zhu, Chenyang
and
Chen, Bin
2019.
Atomic Scale Investigation on Precipitates and Defects of Mg–RE Alloys: A Review.
Advanced Engineering Materials,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 3,
Zhang, Yu
Rong, Wei
Wu, Yujuan
and
Peng, Liming
2020.
Achieving ultra-high strength in Mg–Gd–Ag–Zr wrought alloy via bimodal-grained structure and enhanced precipitation.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology,
Vol. 54,
Issue. ,
p.
160.
Zheng, Jingxu
Kim, Mun Sek
Tu, Zhengyuan
Choudhury, Snehashis
Tang, Tian
and
Archer, Lynden A.
2020.
Regulating electrodeposition morphology of lithium: towards commercially relevant secondary Li metal batteries.
Chemical Society Reviews,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 9,
p.
2701.
Zhang, Yu
Rong, Wei
Wu, Yujuan
and
Peng, Liming
2020.
Tuning texture and precipitation using Y/Gd atomic ratio in iso-concentration Mg–Y–Gd–Ag–Zr extruded alloys.
Materials Characterization,
Vol. 167,
Issue. ,
p.
110473.
Hao, Yiqiang
Chen, Xia
and
Chen, Bin
2021.
The microstructure and property of lamellar interface in ternary Mg–Gd–Cu alloys: a combined experimental and first-principles study.
Journal of Materials Science,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 15,
p.
9470.
Xin, Shiwei
Li, Zehua
Feng, Zhijun
Li, Yufei
Ruan, Ming
and
Wang, Fulin
2023.
Study on the Formation of the Cuboid RE-Dominated Phase and Its Influence on Mechanical Properties of Mg–4Y–2Nd-1Gd Alloy.
International Journal of Metalcasting,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 2,
p.
696.
Guo, Shuang
Liu, Tianyu
Luo, Tianjiao
Li, Yingju
Feng, Xiaohui
Huang, Qiuyan
Zheng, Ce
Zhu, Cheng
Yang, Yuansheng
Li, Weirong
and
Li, Feng
2024.
Effect of Ag on High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Mg–6.5Gd–5.6Y–0.1Nd–0.01Ce–0.4Zr Alloy.
Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters),
Vol. 37,
Issue. 11,
p.
1843.
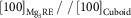 $[100]_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} \,/\,\,/\,[100]_{{{\rm Cuboid}}} $
and
$[100]_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} \,/\,\,/\,[100]_{{{\rm Cuboid}}} $
and 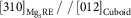 $[310]_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} \,/\,\,/\,[012]_{{{\rm Cuboid}}} $
. The fully coherent interfaces between the precipitates and the cuboid-shaped phases are reconstructed and categorized into two types:
$[310]_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} \,/\,\,/\,[012]_{{{\rm Cuboid}}} $
. The fully coherent interfaces between the precipitates and the cuboid-shaped phases are reconstructed and categorized into two types: 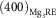 $(400)_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} $
interface and
$(400)_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} $
interface and 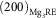 $(200)_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} $
interface.
$(200)_{{{\rm Mg}_{{\rm 3}} {\rm RE}}} $
interface.