Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 January 2021
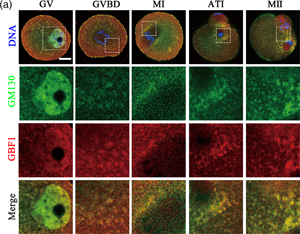
GBF1 [Golgi brefeldin A (BFA) resistance factor 1] is a member of the guanine nucleotide exchange factors Arf family. GBF1 localizes at the cis-Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi intermediate compartment where it participates in ER-Golgi traffic by assisting in the recruitment of the coat protein COPI. However, the roles of GBF1 in oocyte meiotic maturation are still unknown. In the present study, we investigated the regulatory functions of GBF1 in mouse oocyte organelle dynamics. In our results, GBF1 was stably expressed during oocyte maturation, and GBF1 localized at the spindle periphery during metaphase I. Inhibiting GBF1 activity led to aberrant accumulation of the Golgi apparatus around the spindle. This may be due to the effects of GBF1 on the localization of GM130, as GBF1 co-localized with GM130 and inhibiting GBF1 induced condensation of GM130. Moreover, the loss of GBF1 activity affected the ER distribution and induced ER stress, as shown by increased GRP78 expression. Mitochondrial localization and functions were affected, as the mitochondrial membrane potential was altered. Taken together, these results suggest that GBF1 has wide-ranging effects on the distribution and functions of Golgi apparatus, ER, and mitochondria as well as normal polar body formation in mouse oocytes.