No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Fluctuation Microscopy in the STEM
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Abstract
Fluctuation microscopy is an electron microscopy technique sensitive to medium-range order (MRO) in disordered materials. It has been applied to study amorphous germanium and silicon, leading to the conclusion that these materials exhibit more MRO than the conventional continuous random network model for their structure.
As originally proposed by Treacy and Gibson, fluctuation microscopy utilizes mesoscopicresolution (1.5 nm) hollow-cone dark field (HCDF) imaging in a TEM. The normalized variance of such images,
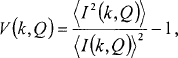
is a measure of the magnitude of fluctuations in the diffracted intensity from mesoscopic volumes of the sample and is sensitive to MRO via the three- and four-body atom distribution functions. Studying V as a function of the diffraction vector magnitude k gives information about the degree of MRO and the internal structure of ordered regions. V as a function of the inverse resolution Q gives information about the characteristic MRO length scale.
- Type
- Quantitative Stem: Imaging and Eels Analysis Honoring the Contributions of John Silcox (Organized by P. Batson, C. Chen and D. Muller)
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America 2001
References
1 Treacy, M. M. J., Gibson, J. M., and Keblinski, P. J., J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 231 99 (1998).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
2 Treacy, M. M. J. and Gibson, J. M., Acta Cryst. A52, 212 (1996).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
3 Gibson, J. M., Treacy, M. M. J., and Voyles, P. M., Ultramicroscopy 83, 169 (2000).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
4 Fan, G. Y. and Cowley, J. M., Ultramicroscopy 17, 345 (1985).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
5 Rodenburg, J. M., Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 78, 103 (1985).Google Scholar


