Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 March 2019
The absence of quantitative in vitro cell–extracellular matrix models represents an important bottleneck for basic research and human health. Randomness of cellular distributions provides an opportunity for the development of a quantitative in vitro model. However, quantification of the randomness of random cell distributions is still lacking. In this paper, we have imaged cellular distributions in an alginate matrix using a multiview light sheet microscope and developed quantification metrics of randomness by modeling it as a Poisson process, a process that has constant probability of occurring in space or time. We imaged fluorescently labeled human mesenchymal stem cells embedded in an alginate matrix of thickness greater than 5 mm with 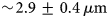 $\sim\! {\rm 2}{\rm. 9} \pm {\rm 0}{\rm. 4}\,\mu {\rm m}$ axial resolution, the mean full width at half maximum of the axial intensity profiles of fluorescent particles. Simulated randomness agrees well with the experiments. Quantification of distributions and validation by simulations will enable quantitative study of cell–matrix interactions in tissue models.
$\sim\! {\rm 2}{\rm. 9} \pm {\rm 0}{\rm. 4}\,\mu {\rm m}$ axial resolution, the mean full width at half maximum of the axial intensity profiles of fluorescent particles. Simulated randomness agrees well with the experiments. Quantification of distributions and validation by simulations will enable quantitative study of cell–matrix interactions in tissue models.